Timing is of the essence when treating brain swelling in mice
2021-01-18
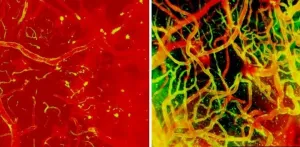
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health have discovered Jekyll and Hyde immune cells in the brain that ultimately help with brain repair but early after injury can lead to fatal swelling, suggesting that timing may be critical when administering treatment. These dual-purpose cells, which are called myelomonocytic cells and which are carried to the brain by the blood, are just one type of brain immune cell that NIH researchers tracked, watching in real-time as the brain repaired itself after injury. The study, published in Nature Neuroscience, ...
Synthesis of potent antibiotic follows unusual chemical pathway
2021-01-18
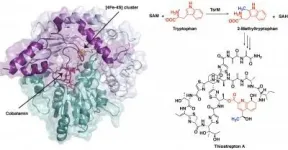
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Images of a protein involved in creating a potent antibiotic reveal the unusual first steps of the antibiotic's synthesis. The improved understanding of the chemistry behind this process, detailed in a new study led by Penn State chemists, could allow researchers to adapt this and similar compounds for use in human medicine.
"The antibiotic thiostrepton is very potent against Gram-positive pathogens and can even target certain breast cancer cells in culture," said Squire Booker, a biochemist at Penn State and investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. "While it has been used ...
New computational tool reliably differentiates between cancer and normal cells from single-cell RNA-sequencing data
2021-01-18
HOUSTON — In an effort to address a major challenge when analyzing large single-cell RNA-sequencing datasets, researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed a new computational technique to accurately differentiate between data from cancer cells and the variety of normal cells found within tumor samples. The work was published today in Nature Biotechnology.
The new tool, dubbed CopyKAT (copy number karyotyping of aneuploid tumors), allows researchers to more easily examine the complex data obtained from large single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments, which deliver gene expression data from ...
Mount Sinai researchers build models using machine learning technique to enhance predictions of COVID-19 outcomes
2021-01-18
Mount Sinai researchers have published one of the first studies using a machine learning technique called "federated learning" to examine electronic health records to better predict how COVID-19 patients will progress. The study was published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research - Medical Informatics on January 18.
The researchers said the emerging technique holds promise to create more robust machine learning models that extend beyond a single health system without compromising patient privacy. These models, in turn, can help triage patients and improve the quality of their care.
Federated ...
Eliminating microplastics in wastewater directly at the source
2021-01-18
A research team from the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) has developed a process for the electrolytic treatment of wastewater that degrades microplastics at the source. The results of this research have been published in the Environmental Pollution journal.
Wastewater can carry high concentrations of microplastics into the environment. These small particles of less than 5 mm can come from our clothes, usually as microfibers. Professor Patrick Drogui, who led the study, points out there are currently no established degradation methods to handle this contaminant during wastewater ...
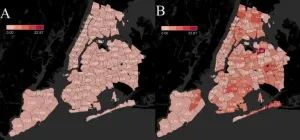
Where COVID-19 hit hardest, sudden deaths outside the hospital increased
2021-01-18
Philadelphia, January 18, 2021 - A new study comparing the incidence of sudden deaths occurring outside the hospital across New York City's highly diverse neighborhoods with the percentage of positive SARS-CoV-19 tests found that increased sudden deaths during the pandemic correlate to the extent of virus infection in a neighborhood. The analysis appears in Heart Rhythm, the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society, the Cardiac Electrophysiology Society, and the Pediatric & Congenital Electrophysiology Society, published by Elsevier.
"Our research shows the highly diverse regional distribution of out-of-hospital sudden death during ...
Many parents say teens with anxiety, depression may benefit from peer confidants at school
2021-01-18
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- An estimated one in five teenagers has symptoms of a mental health disorder such as depression or anxiety, and suicide is the second leading cause of death among teens.
But the first person a teen confides in may not always be an adult - they may prefer to talk to another teen.
And three-quarters of parents in a new national poll think peers better understand teen challenges, compared to teachers or counselors in the school. The majority also agree that peer support leaders at school would encourage more teens to talk with someone about their mental health problems, according to the C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health at Michigan Medicine.
"Peers may provide valuable support for ...
Vermont's BIPOC drivers are most likely to have a run-in with police, study shows
2021-01-18
New research examining more than 800,000 traffic stops in Vermont over the course of five years substantiates the term "driving while Black and Brown."
Compared to white drivers, Black and Latinx drivers in Vermont are more likely to be stopped, ticketed, arrested, and searched. But they are less likely to be found with contraband than white drivers. The report finds evidence not only of racial disparities but also racial bias in policing. What's more, a number of these gaps widened over the years examined in the report. With such comprehensive data encompassing the state of Vermont, the authors also found that Vermont police stop cars at a rate ...
Students returning home may have caused 9,400 secondary COVID-19 infections across UK
2021-01-18
A student infected with COVID-19 returning home from university for Christmas would, on average, have infected just less than one other household member with the virus, according to a new model devised by mathematicians at Cardiff University and published in END ...
Changing diets -- not less physical activity -- may best explain childhood obesity crisis
2021-01-18
Variation in consumption of market-acquired foods outside of the traditional diet -- but not in total calories burned daily -- is reliably related to indigenous Amazonian children's body fat, according to a Baylor University study that offers insight into the global obesity epidemic.
"The importance of a poor diet versus low energy expenditure on the development of childhood obesity remains unclear," said Samuel Urlacher, Ph.D., assistant professor of anthropology at Baylor University, CIFAR Azrieli Global Scholar and lead author of the study. "Using gold-standard measures of energy expenditure, we show that relatively lean, rural forager-horticulturalist children in the Amazon spend approximately the same total number of calories each day as their much ...
Scientists shed light on how and why some people report "hearing the dead"
2021-01-18
Spiritualist mediums might be more prone to immersive mental activities and unusual auditory experiences early in life, according to new research.
This might explain why some people and not others eventually adopt spiritualist beliefs and engage in the practice of 'hearing the dead', the study led by Durham University found.
Mediums who "hear" spirits are said to be experiencing clairaudient communications, rather than clairvoyant ("seeing") or clairsentient ("feeling" or "sensing") communications.
The researchers conducted a survey of 65 clairaudient spiritualist mediums from the Spiritualists' National Union and 143 members of the general population in the ...
Better diet and glucose uptake in the brain lead to longer life in fruit flies
2021-01-16
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have discovered that fruit flies with genetic modifications to enhance glucose uptake have significantly longer lifespans. Looking at the brain cells of aging flies, they found that better glucose uptake compensates for age-related deterioration in motor functions, and led to longer life. The effect was more pronounced when coupled with dietary restrictions. This suggests healthier eating plus improved glucose uptake in the brain might lead to enhanced lifespans.
The brain is a particularly power-hungry part of our bodies, consuming 20% of the oxygen we take in and 25% of the glucose. That's why it's so important that it can stay powered, ...
The COVID-19 pandemic in brazil has overwhelmed its health systems
2021-01-16
The spread of COVID-19 in Brazil overwhelmed the health systems in all the country's regions, particularly in areas where they were already fragile, according to a collaborative effort involving the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, the University of Sao Paulo, the Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro, the D'Or Institute of Research and Education and the Oswaldo Cruz Foundation. The findings, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, reveal that a large percentage of COVID-19 patients that were hospitalised in Brazil required intensive care and respiratory support, and many did not survive.
The COVID-19 pandemic has put an enormous strain on healthcare ...
New study connects religiosity in US South Asians to cardiovascular disease
2021-01-16
BOSTON - The Study on Stress, Spirituality and Health (SSSH), a cutting-edge proteomics analysis, suggests that religious beliefs modulate protein expression associated with cardiovascular disease in South Asians in the United States. The research, published by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) in Scientific Reports, demonstrates that spiritual struggles, in particular, significantly modify the impact of unique proteins on risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) in U.S. South Asians, a community that has especially ...
Rapid blood test identifies COVID-19 patients at high risk of severe disease
2021-01-16
One of the most vexing aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic is doctors' inability to predict which newly hospitalized patients will go on to develop severe disease, including complications that require the insertion of a breathing tube, kidney dialysis or other intensive care. Knowledge of a patient's age and underlying medical conditions can help predict such outcomes, but there are still surprises when younger, seemingly healthier patients suffer severe complications that can lead to death.
Now, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown that a relatively simple and rapid blood test can predict -- within a day of a hospital admission -- which patients with ...
Scientists offer road map to improve environmental observations in the Indian Ocean
2021-01-15
MIAMI--A group of more than 60 scientists have provided recommendations to improve the Indian Ocean Observing System (IndOOS), a basin-wide monitoring system to better understand the impacts of human-caused climate change in a region that has been warming faster than any other ocean.
The group, led by Lisa Beal, professor of ocean sciences at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, provides a road map for an enhanced IndOOS to better meet the scientific and societal needs for more reliable environmental forecasts in the next decade. The 136 actionable recommendations from the three-year, internationally coordinated review were published in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society.
The scientists call for four major ...
USask study finds COVID isolation worsens student diets, inactivity, and alcohol intake
2021-01-15
A University of Saskatchewan study has found that the COVID-19 pandemic has led to significant worsening of already poor dietary habits, low activity levels, sedentary behaviour, and high alcohol consumption among university students.
The findings of the study--the first to assess changes in students' dietary intake, physical activity, and sedentary behaviour before and during the pandemic--are published today in the journal Applied Physiology, Nutrition and Metabolism.
"Our findings are important because university students, especially those most vulnerable for poor nutrition and sedentary behaviour, should be targeted for interventions aimed at maintaining and improving physical activity and dietary practices during this pandemic and beyond," said lead author ...
45% of adults over 65 lack online medical accounts, which could affect COVID vaccination
2021-01-15
As the vaccination of older adults against COVID-19 begins across the country, new poll data suggests that many of them don't yet have access to the "patient portal" online systems that could make it much easier for them to schedule a vaccination appointment.
The poll finds that 45% of adults aged 65 to 80, and 42% of all adults aged 50 to 80, said they had not set up an account with their health provider's portal system. That's according to the newly analyzed data from the National Poll on Healthy Aging, based at the University of Michigan's Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation.
The new number actually represents some progress: 49% of adults in the same age range hadn't set up patient portal access the last time the ...
COVID-19 deaths really are different. But best practices for ICU care should still apply
2021-01-15
Exactly what kills a person with COVID-19?
How do those deaths differ from the deaths of people whose lungs fail rapidly because of other infections or injuries?
And what can hospital teams pressed into service on overtaxed COVID-19 wards do to try to keep patients from dying, despite strained circumstances?
All of these questions have sparked discussion - and even conspiracy theories - since the pandemic began. Now, two studies from Michigan Medicine may help answer them.
The bottom line: COVID-19 deaths are indeed different from other lung failure deaths. But, the researchers conclude, the kind of care needed to help sustain people through the worst cases of all forms of lung failure is highly similar. It just needs to be fine-tuned to focus on the ...
T cells linked to myelin implicated in MS-like disease in monkeys
2021-01-15
Scientists have uncovered new clues implicating a type of herpes virus as the cause of a central nervous system disease in monkeys that's similar to multiple sclerosis in people.
The findings, published in the Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, expand on previous work to understand the cause of the disease and potentially develop antiviral therapies. The work was led by scientists at Oregon Health & Science University.
"This gives us a better understanding of the model," said Scott Wong, Ph.D., senior author of the study and a scientist at the OHSU Vaccine and Gene Therapy Institute and the Oregon National Primate Research Center. "It draws more parallels to MS in people."
The new study reveals the presence of two kinds of T cells, a type of ...
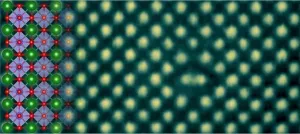
Conductive nature in crystal structures revealed at magnification of 10 million times
2021-01-15
In groundbreaking materials research, a team led by University of Minnesota Professor K. Andre Mkhoyan has made a discovery that blends the best of two sought-after qualities for touchscreens and smart windows--transparency and conductivity.
The researchers are the first to observe metallic lines in a perovskite crystal. Perovskites abound in the Earth's center, and barium stannate (BaSnO3) is one such crystal. However, it has not been studied extensively for metallic properties because of the prevalence of more conductive materials on the planet like metals or semiconductors. The ...
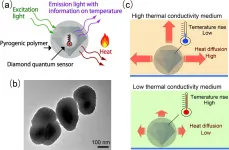
Nanodiamonds feel the heat
2021-01-15
Osaka, Japan - A team of scientists from Osaka University, The University of Queensland, and the National University of Singapore's Faculty of Engineering used tiny nanodiamonds coated with a heat-releasing polymer to probe the thermal properties of cells. When irradiated with light from a laser, the sensors acted both as heaters and thermometers, allowing the thermal conductivity of the interior of a cell to be calculated. This work may lead to a new set of heat-based treatments for killing bacteria or cancer cells.
Even though the cell is the fundamental unit of all living organisms, some physical properties have remained difficult to study in vivo. For example, a cell's thermal conductivity, as well as the rate that heat can flow through an object if ...
Glass frogs living near roaring waterfalls wave hello to attract mates
2021-01-15
Berkeley -- Most frogs emit a characteristic croak to attract the attention of a potential mate. But a few frog species that call near loud streams -- where the noise may obscure those crucial love songs -- add to their calls by visually showing off with the flap of a hand, a wave of a foot or a bob of the head. Frogs who "dance" near rushing streams have been documented in the rainforests of India, Borneo, Brazil and, now, Ecuador.
Conservation ecologist Rebecca Brunner, a Ph.D. candidate at the University of California, Berkeley, has discovered that the glass frog ...
New study compiles four years of corn loss data from 26 states and Ontario, Canada
2021-01-15
Plant pathologists working at universities across 26 corn-producing states in the United States and in Ontario, Canada, compiled data about annual corn reductions caused by diseases. Estimated loss from each disease varied greatly by region.
"This group of plant pathologists takes a step back to estimate what has gone wrong in corn fields in each of their states," said Iowa State University plant pathologist Daren Mueller, who was involved in this project. "Collectively, and across years, corn disease loss estimates provide folks a zoomed out view of what diseases are affecting corn in the U.S. and Canada."
To Mueller, these data represent one of the pieces of a good research project. Researchers can use these data to justify new research projects that can help mitigate the impacts ...
US fishing and seafood industries saw broad declines last summer due to COVID-19
2021-01-15
The U.S. fishing and seafood sector generated more than $200 billion in annual sales and supported 1.7 million jobs in recent years. It experienced broad declines in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 public health crisis, according to a new NOAA Fisheries analysis released today. While losses vary by sector, by region and by industry, data and information from this report may help businesses and communities assess losses and inform long-term recovery and resilience strategies.
According to analysts, COVID-19 protective measures instituted in March across the United States and globe contributed to an almost-immediate impact on seafood sector sales. There was a strong start to the year, with ...
[1] ... [2730]
[2731]
[2732]
[2733]
[2734]
[2735]
[2736]
[2737]
2738
[2739]
[2740]
[2741]
[2742]
[2743]
[2744]
[2745]
[2746]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.