Strategy tested in mice protects against SARS-CoV-2 & coronaviruses that represent human threats
2021-01-12
An immunization strategy tested in mice protects against infection from SARS-CoV-2, as well as from potentially emerging animal coronaviruses, researchers say. The approach could be "used as described or easily adapted" to provide defense against newly discovered zoonotic coronaviruses. In the last 20 years, three betacoronaviruses have caused devastating disease in humans. The global pandemic caused by the latest such virus, SARS-CoV-2, highlights the need to protect against other strains that could present a threat to humans, possibly through a pan-coronavirus vaccine. To support related efforts, ...
New taxonomy of non-skeletal rare disorders with impact on bone
2021-01-12
Thanks to major progress in the understanding and management of rare congenital diseases and syndromes, many patients with these rare disorders are now living longer lives. With this progress it has become apparent that many non-skeletal rare diseases have an impact on bone mass, bone quality and/or bone metabolism, with potentially severe repercussions for quality of life in adults.
The new paper 'Bone fragility in patients affected by congenital diseases non skeletal in origin', published in Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) Skeletal Rare Diseases Working Group (SRDWG), provides ...
Turbulent dynamics in the human brain could revolutionize the understanding of its functionality
2021-01-12
Most people experience turbulence primarily from the experience of flying in an airplane. However, turbulence is a key feature of nature and is found everywhere, from rivers to galaxies.
Turbulent-like dynamics are difficult to capture in a still image. However, Leonardo da Vinci did everything possible to identify the underlying order of the phenomenon, which he observed in eddy currents forming randomly in water. In fact, he was fascinated by trying to understand and describe the generating principles governing such complicated dynamics. This is so much ...
Artificial intelligence puts focus on the life of insects
2021-01-12
Scientists are combining artificial intelligence and advanced computer technology with biological know how to identify insects with supernatural speed. This opens up new possibilities for describing unknown species and for tracking the life of insects across space and time
Insects are the most diverse group of animals on Earth and only a small fraction of these have been found and formally described. In fact, there are so many species that discovering all of them in the near future is unlikely.
This enormous diversity among insects also means that they have very different life histories and roles in the ecosystems.
For ...
Study finds future too warm for baby sharks
2021-01-12
A new study conducted at the New England Aquarium finds that as climate change causes the ocean to warm, baby sharks are born smaller, exhausted, undernourished, and into environments that are already difficult for them to survive in.
In a recently published paper in the journal Scientific Reports, lead author Carolyn Wheeler, a Ph.D. candidate at the University of Massachusetts Boston and at the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University, examined the effects of increased temperatures on the growth, development and physiological performance of epaulette ...
Museum scientists: Prepare for next pandemic now by preserving animal specimens in natural history
2021-01-12
It's been more than a year since the first cases were identified in China, yet the exact origins of the COVID-19 pandemic remain a mystery. Though strong evidence suggests that the responsible coronavirus originated in bats, how and when it crossed from wildlife into humans is unknown.
In a study published online Jan.12 in the journal mBio, an international team of 15 biologists say this lack of clarity has exposed a glaring weakness in the current approach to pandemic surveillance and response worldwide.
In most recent studies of animal-borne pathogens with the potential to spread to humans, known as zoonotic pathogens, physical specimens of suspected wildlife ...
New technology reveals fast and slow twitch muscle fibers respond differently to exercise
2021-01-12
Exercising regularly is one of the best defences against metabolic diseases, such as obesity and diabetes - but why? It's a question that scientists are still struggling to answer. While exercising changes the molecular behaviour of muscles, it's not well understood how these molecular changes improve metabolic health.
Scientists at the University of Copenhagen have now developed a new technology that allows researchers to study muscle biology on a more detailed level - and hopefully find some new answers. They extracted 'fast' and 'slow' twitch muscle fibers from freeze-dried muscle samples that were taken before and after 12 weeks of cycling exercise training. Their comprehensive analysis of the protein expression of the fibers provides new evidence that the ...
Hospitals must help their own COVID long-haulers recover, experts argue
2021-01-12
BOSTON -- By mid-November, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention had reported that 218,439 health care workers in the U.S. had been infected with COVID-19 -- a likely underestimate due to incomplete data from states. About 3% to 4% of health care personnel who recover from coronavirus infection are expected to become "COVID long-haulers" as they cope with debilitating symptoms 12 to 18 months after the acute stage of the infection clears.
"As COVID-19 surges again, hospitals are facing a shortage of skilled frontline providers who can meet the relentless demands of caring for these patients," says Zeina N. Chemali, MD, MPH, a psychiatrist and neurologist at Massachusetts ...
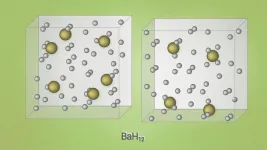
Scientists have synthesized an unusual superconducting barium superhydride
2021-01-12
A group of scientists from Russia, China, and the United States predicted and then experimentally obtained barium superhydrides' new unusual superconductors. The study was published in Nature Communications.
Chemists and physicists have been hunting down room-temperature superconductors since the first half of the 20th century. Initially, high hopes were placed on metallic hydrogen, but solid metallic hydrogen can become superconducting only at extremely high pressures of several million atmospheres, as it later transpired. Chemists then tried adding other elements to hydrogen in the hope of attaining superconductivity by stabilizing the metallic state under less challenging conditions. ...
Rotten egg gas could guard against Alzheimer's disease
2021-01-12
Typically characterized as poisonous, corrosive and smelling of rotten eggs, hydrogen sulfide's reputation may soon get a face-lift thanks to Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers. In experiments in mice, researchers have shown the foul-smelling gas may help protect aging brain cells against Alzheimer's disease. The discovery of the biochemical reactions that make this possible opens doors to the development of new drugs to combat neurodegenerative disease.
The findings from the study are reported in the Jan. 11 issue of the Proceedings of the National Academies of Sciences.
"Our new data firmly link aging, neurodegeneration and cell signaling using hydrogen sulfide and other gaseous molecules within the cell," says Bindu Paul, M.Sc., Ph.D., faculty ...
A bucket of water can reveal climate change impacts on marine life in the Arctic
2021-01-12
Climate changes prompt many important questions. Not least how it affects animals and plants: Do they adapts, gradually migrate to different areas or become extinct? And what is the role played by human activities? This applies not least to Greenland and the rest of the Artic, which are expected to see the greatest effects of climate changes.
'We know surprisingly little about marine species and ecosystems in the Arctic, as it is often costly and difficult to do fieldwork and monitor the biodiversity in this area', says Associate Professor of marine mammals and instigator of the study ...
'Bespoke' analysis of DNA packaging sheds light on intricacies of the fundamental process
2021-01-12
Researchers from Skoltech and their colleagues have optimized data analysis for a common method of studying the 3D structure of DNA in single cells of a Drosophila fly. The new approach allows the scientists to peek with greater confidence into individual cells to study the unique ways DNA is packaged there and get closer to understanding this crucial process's underlying mechanisms. The paper was published in the journal Nature Communications.
The reason a roughly two-meter-long strand of DNA fits into the tiny nucleus of a human cell is that chromatin, a complex of DNA and proteins, packages it ...
Study finds risk factors linked to COVID-19 mental health impacts for college students
2021-01-12
A study of students at seven public universities across the United States has identified risk factors that may place students at higher risk for negative psychological impacts related to the COVID-19 pandemic. Factors associated with greater risk of negative impacts include the amount of time students spend on screens each day, their gender, age and other characteristics.
Research has shown many college students faced significant mental health challenges going into the COVID-19 pandemic, and experts say the pandemic has added new stressors. The findings, published in the journal PLOS ONE, could help experts tailor services ...
Spatial distribution of planktonic ciliates in the western Pacific Ocean: Along the transect from Shenzhen (China) to Pohnpei (Micronesia)
2021-01-12
Announcing a new publication for Marine Life Science & Technology journal. In this research article the authors Hungchia Huang, Jinpeng Yang, Shixiang Huang, Bowei Gu, Ying Wang, Lei Wang and Nianzhi Jiao from Xiamen University, Xiamen, China and Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China consider the spatial distribution of planktonic ciliates in the western Pacific Ocea: along a transect from Shenzhen (China) to Pohnpei (Micronesia).
Planktonic ciliates have been recognized as major consumers of nano- and picoplankton in pelagic ecosystems, playing pivotal roles in the transfer ...
Cats may help increase empathy, decrease anxiety for kids with autism
2021-01-12
COLUMBIA, Mo. - As a former school nurse in the Columbia Public Schools, Gretchen Carlisle would often interact with students with disabilities who took various medications or had seizures throughout the day. At some schools, the special education teacher would bring in dogs, guinea pigs and fish as a reward for good behavior, and Carlisle noticed what a calming presence the pets seemed to be for the students with disabilities.
Now a research scientist at the MU Research Center for Human-Animal Interaction (ReCHAI) in the MU College of Veterinary Medicine, Carlisle studies the benefits that companion animals can have on families. While there is plenty of ...
Shortening college athlete COVID quarantine may boost adherence without increasing risk
2021-01-12
New Orleans, LA - Catherine O'Neal, MD, Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine's branch campus in Baton Rouge, is a co-author of a paper reporting that shortening the length of quarantine due to COVID exposure when supported by mid-quarantine testing may increase compliance among college athletes without increasing risk. The findings are published in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's January 8, 2021 Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), available here.
CDC partnered with representatives of the NCAA conferences to analyze retrospective data collected by participating colleges and universities. De-identified data from a total of 620 ...
Scientists reveal how gut microbes can influence bone strength in mice
2021-01-12
Gut microbes passed from female mice to their offspring, or shared between mice that live together, may influence the animals' bone mass, says a new study published today in eLife.
The findings suggest that treatments which alter the gut microbiome could help improve bone structure or treat conditions that weaken bones, such as osteoporosis.
"Genetics account for most of the variability in human bone density, but non-genetic factors such as gut microbes may also play a role," says lead author Abdul Malik Tyagi, Assistant Staff Scientist at the Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism, and Lipids at Emory Microbiome Research Center, Emory University, Georgia, US. "We wanted to investigate the influence of the microbiome on skeletal growth and bone mass development."
To ...
SARS-CoV-2 can infect neurons and damage brain tissue, study indicates
2021-01-12
Using both mouse and human brain tissue, researchers at Yale School of Medicine have discovered that SARS-CoV-2 can directly infect the central nervous system and have begun to unravel some of the virus's effects on brain cells. The study, published today in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), may help researchers develop treatments for the various neurological symptoms associated with COVID-19.
Though COVID-19 is considered to primarily be a respiratory disease, SARS-CoV-2 can affect many other organs in the body, including, in some patients, the central nervous system, where infection is associated with ...
Texas A&M research explores how melanoma grows and spreads
2021-01-12
The first step in treating cancer is understanding how it starts, grows and spreads throughout the body. A relatively new cancer research approach is the study of metabolites, the products of different steps in cancer cell metabolism, and how those substances interact.
To date, research like this has focused mostly on cancerous tissues; however, normal tissues that surround tumors, known as the extratumoral microenvironment (EM), may have conditions favorable for tumor formation and should also be studied.
In a new study published in the journal PLOS ONE, researchers investigated the metabolites involved in the growth and spread of melanoma, a rare but deadly ...
New treatment allows some people with spinal cord injury to regain hand and arm function
2021-01-12
Almost 18,000 Americans experience traumatic spinal cord injuries every year. Many of these people are unable to use their hands and arms and can't do everyday tasks such as eating, grooming or drinking water without help.
Using physical therapy combined with a noninvasive method of stimulating nerve cells in the spinal cord, University of Washington researchers helped six Seattle area participants regain some hand and arm mobility. That increased mobility lasted at least three to six months after treatment had ended. The research team published these findings Jan. 5 in the journal ...
Study finds NRA stakeholders conflicted in wake of shootings
2021-01-12
A recent study finds that, in the wake of a mass shooting, National Rifle Association (NRA) employees, donors and volunteers had extremely mixed emotions about the organization - reporting higher levels of both positive and negative feelings about the NRA, as compared to people with no NRA affiliation.
"We wanted to see what effect 'in-group' affiliation and political identity had on how people responded to the NRA's actions after a mass shooting," says Yang Cheng, co-author of the study and an assistant professor of communication at North Carolina State University. "The political findings were predictable - Republicans thought more favorably of the NRA than Democrats did. But the in-group affiliation was a lot more complex than ...
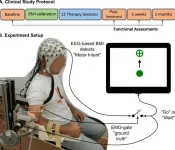
Tapping the brain to boost stroke rehabilitation
2021-01-12
Stroke survivors who had ceased to benefit from conventional rehabilitation gained clinically significant arm movement and control by using an external robotic device powered by the patients' own brains.
The results of the clinical trial were described in the journal NeuroImage: Clinical.
Jose Luis Contreras-Vidal, director of the Non-Invasive Brain Machine Interface Systems Laboratory at the University of Houston, said testing showed most patients retained the benefits for at least two months after the therapy sessions ended, suggesting the potential for long-lasting gains. He is also Hugh Roy and Lillie Cranz Cullen Distinguished Professor of electrical and computer engineering.
The trial involved training stroke survivors with limited movement in one arm to use a brain-machine interface ...
Unsure how to help reverse insect declines? Scientists suggest simple ways
2021-01-12
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Entomologist Akito Kawahara's message is straightforward: We can't live without insects. They're in trouble. And there's something all of us can do to help.
Kawahara's research has primarily focused on answering fundamental questions about moth and butterfly evolution. But he's increasingly haunted by studies that sound the alarm about plummeting insect numbers and diversity.
Kawahara has witnessed the loss himself. As a child, he collected insects with his father every weekend, often traveling to a famous oak outside Tokyo ...
K-State medical director contributes to research behind updated CDC quarantine guidance
2021-01-12
MANHATTAN, KANSAS -- Kyle Goerl, the medical director of Kansas State University's Lafene Health Center, is part of a collaborative team that is providing research-based guidance during the COVID-19 pandemic. The team's latest research contributed to the updated quarantine guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Goerl is a co-author of the publication "Time from Start of Quarantine to SARS-CoV-2 Positive Test Among Quarantined College and University Athletes." The publication appeared in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the CDC on Friday, Jan. 8, and involved researchers from multiple organizations and universities.
The publication was one of many that the ...
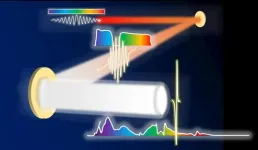
Towards Exawatt-class lasers
2021-01-12
Osaka, Japan -- Ultra-intense lasers with ultra-short pulses and ultra-high energies are powerful tools for exploring unknowns in physics, cosmology, material science, etc. With the help of the famous technology "Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA)" (2018 Nobel Prize in Physics), the current record has reached 10 Petawatts (or 10^16 Watts). In a study recently published in Scientific Reports, researchers from Osaka University proposed a concept for next-generation ultra-intense lasers with a simulated peak power up to the Exawatt class (1 Exawatt equals 1000 Petawatts).
The laser, which was invented by Dr. T. H. Maiman in 1960, has one important characteristic of high intensity (or high peak power for pulse lasers): historically, laser peak ...
[1] ... [2747]
[2748]
[2749]
[2750]
[2751]
[2752]
[2753]
[2754]
2755
[2756]
[2757]
[2758]
[2759]
[2760]
[2761]
[2762]
[2763]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.