Extreme fire weather
2021-01-15
When the Thomas Fire raged through Ventura and Santa Barbara counties in December 2017, Danielle Touma, at the time an earth science researcher at Stanford, was stunned by its severity. Burning for more than a month and scorching 440 square miles, the fire was then considered the worst in California's history.
Six months later the Mendocino Complex Fire upended that record and took out 717 square miles over three months. Record-setting California wildfires have since been the norm, with five of the top 10 occurring in 2020 alone.
The disturbing trend sparked some questions for Touma, who is now a postdoctoral researcher at UC Santa Barbara's Bren School for Environmental ...
Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine collection highlights 15 years of scientific discovery
2021-01-15
DARIEN, IL - Editors of the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine have identified some of the most significant articles in the publication's history, publishing new commentaries on them in a special 15th anniversary collection. The 15 commentaries from associate editors and members of the journal's editorial board describe the impact of the selected articles both at the time of their publication and today.
"The collection highlights some of the most influential publications in clinical sleep research over the past 15 years," JCSM Editor-in-Chief Dr. Nany Collop said. "These studies underscore the remarkable ...
Eating omega-3 fat helps hibernating Arctic ground squirrels warm up during deep cold
2021-01-14
By feeding arctic ground squirrels special diets, researchers have found that omega-3 fatty acids, common in flax seed and fish oil, help keep the animals warmer in deep hibernation.
A University of Alaska Fairbanks-led study fed ground squirrels either a diet high in omega-3s or a normal laboratory diet, and measured how the animals hibernated afterward. Researchers found that the omega-3 diet helped the animals hibernate a little warmer than normal without negatively affecting hibernation. The omega-3 diets also increased the amount of a heat-producing fat, called brown adipose tissue, the animals pack on.
The discovery could add more understanding ...
UNH researchers discover new inhibitor drug combination for rare form of cancer
2021-01-14
DURHAM, N.H.-- Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM), a rare form of lymphoma, does not have any known cure and only one FDA-approved treatment making it challenging to treat patients. Researchers at the University of New Hampshire took the novel approach of targeting specific cell proteins that control DNA information using inhibitors, or drugs, that were effective in reducing the growth of the cancer cells and when combined with a third drug were even more successful in killing the WM cancer cells which could lead to more treatment options.
"This is the first study to report the promising results ...
Researchers rewind the clock to calculate age and site of supernova blast
2021-01-14
Astronomers are winding back the clock on the expanding remains of a nearby, exploded star. By using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, they retraced the speedy shrapnel from the blast to calculate a more accurate estimate of the location and time of the stellar detonation.
The victim is a star that exploded long ago in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy to our Milky Way. The doomed star left behind an expanding, gaseous corpse, a supernova remnant named 1E 0102.2-7219, which NASA's Einstein Observatory first discovered in X-rays. Like detectives, researchers sifted through archival images taken by Hubble, analyzing visible-light observations made 10 years apart.
The research team, led by John Banovetz and Danny Milisavljevic ...
Acute itching in eczema patients linked to environmental allergens
2021-01-14
In addition to a skin rash, many eczema sufferers also experience chronic itching, but sometimes that itching can become torturous. Worse, antihistamines -- the standard treatment for itching and allergy -- often don't help.
New research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates that allergens in the environment often are to blame for episodes of acute itch in eczema patients, and that the itching often doesn't respond to antihistamines because the itch signals are being carried to the brain along a previously unrecognized pathway that current drugs don't target.
The new findings, published ...
Astronomers document the rise and fall of a rarely observed stellar dance
2021-01-14
The sun is the only star in our system. But many of the points of light in our night sky are not as lonely. By some estimates, more than three-quarters of all stars exist as binaries -- with one companion -- or in even more complex relationships. Stars in close quarters can have dramatic impacts on their neighbors. They can strip material from one another, merge or twist each other's movements through the cosmos.
And sometimes those changes unfold over the course of a few generations.
That is what a team of astronomers from the University of Washington, Western Washington University and the University ...
Unexplained 7-fold variation in euthanasia rates across the Netherlands
2021-01-14
There's a 7-fold unexplained variation in rates of euthanasia across The Netherlands, reveals an analysis of health insurance claims data, published online in the journal BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care.
It's not clear if these differences relate to underuse, overuse, or even misuse, say the researchers.
The Netherlands was the first country in the world to legalise euthanasia and physician-assisted suicide, introducing preliminary legislation in 1994, followed by a fully fledged law in 2002. The practice has been tolerated, however, since 1985.
Official data show that the number of euthanasia cases has risen more or less continuously since 2006, reaching 6361 in 2019. These cases ...
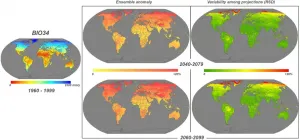
Understanding future species distribution: new data for biogeographers
2021-01-14
Climate change impacts, affecting primarily ecosystems' functions and consequently human sectors, have become a crucial topic. Observed and expected variations in climate conditions can in fact undermine the ecosystems' ecological equilibrium: average climate patterns, mainly represented by intra-annual (monthly to seasonal) temperature and precipitation cycle, directly influence the distribution, abundance and interactions of biological species.
During the long history of scientific research on the relationships between climate and Earth's communities, ...
Metformin use reduces risk of death for patients with COVID-19 and diabetes
2021-01-14
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - Use of the diabetes drug metformin -- before a diagnosis of COVID-19 -- is associated with a threefold decrease in mortality in COVID-19 patients with Type 2 diabetes, according to a racially diverse study at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. Diabetes is a significant comorbidity for COVID-19.
"This beneficial effect remained, even after correcting for age, sex, race, obesity, and hypertension or chronic kidney disease and heart failure," said Anath Shalev, M.D., director of UAB's Comprehensive Diabetes Center and leader of the study.
"Since similar results have now been obtained in different populations from around the world -- including China, France and a UnitedHealthcare analysis -- this suggests that the ...
Common workplace interactions can trigger suicidal thoughts for employees with mood disorders
2021-01-14
Ignoring a colleague's greeting or making a sarcastic comment in the workplace may actually do more harm than intended, according to West Virginia University research.
Perceived low-grade forms of workplace mistreatment, such as avoiding eye contact or excluding a coworker from conversation, can amplify suicidal thoughts in employees with mood disorders, based on a study by Kayla Follmer, assistant professor of management, and Jake Follmer, assistant professor of educational psychology.
"We know from prior research that minor forms of workplace mistreatment reduce employee engagement," Kayla Follmer said. "But our paper provided an explanation for ...
Emotionally neglected or severely sexually abused girls report riskier sexual behavior
2021-01-14
New York, NY (January 14, 2020) -- Girls who are emotionally neglected or severely sexually abused early in their lives report riskier sexual behaviors during adolescence, Mount Sinai researchers report. The findings highlight the need--and suggest the potential for tailored approaches--to promote healthy sexual development in vulnerable populations.
The researchers identified four distinct patterns of neglect and sexual abuse in low-income, predominantly Black and/or Latina girls and young women that led to distinct trajectories of risky sexual behavior during adolescence. Their findings were published in Child Development in January.
The study was the first of its kind to identify categories of maltreatment among adolescent girls of color in an urban setting that correspond with measurable ...
COVID-19 reduced US life expectancy, especially among Black and Latino populations
2021-01-14
The COVID-19 pandemic, which claimed more than 336,000 lives in the United States in 2020, has significantly affected life expectancy, USC and Princeton researchers have found.
The researchers project that, due to the pandemic deaths last year, life expectancy at birth for Americans will shorten by 1.13 years to 77.48 years, according to their study published Thursday in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
That is the largest single-year decline in life expectancy in at least 40 years and is the lowest life expectancy estimated since ...
Research breaks new ground in understanding how a molecular motor generates force
2021-01-14
A team of biophysicists from the University of Massachusetts Amherst and Penn State College of Medicine set out to tackle the long-standing question about the nature of force generation by myosin, the molecular motor responsible for muscle contraction and many other cellular processes. The key question they addressed - one of the most controversial topics in the field - was: how does myosin convert chemical energy, in the form of ATP, into mechanical work?
The answer revealed new details into how myosin, the engine of muscle and related motor proteins, transduces energy.
In the end, their unprecedented research, meticulously ...
Behavioral traits converge for humans and animals sharing an environment
2021-01-14
Humans, mammals and birds that live in a particular environment share a common set of behavioral traits, according to a new study, which identifies a local convergence of foraging, reproductive and social behaviors across species. The findings, based on studying more than 300 small-scale human hunter-gatherer populations, support one of the central tenets of human behavioral ecology - that ecological forces select for various behaviors in distinct environments, driving behavioral diversity worldwide. The origin and evolution of human behavior are uncertain and debated. While some suggest ...
Plant roots sense compacted soil through gaseous hormone signals
2021-01-14
The volatile plant hormone ethylene allows plant roots to sense and avoid compacted soils, researchers report. Rendering roots insensitive to ethylene allowed them to penetrate compacted soils more effectively, the same group showed. The findings reveal how plants regulate their growth in response to soil compaction - a growing challenge facing modern agriculture worldwide - and could serve as a pathway for how breeders might select or develop new crops resilient to soil compaction. Driven in part by a growing reliance on heavy machinery and poor soil management practices, soil compaction can lead to declining crop yields by restricting root growth and limiting the availability ...
Sperm-specific gene expression in organisms including mice, macaques and men
2021-01-14
A large class of mammalian genes is not completely shared throughout sperm development and differentiation, according to a new study of sperm in organisms including mice, macaques and men. The findings provide an explanation to why testis gene expression patterns often appear as an outlier relative to all other tissues. In mammals, spermatogenesis includes a long stage of haploid gene expression, which could lead to variation between individual sperm cells, resulting in sperm-level natural selection and trait inheritance. However, during differentiation, maturing haploid spermatids ...
Foraging humans, mammals and birds who live in the same place behave similarly
2021-01-14
Foraging humans find food, reproduce, share parenting, and even organise their social groups in similar ways as surrounding mammal and bird species, depending on where they live in the world, new research has found.
The study, published today in Science, shows environmental factors exert a key influence on how foraging human populations and non-human species behave, despite their very different backgrounds.
The team of international researchers analysed data from more than 300 locations around the world, observing the behaviours of foraging human populations ...
Hard to crack research reveals how crop roots penetrate hard soils
2021-01-14
Scientists have discovered a signal that causes roots to stop growing in hard soils which can be 'switched off' to allow them to punch through compacted soil - a discovery that could help plants to grow in even the most damaged soils.
An international research team, led by scientists from the University of Nottingham's Future Food Beacon and Shanghai Jiao Tong University has discovered how the plant signal 'ethylene' causes roots to stop growing in hard soils, but after this signal is disabled, roots are able to push through compacted soil. The research has been published in Science.
Hard (compacted) soils represent a major challenge facing modern agriculture that can reduce crop yields over 50% by reducing root growth, causing significant losses annually. Europe has over 33-million-hectares ...
Model analyzes how viruses escape the immune system
2021-01-14
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- One reason it's so difficult to produce effective vaccines against some viruses, including influenza and HIV, is that these viruses mutate very rapidly. This allows them to evade the antibodies generated by a particular vaccine, through a process known as "viral escape."
MIT researchers have now devised a new way to computationally model viral escape, based on models that were originally developed to analyze language. The model can predict which sections of viral surface proteins are more likely to mutate in a way that enables viral escape, and it can also identify sections that are less likely to mutate, making them good targets ...
New state of matter in one-dimensional quantum gas
2021-01-14
As the story goes, the Greek mathematician and tinkerer Archimedes came across an invention while traveling through ancient Egypt that would later bear his name. It was a machine consisting of a screw housed inside a hollow tube that trapped and drew water upon rotation. Now, researchers led by Stanford University physicist Benjamin Lev have developed a quantum version of Archimedes' screw that, instead of water, hauls fragile collections of gas atoms to higher and higher energy states without collapsing. Their discovery is detailed in a paper published Jan. 14 in Science.
"My expectation for ...
Measuring the belowground world
2021-01-14
If you asked people which group of animals is the most abundant on earth, hardly anyone would know the right answer. Ants? Fish? No, and not humans either. The answer is nematodes, also known as roundworms. Four out of five animals on earth belong to this group, and the reason hardly anyone is aware of the fact is that they live underground, invisible to us. Together with thousands of other soil organisms, they quietly, discreetly and constantly perform enormously important services for the world above them.
The soil is one of the most species-rich habitats in existence. Living under one square meter ...
Quantum computers to study the functioning of the molecules of life
2021-01-14
The human body is like a construction site where hundreds of thousands of different molecular nanomachines, called proteins, are simultaneously at work. Each one of these biomolecules, which are chains of amino acids essential to living organisms, perform a different biological function, often in synergy with other proteins. During their formation (the folding process) or in the performance of their biological functions, proteins change their shape in a very specific way. In many cases it is possible to conduct experiments that provide images of proteins at near atomic resolution, but only when they are in the stable and biologically ...
The role of T cells in fighting cancer
2021-01-14
New research from CU Cancer Center member Jing Hong Wang, MD, PhD, and recent University of Colorado Immunology program graduate Rachel Woolaver, PhD, may help researchers develop more effective personalized immunotherapy for cancer patients.
Working within Wang's specialty of cancer immunology and head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs), the researchers worked to establish a mouse model that would help them understand why some hosts' immune systems reject tumors easily, while others have a harder time doing so. Their research was published last week in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.
"It's particularly interesting now because the field of cancer treatment has really been going in the direction of immunotherapy, ...
Exposure to violence takes a toll on the socioemotional well-being of Californians
2021-01-14
Researchers at the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Program (VPRP) assessed the prevalence of exposure to violence, such as robbery or assault, and its impacts on the mental health and social functioning of California adults. Their study, published in the Journal of Interpersonal Violence, shows the far-reaching psychological effects an incident of gun violence can have on victims and those close to them.
The study's findings are based on data from 2,558 adults who responded to the 2018 California Safety and Wellbeing Survey (CSaWS). CSaWS is an ongoing survey research project on firearm ownership and the consequences of exposure to violence in California. Responses were weighted to be statistically representative of the state's adult population.
These ...
[1] ... [2742]
[2743]
[2744]
[2745]
[2746]
[2747]
[2748]
[2749]
2750
[2751]
[2752]
[2753]
[2754]
[2755]
[2756]
[2757]
[2758]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.