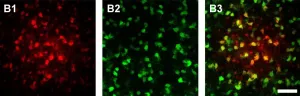
An anode-free zinc battery that could someday store renewable energy
2021-01-20
Renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, could help decrease the world's reliance on fossil fuels. But first, power companies need a safe, cost-effective way to store the energy for later use. Massive lithium-ion batteries can do the job, but they suffer from safety issues and limited lithium availability. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Nano Letters have made a prototype of an anode-free, zinc-based battery that uses low-cost, naturally abundant materials.
Aqueous zinc-based batteries have been previously explored for grid-scale energy storage ...
Mayo Clinic study indicates age influences sex-related outcomes after heart attack
2021-01-20
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Approximately 1.5 million heart attacks and strokes occur every year in men and women in the U.S. Sex and age play a large part in who experiences a heart attack, the methods used to treat these heart attacks, and the eventual post hospital outcomes of the people who experience heart attacks. Mayo Clinic researchers discuss these sex and age differences in study findings published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
In this study, Mayo Clinic researchers wanted to see if age was a key factor in sex-related differences in patients with a heart attack. Using public all-payer hospitalization data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, the team of researchers ...
Study shows how network of marine protected areas could help safeguard Antarctic penguins
2021-01-20
New research led by BirdLife International, the University of East Anglia (UEA) and British Antarctic Survey highlights how a proposed network of marine protected areas could help safeguard some of the most important areas at sea for breeding Antarctic penguins.
The findings, published today in the journal Frontiers in Marine Science, show that if all the Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) proposed around Antarctica were adopted, the permanent conservation of high-quality areas for a flagship group of Antarctic wildlife - the penguins - would increase by between 49% and 100% depending on the species.
The Southern Ocean surrounding Antarctica is home to thousands of unique species, including seals, whales and four species ...
Severe menopause symptoms often accompany premature ovarian insufficiency
2021-01-20
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Jan. 20, 2021)--Hot flashes, insomnia, and vaginal dryness are commonly reported symptoms that accompany the menopause transition. A new study suggests that such symptoms--especially psychological and sexual problems--are worse for women who have premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) than for women undergoing natural menopause. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Premature ovarian insufficiency is defined as the cessation of ovarian function that leads to menopause before the age of 40 years. The ...
Making microwaves safer for children
2021-01-20
A 15-year research and advocacy effort to make microwave ovens safer has led to a change in national manufacturing standards that will make microwaves more difficult for young children to open, protecting them from the severe microwave-related burns that scar hundreds of kids under 5 years old in the United States each year. Researchers at Rush University Medical Center and other leaders of the campaign, who worked diligently to document the frequency and severity of these injuries and young children's vulnerability to them, published the results of their efforts in The Journal of Pediatrics ...
Stealing the spotlight in the field and kitchen
2021-01-20
January 20, 2021 - Plant breeders are constantly working to develop new bean varieties to meet the needs and desires of the food industry. But not everyone wants the same thing.
Many consumers desire heirloom-type beans, which have great culinary quality and are visually appealing. On the other hand, farmers desire beans with better END ...
Breakthrough in understanding 'tummy bug' bacteria
2021-01-20
Scientists have discovered how bacteria commonly responsible for seafood-related stomach upsets can go dormant and then "wake up".
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a marine bacterium that can cause gastroenteritis in humans when eaten in raw or undercooked shellfish such as oysters and mussels.
Some of these bacteria are able to turn dormant in poor growth conditions such as cold temperatures - and can remain in that state of hibernation for long periods before resuscitating.
University of Exeter scientists have identified a population of these dormant cells that are better at waking up, and have discovered an enzyme involved in that waking up process.
"Most of these bacteria die when they encounter poor growth conditions, but we identified sub-populations ...
New Parkinson's disease therapeutics discovered by Ben-Gurion U researchers
2021-01-20
BEER-SHEVA, Israel...January 20, 2021 -Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers have discovered that the protein BMP5/7 offers promising therapeutics that could slow down or halt the progression of Parkinson's disease.
The findings were published in the prestigious clinical neurology journal, END ...
New negative pressure ventilator requiring fewer staffing resources developed in fight against COVID-19
2021-01-20
A new negative pressure ventilator which could provide additional treatment options for patients with respiratory failure, including those with COVID-19 - and whose design can be easily adapted to developing countries - has been created by a team that includes anaesthetists, nurses and engineers. Details on the new exovent system - which is similar in design but much smaller in scale and easier to use than the devices used to help treat polio patients during the 1950s - are published in Anaesthesia (a journal of the Association of Anaesthetists).
Use of this system ...
Protected areas vulnerable to growing emphasis on food security
2021-01-20
Protected areas are critical to mitigating extinction of species; however, they may also be in
conflict with efforts to feed the growing human population. A new study shows that 6% of all
global terrestrial protected areas are already made up of cropland, a heavily modified habitat
that is often not suitable for supporting wildlife. Worse, 22% of this cropland occurs in areas
supposedly enjoying the strictest levels of protection, the keystone of global biodiversity
protection efforts.
This finding was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by
researchers at the University of Maryland's National Socio-Environmental ...
Exploration of toxic Tiger Rattlesnake venom advances use of genetic science techniques
2021-01-20
The Tiger Rattlesnake possesses the simplest, yet most toxic venom of any rattlesnake species, and now new research from a team lead by a University of South Florida biologist can explain the genetics behind the predator's fearsome bite.
Published in the new edition of "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences," USF Department of Integrative Biology Assistant Professor Mark Margres and colleagues across the southeastern United States have sequenced the genome of the Tiger Rattlesnake to understand the genotype of the venom trait. Despite the simplicity of the Tiger Rattlesnake's venom, Margres says it is roughly 40 times more toxic than the venom of the Eastern Diamondback ...
Rush researchers demonstrate success with new therapy for COVID-19
2021-01-20
A new therapy developed by researchers at Rush University Medical Center is showing success as a way to prevent COVID-19 symptoms in mice.
In a study published in the Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology, mouse models with COVID-19 showed positive results when a small peptide was introduced nasally. The peptide proved effective in reducing fever, protecting the lungs, improving heart function and reversing cytokine storm -- a condition in which an infection triggers the immune system to flood the bloodstream with inflammatory proteins. The researchers also report success in preventing the disease from progression.
"This ...
Worker safety goes beyond human error
2021-01-19
Disasters in high-risk industries can have catastrophic environmental, financial and human safety consequences. One way these industries help prevent and mitigate disasters is formal procedures designed to standardize how work is done. These procedures typically come in the form of a written document workers use while performing a task.
Camille Peres, associate professor at the Texas A&M University School of Public Health, said that there are two models of safety companies usually follow to varying degrees, whether they realize it or not. Safety model one "is very much a control paradigm," Peres said. "The idea the company has is that if they control absolutely everything that's going on, then they will be safe." This ...
How to train a robot (using AI and supercomputers)
2021-01-19
Before he joined the University of Texas at Arlington as an Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering and founded the Robotic Vision Laboratory there, William Beksi interned at iRobot, the world's largest producer of consumer robots (mainly through its Roomba robotic vacuum).
To navigate built environments, robots must be able to sense and make decisions about how to interact with their locale. Researchers at the company were interested in using machine and deep learning to train their robots to learn about objects, but doing so requires a large dataset of images. While there are millions of photos and videos of rooms, none were shot from the vantage point of a robotic vacuum. Efforts to train using images with human-centric perspectives failed.
Beksi's ...
Constructing termite turrets without a blueprint
2021-01-19
Following a series of studies on termite mound physiology and morphogenesis over the past decade, researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences have now developed a mathematical model to help explain how termites construct their intricate mounds.
The research is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Termite mounds are amongst the greatest examples of animal architecture on our planet," said L. Mahadevan, the Lola England de Valpine Professor of Applied Mathematics, of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, and ...
Do simulations represent the real world at the atomic scale?
2021-01-19
Computer simulations hold tremendous promise to accelerate the molecular engineering of green energy technologies, such as new systems for electrical energy storage and solar energy usage, as well as carbon dioxide capture from the environment. However, the predictive power of these simulations depends on having a means to confirm that they do indeed describe the real world.
Such confirmation is no simple task. Many assumptions enter the setup of these simulations. As a result, the simulations must be carefully checked by using an appropriate "validation protocol" involving experimental measurements.
"We focused on a solid/liquid interface because interfaces are ubiquitous in materials, and those between oxides and water are key in many energy applications." -- Giulia Galli, theorist ...
Genome editing to treat human retinal degeneration
2021-01-19
New Rochelle, NY, January 19, 2021--Gene editing therapies, including CRISPR-Cas systems, offer the potential to correct mutations causing inherited retinal degenerations, a leading cause of blindness. Technological advances in gene editing, continuing safety concerns, and strategies to overcome these challenges are highlighted in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy. Click here to read the full-text article free on the Human Gene Therapy website.
"Currently, the field is undergoing rapid development with a number of competing gene editing strategies, including allele-specific knock-down, base editing, prime editing, and RNA editing, are under investigation. Each offers a ...
Appearance, social norms keep students off Zoom cameras
2021-01-19
ITHACA, N.Y. - When the semester shifted online amid the COVID-19 pandemic last spring, Cornell University instructor Mark Sarvary, and his teaching staff decided to encourage - but not require - students to switch on their cameras.
It didn't turn out as they'd hoped.
"Most of our students had their cameras off," said Sarvary, director of the Investigative Biology Teaching Laboratories in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences (CALS).
"Students enjoy seeing each other when they work in groups. And instructors like seeing students, because it's a way to assess whether or not they understand the material," Sarvary said. "When we switched to online learning, that component got lost. We wanted to investigate the reasons ...
NASA explores solar wind with new view of small sun structures
2021-01-19
Scientists have combined NASA data and cutting-edge image processing to gain new insight into the solar structures that create the Sun's flow of high-speed solar wind, detailed in new research published today in The Astrophysical Journal. This first look at relatively small features, dubbed "plumelets," could help scientists understand how and why disturbances form in the solar wind.
The Sun's magnetic influence stretches billions of miles, far past the orbit of Pluto and the planets, defined by a driving force: the solar wind. This constant outflow of solar material carries the Sun's magnetic field out into space, where it shapes the environments around Earth, other worlds, and in the reaches of deep space. Changes in the solar wind ...
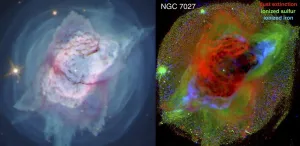
Astronomers dissect the anatomy of planetary nebulae using Hubble Space Telescope images
2021-01-19
Images of two iconic planetary nebulae taken by the Hubble Space Telescope are revealing new information about how they develop their dramatic features. Researchers from Rochester Institute of Technology and Green Bank Observatory presented new findings about the Butterfly Nebula (NGC 6302) and the Jewel Bug Nebula (NGC 7027) at the 237th meeting of the American Astronomical Society on Friday, Jan. 15.
Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 observed the nebulae in 2019 and early 2020 using its full, panchromatic capabilities, and the astronomers involved in the project ...
Unlocking 'the shape of water' in mechanisms of antibiotic resistance
2021-01-19
New high-resolution structures of the bacterial ribosome determined by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago show that a single water molecule may be the cause -- and possible solution -- of antibiotic resistance.
The findings of the new UIC study are published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology.
Pathogenic germs become resistant to antibiotics when they develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them. Each year in the U.S., millions of people suffer from antibiotic-resistant infections, and thousands of people die as a result.
Developing new drugs is a key way the scientific community is trying to reduce the impact of antibiotic resistance.
"The first thing we need to do to make improved drugs is to better understand how antibiotics work and how 'bad ...
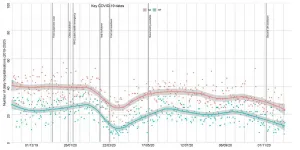
Heart attack patients in England 'fearful' of seeking medical help amid COVID crisis
2021-01-19
Data analysis is revealing a second sharp drop in the number of people admitted to hospital in England with acute heart failure or a heart attack.
The decline began in October as the numbers of COVID-19 infections began to surge ahead of the second lockdown, which came into force in early November.
The findings, from a research group led by the University of Leeds, have been revealed in a letter to the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The decline - 41 percent fewer people attending with heart failure and 34 percent with a heart attack compared to pre-pandemic levels ...
Brain cell network supplies neurons with energy
2021-01-19
The human brain has about as many neurons as glial cells. These are divided into four major groups: the microglia, the astrocytes, the NG2 glial cells, and the oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrocytes function primarily as a type of cellular insulating tape: They form long tendrils, which consist largely of fat-like substances and do not conduct electricity. These wrap around the axons, which are the extensions through which the nerve cells send their electrical impulses. This prevents short circuits and accelerates signal forwarding.
Astrocytes, on the other hand, supply the nerve cells with energy: Through their appendages they come into contact with blood vessels and absorb glucose from these. ...
Light-controlled Higgs modes found in superconductors; potential sensor, computing uses
2021-01-19
AMES, Iowa - Even if you weren't a physics major, you've probably heard something about the Higgs boson.
There was the title of a 1993 book by Nobel laureate Leon Lederman that dubbed the Higgs "The God Particle." There was the search for the Higgs particle that launched after 2009's first collisions inside the Large Hadron Collider in Europe. There was the 2013 announcement that Peter Higgs and Francois Englert won the Nobel Prize in Physics for independently theorizing in 1964 that a fundamental particle - the Higgs - is the source of mass in subatomic ...
New COVID-19 model shows little benefit in vaccinating high-risk individuals first
2021-01-19
BROOKLYN, New York, Tuesday, January 19, 2021 - The World Health Organization END ...
[1] ... [2734]
[2735]
[2736]
[2737]
[2738]
[2739]
[2740]
[2741]
2742
[2743]
[2744]
[2745]
[2746]
[2747]
[2748]
[2749]
[2750]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.