IOF and IFCC review calls for harmonization of assays for reference bone turnover markers
2021-01-15
Bone turnover markers (BTMs) in blood and urine are useful tools in monitoring osteoporosis treatment effects and may be useful for improving patient adherence.
In 2011, a Joint Committee on Bone Metabolism of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (IFCC) designated Procollagen type I N-propeptide (PINP) and the C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (β-CTX) in blood as reference bone turnover markers for bone formation and bone resorption, respectively, in osteoporosis. However, the effective clinical implementation of ...
Climate impacts on health and urban areas: Heatwaves and death rate
2021-01-15
Over the last half-century, the probability of heat extreme events has changed by orders of magnitude in almost every region of the world, with occurrences that are now up to a hundred times more in respect to a century ago. Of all-natural disasters, extreme high temperature events are the main cause of weather-related mortality and they are also expected to be the main factor responsible for additional deaths due to climate change in the coming years.
In cities, the heat island effect creates higher temperatures than in vegetated areas. But conditions within urban areas are not equal in all their parts - either due to their physical form or to the specific needs or vulnerabilities of inhabitants - therefore not all districts ...
Hubble pinpoints supernova blast
2021-01-15
The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has observed the supernova remnant named 1E 0102.2-7219. Researchers are using Hubble's imagery of the remnant object to wind back the clock on the expanding remains of this exploded star in the hope of understanding the supernova event that caused it 1700 years ago.
The featured star that exploded long ago belongs to the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of our Milky Way located roughly 200 000 light-years away. The doomed star left behind an expanding, gaseous corpse -- a supernova remnant -- known as 1E 0102.2-7219.
Because the gaseous knots in this supernova ...
Designer cytokine makes paralyzed mice walk again
2021-01-15
The researchers published their report in the Journal Nature Communications from 15 January 2021.
When the communication breaks down
Spinal cord injuries caused by sports or traffic accidents often result in permanent disabilities such as paraplegia. This is caused by damage to nerve fibers, so-called axons, which carry information from the brain to the muscles and back from the skin and muscles. If these fibers are damaged due to injury or illness, this communication is interrupted. Since severed axons in the spinal cord can't grow back, the patients suffer from paralysis and numbness for life. To date, there are still no treatment options that could restore the lost functions ...
Intertropical Convergence Zone limits climate predictions in the tropical Atlantic
2021-01-15
El Niño or correctly El Niño - Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is the strongest natural climate fluctuation on time scales of a few years. Through ocean and atmosphere interactions, El Niño (Spanish for The Christ Child) events cause significant warming of the eastern Pacific, accompanied by catastrophic rainfall over South America and droughts in the Indo-Pacific region. Powerful events have global effects that reach even into the extra-tropics. There is also an El Niño variant in the Atlantic, called the Atlantic Niño, which, for example, has effects on rainfall in West Africa as well as the development of tropical cyclones over the eastern tropical Atlantic. A better understanding of the poorly investigated little ...
CHOP researchers Find NTRK fusions more common than expected in pediatric tumors
2021-01-15
Philadelphia, January 14, 2021--In a large study of pediatric cancer patients, researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have analyzed the frequency, fusion partners, and clinical outcome of neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) fusions, which are clinical biomarkers that identify patients suitable for treatment with FDA-approved TRK inhibitors. The researchers found that NTRK fusions are more common in pediatric tumors and also involve a wider range of tumors than adult cancers, information that could help prioritize screening for NTRK fusions in pediatric cancer patients who might benefit from treatment with TRK inhibitors.
The ...
Helium nuclei at the surface of heavy nuclei discovered
2021-01-15
The experiment was performed at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) in Osaka. The research team, lead by scientists from TU Darmstadt and the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy-Ion Research, and from the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science, discuss the new findings in a contribution to the latest issue of the journal "Science".
The strong interaction binds neutrons and protons together to atomic nuclei. The knowledge of properties of nuclei and their theoretical description is basis for our understanding of nuclear matter and the development of the universe. Laboratory-based studies of reactions between atomic nuclei provide means to explore nuclear properties. These experiments ...
ADA lowers target HbA1C levels for children with type-1 diabetes
2021-01-15
Diabetes is characterized by elevated levels of sugar or glucose (hyperglycemia) in the blood. This occurs due to the lack of the hormone insulin in type 1 diabetes, and to reduced insulin levels in combination with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. A recent review of data supports stricter control of hemoglobin A1C levels (HbA1C) among pediatric patients with T1D. This review was led by Dr. Maria J. Redondo, pediatric endocrinologist at Texas Children's Hospital and professor at Baylor College of Medicine, in collaboration with Dr. Sarah Lyons, pediatric endocrinologist at Texas Children's and assistant professor at Baylor College of Medicine, ...
Towards applications: ultra-low-loss on-chip zero-index materials
2021-01-15
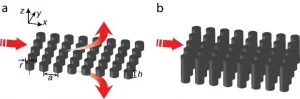
A refractive index of zero induces a wave vector with zero amplitude and undefined direction. Therefore, light propagating inside a zero-index medium does not accumulate any spatial phase advance, resulting in perfect spatial coherence. Such coherence brings several potential applications, including arbitrarily shaped waveguides, phase-mismatch-free nonlinear propagation, large-area single-mode lasers, and extended super radiance. A promising platform to achieve these applications is an integrated Dirac-cone material that features an impedance-matched zero index. However, although this platform eliminates ohmic losses via its purely dielectric structure, it still entails out-of-plane radiation loss (about 1 dB/μm), restricting the applications to a small scale.
In ...
Dual-shot dynamics and ultimate frequency of all-optical magnetic recording on GdFeCo
2021-01-15
The development of ultrafast all-optical switches has long been a popular topic in photonics, while the speed of magnetization reversal triggered by means other than magnetic fields has recently attracted intense interest in spintronics. The discovery of all-optical helicity-dependent switching in metallic GdFeCo has promised a merger of the fields of photonics and spintronics, paving the way for faster and more energy-efficient information processing technologies. However, the real potential of all-optical switching is still poorly understood because it is still unclear whether magnetic switching by light can keep up with the GHz frequencies required by photonics technologies. ...
Bio-inspired spiral hydrogel fiber qualified to be surgical suture
2021-01-15
"The lotus roots may break, but the fiber remains joined" is an old Chinese saying that reflects the unique structure and mechanical properties of the lotus fiber. The outstanding mechanical properties of lotus fibers can be attributed to their unique spiral structure, which provides an attractive model for biomimetic design of artificial fibers.
In a new study published in Nano Letters, a team led by Prof. YU Shuhong from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported a bio-inspired lotus-fiber-mimetic spiral structure bacterial cellulose (BC) hydrogel fiber with high strength, ...
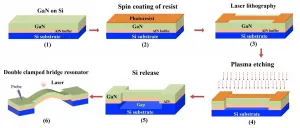
Newly developed GaN based MEMS resonator operates stably even at high temperature
2021-01-15
Liwen Sang, independent scientist at International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics, National Institute for Materials Science (also JST PRESTO researcher) developed a MEMS resonator that stably operates even under high temperatures by regulating the strain caused by the heat from gallium nitride (GaN).
High-precision synchronization is required for the fifth generation mobile communication system (5G) with a high speed and large capacity. To that end, a high-performance frequency reference oscillator which can balance the temporal stability and temporal resolution is necessary as a timing device to generate signals ...
WSU scientists identify contents of ancient Maya drug containers
2021-01-15
PULLMAN, Wash. - Scientists have identified the presence of a non-tobacco plant in ancient Maya drug containers for the first time.
The Washington State University researchers detected Mexican marigold (Tagetes lucida) in residues taken from 14 miniature Maya ceramic vessels.
Originally buried more than 1,000 years ago on Mexico's Yucatán peninsula, the vessels also contain chemical traces present in two types of dried and cured tobacco, Nicotiana tabacum and N. rustica. The research team, led by anthropology postdoc Mario Zimmermann, thinks the Mexican marigold was mixed with the tobacco to make smoking more enjoyable.
The discovery of the vessels' contents paints a clearer picture of ancient Maya drug use practices. The research, which was published ...
Are partially protected areas the 'red herrings' of marine conservation?
2021-01-15
Partially protected areas - marine reserves that allow some forms of fishing - are no more effective socially or ecologically than open marine areas in Australia's Great Southern Reef, a new UNSW study has concluded.
The research, published in Conservation Biology today, comes at a time when the High Ambition Coalition of 50 countries of the world (which does not include Australia) have pledged to protect more than 30 per cent of the planet's lands and seas by the end of this decade. But not all protected areas are created equal.
The UNSW study discovered partially protected areas in southern Australia had no more fish, invertebrates or algae and no difference in ...
The end of domestic wine in 17th century Japan
2021-01-15
Researchers from Kumamoto University (Japan) have found an Edo period document that clearly indicates the Hosokawa clan, rulers of the Kokura Domain (modern-day Fukuoka Prefecture), completely stopped producing wine in 1632, the year before the shogunate ordered them to move to the Higo Domain (now Kumamoto Prefecture). The researchers believe that the discontinuation of wine production was directly related to this move and because it was considered to be a drink of a religion that was harshly suppressed in Japan at that time, Christianity.
Previous analysis of historical documents revealed that the lord of the Hosokawa clan, Tadatoshi Hosokawa, ordered wine production from 1627 to 1630 for medicinal use. His ...
Divergences between scientific and Indigenous and Local Knowledge can be helpful
2021-01-15
Divergences between scientific and Indigenous and Local Knowledge can provide a better understanding of why local pastoralists may be willing, or not, to participate in conservation initiatives for carnivores, a study from University of Helsinki suggests.
Carnivore conservation has historically been based primarily on scientific knowledge using a wide range of sampling methods, such as camera trapping and track surveys. However, the estimates of these common ecological sampling methods can be quite uncertain and can depend on accessibility and geology, which is the case of many remote areas, such as Sibiloi National Park in Northern Kenya. For this reason, the inclusion of local communities that share ...
Filling a crucial gap in aquafarming: ion beam breeding to the rescue
2021-01-15
A research team led by scientists at the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science (RNC) has successfully created larger-than-usual strains of zooplankton -- which are used in fish nurseries -- by creating mutations with a heavy ion beam. The new strains of zooplankton could contribute to improving the survival rate and optimizing the growth of juvenile fish in aquaculture.
Economically important fish species, such as bluefin tuna, yellowtail, flatfish and groupers, are fed live bait until they are large enough to be fed with artificial foods. ...
A new tool to facilitate quicker, error-free software design
2021-01-15
Any building project requires the formulation of a series of initial plans prior to starting construction to serve as a basis and guide for the whole process. A similar procedure is followed in software development, with the inclusion of a specific step known as modelling. "The process is equivalent to the production of a set of plans for a building before its construction," explained Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) Faculty of Computer Science, Multimedia and Telecommunications professor and member of the SOM Research Lab research group -from the Internet Interdisciplinary Institute (IN3)-, Robert Clarisó.
Engineers use modelling to describe ...
Artificial Intelligence beats us in chess, but not in memory
2021-01-15
In the last decades, Artificial Intelligence has shown to be very good at achieving exceptional goals in several fields. Chess is one of them: in 1996, for the first time, the computer Deep Blue beat a human player, chess champion Garry Kasparov. A new piece of research shows now that the brain strategy for storing memories may lead to imperfect memories, but in turn, allows it to store more memories, and with less hassle than AI. The new study, carried out by SISSA scientists in collaboration with Kavli Institute for Systems Neuroscience & Centre for Neural Computation, Trondheim, Norway, has just been published in Physical Review Letters.
Neural networks, real or artificial, learn by tweaking the connections ...
Altering mealtimes could prevent development of Type 2 diabetes
2021-01-15
An innovative new study is set to examine if changing our mealtimes to earlier or later in the day could reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Led by Dr Denise Robertson, Professor Jonathan Johnston and post graduate researcher Shantel Lynch from the University of Surrey, the study, outlined in the journal Nutrition Bulletin, will investigate if changing the time we eat during the day could reduce risk factors such as obesity and cholesterol levels that are typically associated with the development of Type 2 diabetes. The team of researchers will also for the first time investigate, via a series of interviews with participants and their friends and family, the impact of such changes on home life, work/social commitments and whether co-habitants of those who make such ...
Genital shape key to male flies' sexual success
2021-01-15
Having genitals of a certain shape and size gives male flies a major reproductive advantage, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists examined the reproductive success of male Drosophila simulans flies both alone with a female and in various states of competition with other males.
Certain genital shapes were consistently better in terms of number of offspring sired.
However - surprisingly, given how fast genital form evolves - the selection documented was rather weak.
"Male genitals generally, and in Drosophila specifically, evolve very quickly, so we were really surprised to find this weak selection," said Professor David Hosken, of the University of Exeter.
"Selection is the major mechanism of evolution and hence where we see rapid evolution, ...
Basis for the essential cellular powerhouses
2021-01-15
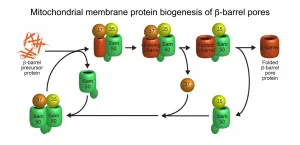
Mitochondria are vital for the human body as cellular powerhouses: They possess more than 1,000 different proteins, required for many central metabolic pathways. Disfunction of these lead to severe diseases, especially of the nervous system and the heart. In order to transport proteins and metabolites, mitochondria contain a special group of so-called beta-barrel membrane proteins, which form transport pores in the outer mitochondrial membrane. So far, scientists have not been able to explain the operating mode of the sorting and assembly machinery (SAM) for the biogenesis of these beta-barrel proteins. A team led by Prof. Dr. Toshiya Endo from Kyoto University/Japan, Prof. Dr. Nils Wiedemann and ...
<i>BIO Integration</i> journal, Volume 1, Issue number 4, publishes
2021-01-15
Guangzhou, January 15, 2021: New journal BIO Integration (BIOI) publishes its fourth issue, volume 1, issue 4. BIOI is a peer-reviewed, open access, international journal, which is dedicated to spreading multidisciplinary views driving the advancement of modern medicine. Aimed at bridging the gap between the laboratory, clinic, and biotechnology industries, it will offer a cross-disciplinary platform devoted to communicating advances in the biomedical research field and offering insights into different areas of life science, in order to encourage cooperation and exchange among scientists, clinical researchers, and health care providers.
The issue contains an original article, three review ...
<i>New England Journal of Medicine</i> publishes COVID-19 treatment trial results
2021-01-15
A clinical trial involving COVID-19 patients hospitalized at UT Health San Antonio and University Health, among roughly 100 sites globally, found that a combination of the drugs baricitinib and remdesivir reduced time to recovery, according to results published Dec. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine. Six researchers from UT Health San Antonio and University Health are coauthors of the publication because of the San Antonio site's sizable patient enrollment in the trial.
The Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial 2 (ACTT-2), which compared the combination therapy versus remdesivir paired with an inactive placebo in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), ...
Snakes evolve a magnetic way to be resistant to venom
2021-01-15
Certain snakes have evolved a unique genetic trick to avoid being eaten by venomous snakes, according to University of Queensland research.
Associate Professor Bryan Fry from UQ's Toxin Evolution Lab said the technique worked in a manner similar to the way two sides of a magnet repel each other.
"The target of snake venom neurotoxins is a strongly negatively charged nerve receptor," Dr Fry said.
"This has caused neurotoxins to evolve with positively charged surfaces, thereby guiding them to the neurological target to produce paralysis.
"But some snakes have evolved to replace a negatively charged amino acid on their receptor with a positively charged one, meaning the neurotoxin is repelled.
"It's an inventive genetic mutation and it's been completely missed until now.
"We've ...
[1] ... [2732]
[2733]
[2734]
[2735]
[2736]
[2737]
[2738]
[2739]
2740
[2741]
[2742]
[2743]
[2744]
[2745]
[2746]
[2747]
[2748]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.