A new carbon budget framework provides a clearer view of our climate deadlines
2021-01-19
Just how close are the world's countries to achieving the Paris Agreement target of keeping climate change limited to a 1.5°C increase above pre-industrial levels?
It's a tricky question with a complex answer. One approach is to use the remaining carbon budget to gauge how many more tonnes of carbon dioxide we can still emit and have a chance of staying under the target laid out by the 2015 international accord. However, estimates of the remaining carbon budget have varied considerably in previous studies because of inconsistent approaches and assumptions used by researchers.
Nature Communications Earth and Environment just published a paper by a group of researchers led by Damon Matthews, professor in the Department of Geography, Planning and Environment. In it, ...
Moffitt researchers identify how cancer cells adapt to survive harsh tumor microenvironments
2021-01-19
TAMPA, Fla. - Cells need energy to survive and thrive. Generally, if oxygen is available, cells will oxidize glucose to carbon dioxide, which is very efficient, much like burning gasoline in your car. However, even in the presence of adequate oxygen, many malignant cells choose instead to ferment glucose to lactic acid, which is a much less efficient process. This metabolic adaptation is referred to as the Warburg Effect, as it was first described by Otto Warburg almost a century ago. Ever since, the conditions that would evolutionarily select for cells to exhibit a Warburg Effect have been in debate, as it is much less efficient and produces toxic waste ...
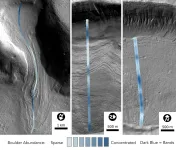
Mystery of Martian glaciers revealed
2021-01-19
In a new paper published today in the Proceedings of the National Academies of ScienceS (PNAS), planetary geologist Joe Levy, assistant professor of geology at Colgate University, reveals a groundbreaking new analysis of the mysterious glaciers of Mars.
On Earth, glaciers covered wide swaths of the planet during the last Ice Age, which reached its peak about 20,000 years ago, before receding to the poles and leaving behind the rocks they pushed behind. On Mars, however, the glaciers never left, remaining frozen on the Red Planet's cold surface for more than 300 million years, covered in debris. "All the rocks and sand carried on that ice have remained ...
State responses, not federal, influenced rise in unemployment claims early in the pandemic
2021-01-19
ATLANTA--Early in the U.S. COVID-19 pandemic, unemployment claims were largely driven by state shutdown orders and the nature of a state's economy and not by the virus, according a new article by Georgia State University economists.
David Sjoquist and Laura Wheeler found no evidence the Payroll Protection Program (PPP) affected the number of initial claims during the first six weeks of the pandemic.
Their research explores state differences in the magnitude of weekly unemployment insurance claims for the weeks ending March 14 through April 25 by focusing on three factors: the impact of COVID-19, the effects of state economic structures and state orders closing non-essential ...
With a little help from their friends, older birds breed successfully
2021-01-19
The offspring of older animals often have a lower chance of survival because the parents are unable to take care of their young as well as they should. The Seychelles warbler is a cooperatively breeding bird species, meaning that parents often receive help from other birds when raising their offspring. A study led by biologists from the University of Groningen shows that the offspring of older females have better prospects when they are surrounded by helpers. This impact of social behaviour on reproductive success is described in a paper that was published ...
Study identifies a nonhuman primate model that mimics severe COVID-19 similar to humans
2021-01-19
Philadelphia, January 19, 2021 - Aged, wild-caught African green monkeys exposed to the SARS-CoV-2 virus developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) with clinical symptoms similar to those observed in the most serious human cases of COVID-19, report researchers in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier. This is the first study to show that African green monkeys can develop severe clinical disease after SARS-CoV-2 infection, suggesting that they may be useful models for the study of COVID-19 in humans.
"Animal models greatly enhance our understanding of diseases. The lack of an animal model for severe manifestations of COVID-19 has hampered our understanding of this form of the disease," explained lead investigator Robert V. Blair, DVM, PhD, ...
Study finds COVID-19 attack on brain, not lungs, triggers severe disease in mice
2021-01-19
ATLANTA--Georgia State University biology researchers have found that infecting the nasal passages of mice with the virus that causes COVID-19 led to a rapid, escalating attack on the brain that triggered severe illness, even after the lungs were successfully clearing themselves of the virus.
Assistant professor Mukesh Kumar, the study's lead researcher, said the findings have implications for understanding the wide range in symptoms and severity of illness among humans who are infected by SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
"Our thinking that it's more of a respiratory disease is not necessarily ...
A little friction goes a long way toward stronger nanotube fibers
2021-01-19
HOUSTON - (Jan. 19, 2021) - Carbon nanotube fibers are not nearly as strong as the nanotubes they contain, but Rice University researchers are working to close the gap.
A computational model by materials theorist Boris Yakobson and his team at Rice's Brown School of Engineering establishes a universal scaling relationship between nanotube length and friction between them in a bundle, parameters that can be used to fine-tune fiber properties for strength.
The model is a tool for scientists and engineers who develop conductive fibers for aerospace, automotive, medical and textile applications like smart clothing. Carbon nanotube fibers have been considered as a possible basis for a space elevator, a project Yakobson has studied.
The research ...
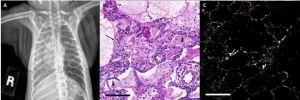
New research finds connection: Inflammation, metabolism and scleroderma scarring
2021-01-19
Scleroderma, a chronic and currently incurable orphan disease where tissue injury causes potentially lethal skin and lung scarring, remains poorly understood.
However, the defining characteristic of systemic sclerosis, the most serious form of scleroderma, is irreversible and progressive scarring that affects the skin and internal organs.
Published in iScience, Michigan Medicine's Scleroderma Program and the rheumatology and dermatology departments partnered with the Northwestern Scleroderma Program in Chicago and Mayo Clinic to investigate the causes of ...
Scientists reveal structure of plants' energy generators
2021-01-19
Researchers have revealed the first atomic structures of the respiratory apparatus that plants use to generate energy, according to a study published today in eLife.
The 3D structures of these large protein assemblies - the first described for any plant species - are a step towards being able to develop improved herbicides that target plant respiration. They could also aid the development of more effective pesticides, which target the pest's metabolism while avoiding harm to crops.
Most organisms use respiration to harvest energy from food. Plants use photosynthesis to convert sunlight into sugars, and then respiration to break down the sugars into energy. This involves tiny cell components called mitochondria and a set of five protein assemblies ...
Set clear rules for vaccinating health care workers against SARS-CoV-2
2021-01-19
Provincial and territorial governments should set clear rules for vaccinating health care workers against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, in public and private settings, and should not leave this task to employers, according to an analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"An effective vaccine provided to health care workers will protect both the health workforce and patients, reducing the overall burden of COVID-19 on services and ensuring adequate personnel to administer to people's health needs through the pandemic," writes Dr. Colleen M. Flood, University of Ottawa Research Chair in Health Law & Policy and a ...
Canadian researchers create new form of cultivated meat
2021-01-19
HAMILTON, ON, Jan. 19, 2021 -- McMaster researchers have developed a new form of cultivated meat using a method that promises more natural flavour and texture than other alternatives to traditional meat from animals.
Researchers Ravi Selvaganapathy and Alireza Shahin-Shamsabadi, both of the university's School of Biomedical Engineering, have devised a way to make meat by stacking thin sheets of cultivated muscle and fat cells grown together in a lab setting. The technique is adapted from a method used to grow tissue for human transplants.
The sheets of living cells, each about the thickness of a sheet of printer paper, are first grown in culture and then concentrated on growth plates before being peeled ...
Research news tip sheet: Story ideas from Johns Hopkins Medicine
2021-01-19
NANOTECHNOLOGY PREVENTS PREMATURE BIRTH IN MOUSE STUDIES
Media Contact: Rachel Butch, rbutch1@jhmi.edu
In a study in mice and human cells, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say that they have developed a tiny, yet effective method for preventing premature birth. The vaginally delivered treatment contains nanosized (billionth of a meter) particles of drugs that easily penetrate the vaginal wall to reach the uterine muscles and prevent them from contracting. If proven effective in humans, the treatment could be one of the only clinical options available to prevent ...
Cyber-evolution: How computer science is harnessing the power of Darwinian transformation
2021-01-19
From a pair of simple principles of evolution--chance mutation and natural selection--nature has constructed an almost unfathomable richness of life around us. Despite our scientific sophistication, human design and engineering have struggled to emulate nature's techniques and her inexhaustible inventiveness. But that may be changing.
In a new perspective article, Stephanie Forrest and Risto Miikkulainen explore a domain known as evolutionary computation (EC), in which aspects of Darwinian evolution are simulated in computer systems.
The study highlights the progress our machines have made in replicating evolutionary processes and what this could mean for engineering design, software refinement, gaming strategy, robotics and even medicine, while fostering a deeper insight ...
What the lungfishes' genome teaches us about the vertebrates' conquest of land
2021-01-19
Using cutting-edge DNA sequencing technologies, a group of laboratories in Konstanz, Würzburg, Hamburg and Vienna, led by evolutionary biologist Professor Axel Meyer from the University of Konstanz, succeeded in fully sequencing the genome of the Australian lungfish. The genome, with a total size of more than 43 billion DNA building blocks, is nearly 14 times larger than that of humans and the largest animal genome sequenced to date. Its analysis provides valuable insights into the genetic and developmental evolutionary innovations that made it possible for fish to colonize land. The findings, published online in the journal Nature, expand our understanding of this major evolutionary ...
A master cancer gene hijacks a 'molecular crowbar' to make breast cancer cells invasive
2021-01-19
Researchers at the University of Helsinki have defined a cancer invasion machinery, which is orchestrated by a frequently mutated cancer gene called Ras. When signaling from Ras protein becomes abnormally high, like it does in many cancers, this switches on the cellular machinery that helps the cancer cells to depart from the tissue from which the cells have developed.
It has been unclear how the cancer invasion machinery works exactly, until now, as the study finds Ras in the role of Friar Lawrence in Shakespeare's famous play, "Get me an iron crow and bring it straight unto my cell (Romeo and Juliet, 5.2.21-23)." ...
No insect crisis in the Arctic - yet
2021-01-19
Climate change is more pronounced in the Arctic than anywhere else on the planet, raising concerns about the ability of wildlife to cope with the new conditions. A new study shows that rare insects are declining, suggesting that climatic changes may favour common species.
As part of a new volume of studies on the global insect decline, researchers are presenting the first Arctic insect population trends from a 24-year monitoring record of standardized insect abundance data from North-East Greenland.
The work took place during 1996-2018 as part of the ecosystem-based monitoring program Greenland Ecosystem Monitoring at the field station Zackenberg, located in the world's largest national ...
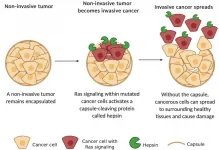
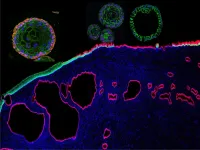
Novel organoid models: Illuminating path to cervical cancers
2021-01-19
Organoids are increasingly being used in biomedical research. These are organ-like structures created in the laboratory that are only a few millimetres in size. Organoids can be used to study life processes and the effect of drugs. Because they closely resemble real organs, they offer several advantages over other cell cultures.
Now there are also organoid models developed for the cervix. This part of the female body is particularly at risk to develop cancers. By creating novel organoid models, a group led by Cindrilla Chumduri (Würzburg), Rajendra Kumar Gurumurthy (Berlin) and Thomas F. Meyer ...
NIH officials highlight COVID-19 vaccine facts, unknowns for healthcare providers
2021-01-19
WHAT:
Healthcare providers must be able to explain the latest data supporting the safety and efficacy of vaccines for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) so they can strongly encourage vaccination when appropriate while acknowledging that uncertainty and unknowns remain. This message comes from a new commentary co-authored by Anthony S. Fauci, M.D., director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and other leading NIAID scientists in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine.
The commentary provides an overview of the seven COVID-19 vaccines furthest along in development in the United States. For each vaccine candidate, the authors describe ...
Rethinking spin chemistry from a quantum perspective
2021-01-19
Understanding how the natural world works enables us to mimic it for the benefit of humankind. Think of how much we rely on batteries. At the core is understanding molecular structures and the behavior of electrons within them. Calculating the energy differences between a molecule's electronic ground and excited spin states helps us understand how to better use that molecule in a variety of chemical, biomedical and industrial applications. We have made much progress in molecules with closed-shell systems, in which electrons are paired up and stable. Open-shell systems, on the ...
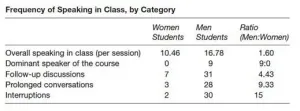
College classrooms are still chilly for women, as men speak more
2021-01-19
Men speak 1.6 times more often than women in college classrooms, revealing how gender inequities regarding classroom participation still exist, according to a Dartmouth study. By comparison, women are more hesitant to speak and are more apt to use apologetic language. The findings are published in Gender & Society.
When students didn't have to raise their hands to participate in class, men spoke three times more often than women. "You would think that it would be more equitable for students to not have to raise their hands to speak in class because then anyone could talk ...
E-cigarettes stress lungs, impair protein function
2021-01-19
RICHLAND, Wash.--E-cigarettes stress and inflame the lungs of rats, compromising important regulatory proteins through exposure, according to research recently published in the journal Redox Biology. The findings, made possible by a biomolecular technique developed by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, reveal that vaping induces subtle structural changes in proteins, marking the first time researchers have measured such damage. The results suggest that common compounds in the electronic alternative to conventional cigarettes are not without their own harms.
After exposing rats to e-cigarette vapor for three one-hour sessions ...
NUS engineers create 'smart' aerogel that turns air into drinking water
2021-01-19
Some say future wars will be fought over water, and a billion people around the world are already struggling to find enough water to live.
Now, researchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) are coming to the rescue. They have created a substance that extracts water from air without any external power source.
In the earth's atmosphere, there is water that can fill almost half a trillion Olympic swimming pools. But it has long been overlooked as a source for potable water.
To extract water from this under utilised source, a team led by Professor Ho Ghim Wei from the NUS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering created a type of aerogel, a solid material that weighs almost nothing. Under the microscope, it looks like a sponge, but it ...
World's first test to accurately predict depression and bipolar disorder
2021-01-19
University of South Australia scientists have developed the world's first test to accurately predict mood disorders in people, based on the levels of a specific protein found in the brain.
Links between low levels of mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor (mBDNF) and depression are well known but, until now, it hasn't been possible to distinguish between the three forms of the BDNF protein in blood samples.
The mature form promotes the growth of neurons and protects the brain, but the other two BDNF forms - its precursor and the prodomain of BDNF - bind to different receptors, causing nerve degeneration ...
Armouring anti-cancer T cells against immunosuppressants
2021-01-19
SINGAPORE, 19 January 2021 - Duke-NUS Medical School researchers, together with collaborators in Singapore, have designed armoured immune cells that can attack recurring cancer in liver transplant patients, while temporarily evading immunosuppressant drugs patients take to avoid organ rejection. The findings were published in the journal Hepatology.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of primary liver cancer and the sixth most common cancer worldwide. It often develops in people with chronic liver disease following hepatitis B infection.
A common treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma is to completely ...
[1] ... [2737]
[2738]
[2739]
[2740]
[2741]
[2742]
[2743]
[2744]
2745
[2746]
[2747]
[2748]
[2749]
[2750]
[2751]
[2752]
[2753]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.