Controlling chemical catalysts with sculpted light
2021-01-15
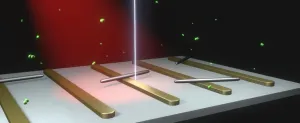
Like a person breaking up a cat fight, the role of catalysts in a chemical reaction is to hurry up the process - and come out of it intact. And, just as not every house in a neighborhood has someone willing to intervene in such a battle, not every part of a catalyst participates in the reaction. But what if one could convince the unengaged parts of a catalyst to get involved? Chemical reactions could occur faster or more efficiently.
Stanford University material scientists led by Jennifer Dionne have done just that by using light and advanced fabrication and characterization techniques to endow catalysts with new abilities.
In a proof-of-concept experiment, rods of palladium that were approximately 1/200th the width of a human hair served as catalysts. ...
Special interests can be assets for youth with autism
2021-01-15
COLUMBIA, Mo. - When he was in middle school, teachers would give Sam Curran a list of words to type in a computer to practice his vocabulary. But Sam, who has autism, was unable to stay focused on the task and required a significant amount of one-to-one direction from a teacher to complete his work. After his mother, Alicia, persuaded his teachers to allow Sam to change the colors of the words, he was able to complete work more independently and began making remarkable progress.
Now 20 years old, Sam's mother continues to ensure his special interests are leveraged in an effort to continue to help him grow and develop. A new survey from the MU Thompson Center for Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disorders has found that similar strategies for children with disabilities can help reduce anxiety ...
New videos show RNA as it's never been seen
2021-01-15
A new Northwestern University-led study is unfolding the mystery of how RNA molecules fold themselves to fit inside cells and perform specific functions. The findings could potentially break down a barrier to understanding and developing treatments for RNA-related diseases, including spinal muscular atrophy and perhaps even the novel coronavirus.
"RNA folding is a dynamic process that is fundamental for life," said Northwestern's Julius B. Lucks, who led the study. "RNA is a really important piece of diagnostic and therapeutic design. The more we know about RNA folding and complexities, the better we can design treatments."
Using data from RNA-folding experiments, the researchers generated the first-ever data-driven movies of how RNA folds as it is made by cellular ...
USC study measures brain volume differences in people with HIV
2021-01-15
Nearly 38 million people around the world are living with HIV, which, with access to treatment, has become a lifelong chronic condition. Understanding how infection changes the brain, especially in the context of aging, is increasingly important for improving both treatment and quality of life.
In January, researchers at the Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute (USC Stevens INI), part of the Keck School of Medicine of USC, and other international NeuroHIV researchers, published one of the largest-ever neuroimaging studies of HIV. The researchers pooled magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data from 1,203 HIV-positive individuals across Africa, ...
Large mammals make soil more fertile in tropical forests
2021-01-15
The White-lipped peccary Tayassu pecari is a boar-like hoofed mammal found throughout Central and South America. These animals roam the forest in bands of 50 to 100 individuals, eating a wide variety of foods. In Brazil's Atlantic Rainforest, they prefer the fruit of the jussara palm Euterpe edulis.
The jussara is very abundant in this biome, probably thanks to vast amounts of dung, urine, and soil trampling by peccaries as well as tapirs (Tapirus terrestris) and other fruit-eating animals, or frugivores. This behavior releases forms of nitrogen, a key element in plant growth.
A study supported ...
Principles of care established for young adults with substance use disorders
2021-01-15
Boston - A national group of pediatric addiction medicine experts have released newly-established principles of care for young adults with substance use disorder. Led by the Grayken Center for Addiction at Boston Medical Center, the collection of peer-reviewed papers was developed to guide providers on how to treat young adults with substance use disorder given their age-specific needs, as well as elevate national discussions on addressing these challenges more systematically.
Published in Pediatrics, the 11-paper supplement is the result of a convening of national experts in the treatment of young adults to determine the most important principles to address when caring for this unique population of patients with substance use disorder. ...
Physicists propose a new theory to explain one dimensional quantum liquids formation
2021-01-15
Liquids are ubiquitous in Nature: from the water that we consume daily to superfluid helium which is a quantum liquid appearing at temperatures as low as only a few degrees above the absolute zero. A common feature of these vastly different liquids is being self-bound in free space in the form of droplets. Understanding from a microscopic perspective how a liquid is formed by adding particles one by one is a significant challenge.
Recently, a new type of quantum droplets has been experimentally observed in ultracold atomic systems. These ones ...
Is your skin thirsty? Optoacoustic sensor measures water content in living tissue
2021-01-15
Researchers from Skoltech and the University of Texas Medical Branch (US) have shown how optoacoustics can be used for monitoring skin water content, a technique which is promising for medical applications such as tissue trauma management and in cosmetology. The paper outlining these results was published in the Journal of Biophotonics.
(swelling caused by fluid accumulation) or dehydration, which can also have cosmetic impacts. Right now, electrical, mechanical and spectroscopic methods can be used to monitor water content in tissues, but there is no accurate and noninvasive technique that would also provide a high resolution and significant probing depth required for potential clinical applications.
Sergei Perkov of the Skoltech Center for Photonics ...
Want a hot stock tip? Avoid this type of investment fund
2021-01-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio - "Buy low and sell high" says the old adage about investing in the stock market.
But a relatively new type of investment fund is luring unsophisticated investors into buying when values are at their highest, resulting in losses almost immediately, a new study has found.
The lure? Buying into trendy investment areas like cannabis, cybersecurity and work-from-home businesses.
"As soon as people buy them, these securities underperform as the hype around them vanishes," said Itzhak Ben-David, co-author of the study and professor of finance at The Ohio State University's Fisher College of Business.
"They appeal to people who are not sophisticated ...
Biodistribution of AAV gene transfer vectors in nonhuman primate
2021-01-15
New Rochelle, NY, January 15, 2021--The biodistribution of adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene transfer vectors can be measured in nonhuman primates using a new method. The method quantifies whole-body and organ-specific AAV capsids from 1 to 72 hours after administration. Study design and results are presented in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy. Click here to read the full-text article free on the Human Gene Therapy website through February 15, 2021.
AAV capsids were labeled with I-124 and delivered using two routes of administration: intravenous and directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Biodistribution was measured by quantitative positron emission tomography (PET) at 1, 24, 48, and 72 hours after AAV administration. Two AAV vectors - AAVrsh.10 and AAV9 - were compared.
"Following ...
New delivery method promises relief from antipsychotic medication's adverse side effects
2021-01-15
HAMILTON, ON, Jan. 15, 2021 -- A team of neuroscientists and engineers at McMaster University has created a nasal spray to deliver antipsychotic medication directly to the brain instead of having it pass through the body.
The leap in efficiency means patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and other conditions could see their doses of powerful antipsychotic medications cut by as much as three quarters, which is expected to spare them from sometimes-debilitating side effects while also significantly reducing the frequency of required treatment.
The new method delivers medication in a spray that reaches the brain directly through ...
Breathing easier with a better tracheal stent
2021-01-15
Pediatric laryngotracheal stenosis (LTS), a narrowing of the airway in children, is a complex medical condition. While it can be something a child is born with or caused by injury, the condition can result in a life-threatening emergency if untreated.
Treatment, however, is challenging. Depending on the severity, doctors will use a combination of endoscopic techniques, surgical repair, tracheostomy, or deployment of stents to hold the airway open and enable breathing.
While stents are great at holding the airway open and simultaneously allowing the trachea to continue growing, they can move around, ...
Target discovered that halts osteoarthritis-type knee cartilage degeneration
2021-01-15
There is currently no cure for osteoarthritis, but a group of scientists believe they've discovered a method through which a simple knee injection could potentially stop the disease's effects. These researchers showed that they could target a specific protein pathway in mice, put it into overdrive and halt cartilage degeneration over time. Building on that finding, they were able to show that treating mice with surgery-inducedknee cartilage degeneration through the same pathway via the state of the art of nanomedicine could dramatically reduce the cartilage degeneration and knee pain. These findings were published in Science Translational Medicine.
"Our lab is one of the few in the world studying epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) ...
Researchers trace geologic origins of Gulf of Mexico 'super basin' success
2021-01-15
The Gulf of Mexico holds huge untapped offshore oil deposits that could help power the U.S. for decades.
The energy super basin's longevity, whose giant offshore fields have reliably supplied consumers with oil and gas since the 1960s, is the result of a remarkable geologic past - a story that began 200 million years ago among the fragments of Pangea, when a narrow, shallow seaway grew into an ocean basin, while around it mountains rose then eroded away.
The processes that shaped the basin also deposited and preserved vast reserves of oil and gas, of which only a fraction has been extracted. Much of the remaining oil lies buried beneath ancient salt layers, just recently illuminated ...
UW researchers develop tool to equitably distribute limited vaccines
2021-01-15
MADISON, Wis. -- The demand for COVID-19 vaccines continues to outpace supply, forcing public health officials to decide who should be first in line for a shot, even among those in the same pool of eligible vaccine recipients.
To assist these efforts, researchers at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health and UW Health have developed a tool that incorporates a person's age and socioeconomic status to prioritize vaccine distribution among people who otherwise share similar risks due to their jobs. The tool helps identify those who are at greater risk of severe ...
NIH scientists identify nutrient that helps prevent bacterial infection
2021-01-15
WHAT:
Scientists studying the body's natural defenses against bacterial infection have identified a nutrient--taurine--that helps the gut recall prior infections and kill invading bacteria, such as Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kpn). The finding, published in the journal Cell by scientists from five institutes of the National Institutes of Health, could aid efforts seeking alternatives to antibiotics.
Scientists know that microbiota--the trillions of beneficial microbes living harmoniously inside our gut--can protect people from bacterial infections, but little is known about how they provide protection. Scientists are studying the microbiota with an eye to finding or enhancing natural treatments to replace antibiotics, which ...
Study: X-Rays surrounding 'Magnificent 7' may be traces of sought-after particle
2021-01-15
A new study, led by a theoretical physicist at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), suggests that never-before-observed particles called axions may be the source of unexplained, high-energy X-ray emissions surrounding a group of neutron stars.
First theorized in the 1970s as part of a solution to a fundamental particle physics problem, axions are expected to be produced at the core of stars, and to convert into particles of light, called photons, in the presence of a magnetic field.
Axions may also make up dark matter - the mysterious stuff that accounts for an estimated 85 percent of the total mass of the universe, yet we have so far only seen its gravitational effects on ordinary matter. Even if the X-ray excess turns out not to be ...
Simulating evolution to understand a hidden switch
2021-01-15
Computer simulations of cells evolving over tens of thousands of generations reveal why some organisms retain a disused switch mechanism that turns on under severe stress, changing some of their characteristics. Maintaining this "hidden" switch is one means for organisms to maintain a high degree of gene expression stability under normal conditions.
Tomato hornworm larvae are green in warmer regions, making camouflage easier, but black in cooler temperatures so that they can absorb more sunlight. This phenomenon, found in some organisms, is called phenotypic switching. Normally hidden, this switching is activated in response to dangerous genetic or environmental changes.
Scientists have typically studied this ...
Scientists' discovery is paving the way for novel ultrafast quantum computers
2021-01-15
Scientists at the Institute of Physics of the University of Tartu have found a way to develop optical quantum computers of a new type. Central to the discovery are rare earth ions that have certain characteristics and can act as quantum bits. These would give quantum computers ultrafast computation speed and better reliability compared to earlier solutions. The University of Tartu researchers Vladimir Hizhnyakov, Vadim Boltrushko, Helle Kaasik and Yurii Orlovskii published the results of their research in the scientific journal Optics Communications.
While in ordinary computers, the units of information are binary digits or bits, in quantum computers the units are quantum bits or qubits. In an ordinary computer, information is mostly ...
Stuck in a rut: Ocean acidification locks algal communities in a simplified state
2021-01-15
Tsukuba, Japan - Out with the old, in with the new, as the New Year's saying goes, but not where the marine environment is concerned. Researchers from Japan have discovered that ocean acidification keeps algal communities locked in a simplified state of low biodiversity.
In a study published on 11th January 2021 in Global Change Biology, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that as oceanic carbon dioxide levels rise, the biodiversity and ecological complexity of marine algal communities decline.
Ocean acidification is the continuing increase in the acidity of the Earth's oceans, caused by the absorption of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). ...
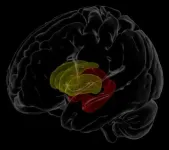
Revisiting the Global Workspace orchestrating the hierarchical organisation of the human brain
2021-01-15
The celebrations in the 250th anniversary of the birth of Ludwig van Beethoven would not be the same without Herbert von Karajan's brilliant performances conducting Beethoven's memorable symphonies. The execution of any musical symphony is a hugely difficult task, demanding very significant skills on the part of each individual musician - but perhaps the most difficult task lies with the conductor who has to orchestrate the musicians into making the music cohesively come alive and speak to our deepest emotions.
In many ways the human brain is like an orchestra, where different regions perform very different types of processing, such ...
Increased risk of Parkinson's disease in patients with schizophrenia
2021-01-15
A new study conducted at the University of Turku, Finland, shows that patients with a schizophrenia spectrum disorder have an increased risk of Parkinson's disease later in life. The increased risk may be due to alterations in the brain's dopamine system caused by dopamine receptor antagonists or neurobiological effects of schizophrenia.
The record-based case-control study was carried out at the University of Turku in collaboration with the University of Eastern Finland. The study examined the occurrences of previously diagnosed psychotic disorders and schizophrenia in over 25,000 Finnish Parkinson's disease (PD) patients ...
Spreading the sound
2021-01-15
Tsukuba, Japan - A team of researchers lead by the University of Tsukuba have created a new theoretical model to understand the spread of vibrations through disordered materials, such as glass. They found that as the degree of disorder increased, sound waves traveled less and less like ballistic particles, and instead began diffusing incoherently. This work may lead to new heat- and shatter-resistant glass for smartphones and tablets.
Understanding the possible vibrational modes in a material is important for controlling its optical, thermal, and mechanical properties. The propagation of vibrations in the form of sound of a single ...
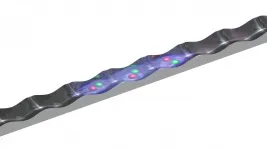
Scientists synthetize new material for high-performance supercapacitors
2021-01-15
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University jointly with colleagues from the University of Lille (Lille, France) synthetized a new material based on reduced graphene oxide (rGO) for supercapacitors, energy storage devices. The rGO modification method with the use of organic molecules, derivatives of hypervalent iodine, allowed obtaining a material that stores 1.7 times more electrical energy. The research findings are published in Electrochimica Acta academic journal (IF: 6,215; Q1).
Photo: modified rGO supercapacitor electrodes
A supercapacitor is an electrochemical device for storage and release ...
IOF and IFCC review calls for harmonization of assays for reference bone turnover markers
2021-01-15
Bone turnover markers (BTMs) in blood and urine are useful tools in monitoring osteoporosis treatment effects and may be useful for improving patient adherence.
In 2011, a Joint Committee on Bone Metabolism of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (IFCC) designated Procollagen type I N-propeptide (PINP) and the C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (β-CTX) in blood as reference bone turnover markers for bone formation and bone resorption, respectively, in osteoporosis. However, the effective clinical implementation of ...
[1] ... [2731]
[2732]
[2733]
[2734]
[2735]
[2736]
[2737]
[2738]
2739
[2740]
[2741]
[2742]
[2743]
[2744]
[2745]
[2746]
[2747]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.