Researchers demonstrate snake venom evolution for defensive purposes
2021-01-21
Researchers from LSTM's Centre for Snakebite Research and Interventions (CSRI) have led an international team investigating the evolutionary origins of a novel defensive trait by snakes - venom spitting - and demonstrated that defensive selection pressures can influence venom composition in snakes in a repeatable manner.
In a paper published in the journal Science, the team, which includes authors from the UK, USA, Australia, the Netherlands, Spain, Norway, Brazil and Costa Rica, provide the first example of snake venom evolution being demonstrated to be associated with a role in defence, ...
Developmental origins of eczema and psoriasis discovered
2021-01-21
Scientists have created a highly detailed map of skin, which reveals that cellular processes from development are re-activated in cells from patients with inflammatory skin disease. The researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Newcastle University and Kings College London, discovered that skin from eczema and psoriasis patients share many of the same molecular pathways as developing skin cells. This offers potential new drug targets for treating these painful skin diseases.
Published on 22nd January in Science, the study also provides a completely new understanding of inflammatory disease, opening up new avenues for research on other inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Part of the global ...
Rethink immigration policy for STEM doctorates
2021-01-21
ITHACA, N.Y. - A streamlined process for awarding green cards to international STEM doctoral students graduating from U.S. universities could benefit American innovation and competitiveness, including leveling the field for startups eager to attract such highly skilled workers, according to a new study by researchers from Cornell University and the University of California, San Diego.
The new Biden administration backs policy reform aimed at achieving that end, which was part of bipartisan legislation proposed more than a decade ago. But progress has been stalled by broader concerns about visas ...
A closer look at T cells reveals big differences in mild vs. severe COVID-19 cases
2021-01-21
LA JOLLA, CA--A big question on people's minds these days: how long does immunity to SARS-CoV-2 last following infection?
Now a research team from La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI), The University of Liverpool and the University of Southampton has uncovered an interesting clue. Their new study suggests that people with severe COVID-19 cases may be left with more of the protective "memory" T cells needed to fight reinfection.
"The data from this study suggest people with severe COVID-19 cases may have stronger long-term immunity," says study co-leader LJI Professor Pandurangan Vijayanand, M.D., Ph.D.
The research, published Jan. 21 in Science Immunology, is the first to describe the T cells that fight SARS-CoV-2 in "high resolution" ...
Age-based COVID-19 vaccine strategy that saves most lives prioritizes elderly, modeling shows
2021-01-21
Vaccinating people over 60 is the most effective way to mitigate mortality from COVID-19, a new age-based modeling study suggests. Although vaccination of younger adults is projected to avert the greatest incidence of disease, vaccinating older adults will most effectively reduce deaths, the analysis shows. Less than one year after SARS-CoV-2 was identified, deployment of multiple vaccines against the virus has been initiated in several countries. Although vaccine production is being rapidly scaled up, demand will exceed supply for the next several months. An urgent challenge is the optimization of vaccine allocation to maximize public health benefit. To quantify the impact of COVID-19 vaccine ...
Why older adults must go to the front of the vaccine line
2021-01-21
Vaccinating older adults for COVID-19 first will save substantially more U.S. lives than prioritizing other age groups, and the slower the vaccine rollout and more widespread the virus, the more critical it is to bring them to the front of the line.
That's one key takeaway from a new University of Colorado Boulder paper, published today in the journal Science, which uses mathematical modeling to make projections about how different distribution strategies would play out in countries around the globe.
The research has already informed policy recommendations by the Centers for Disease ...
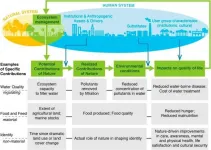
The downward trend: Nature's decline risks our quality of life
2021-01-21
It is no secret that over the last few decades, humans have changed nature at an ever-increasing rate. A growing collection of research covers the many ways this is impacting our quality of life, from air quality to nutrition and income. To better understand how which areas are most at risk, scientists have combed through volumes of literature to present global trends in the relationship between human wellbeing and environmental degradation.
Their work, which included Fabrice DeClerck from the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT, was summarized in "Global trends in nature's contributions to people", which was recently published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
This systematic ...
Combining best of both worlds for cancer modeling
2021-01-21
WASHINGTON, January 21, 2021 -- Despite cancer being a leading cause of death worldwide, treatment options for many types of cancers remain limited. This is partly due to the in vitro tools used to model cancers, which cannot adequately predict the behavior of a cancer or its sensitivity to drugs.
Further, animal models, like mice, biologically differ from humans in ways that play a critical role in immunotherapy, and results from animal studies do not always translate well to human disease.
These shortcomings point to a clear need for a better, patient-specific model to improve the understanding of cancer cells and their impacts.
Researchers from the University of Wisconsin and the University ...
Medicated drops may help close macular holes, helping some patients avoid surgery
2021-01-21
Medicated drops may help close small macular holes over a two- to eight-week period, allowing some people to avoid surgery to fix the vision problem, a new study suggests.
The findings, based on a retrospective multicenter case series published Dec. 15, 2020, in Ophthalmology Retina, could lead to a better understanding of which patients may benefit from the treatment, as well as the timeline of the treatment's effectiveness.
"For certain patients, medicated drops may heal their macular hole by decreasing inflammation and increasing fluid absorption in the retina," said ophthalmologist and retinal surgeon Dimitra Skondra, MD, PhD, senior author of the study. Skondra is an associate professor of ophthalmology and visual ...
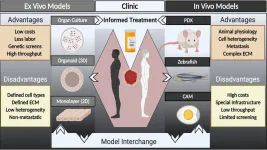
Personalizing cancer care with improved tumor models
2021-01-21
WASHINGTON, January 21, 2021 -- Cancer is a major, worldwide challenge, and its impact is projected to escalate due to aging and growth of the population. Researchers recognize that new approaches to diagnose and treat deadly cancers, including identifying new drugs to treat cancer, will be essential to curbing the growing impact of the disease.
While decades of investment in research have resulted in substantial improvements in surviving cancer, a key challenge remains in identifying new drugs that improve outcomes for cancer patients, particularly for cancers when tumors have spread throughout the body.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers suggest a major hurdle to identifying new drugs is the paucity of models -- organisms ...
Study finds bilateral agreements help developing economies spur foreign investment
2021-01-21
EUGENE, Ore. -- Jan. 21, 2021 -- Developing economies suffer from a paradox: they don't receive investment flows from developed economies because they lack stability and high-quality financial and lawmaking institutions, but they can't develop those institutions without foreign funds.
A study co-authored by Brandon Julio, a professor in the Department of Finance at the University of Oregon's Lundquist College of Business, found that bilateral investment treaties, commonly known as BITs, can help developing economies overcome this paradox, but only as long as those ...
Study finds genetic clues to pneumonia risk and COVID-19 disparities
2021-01-21
Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and colleagues have identified genetic factors that increase the risk for developing pneumonia and its severe, life-threatening consequences.
Their findings, published recently in the American Journal of Human Genetics, may aid efforts to identify patients with COVID-19 at greatest risk for pneumonia, and enable earlier interventions to prevent severe illness and death.
Despite the increasing availability of COVID-19 vaccines, it will take months to inoculate enough people to bring the pandemic under control, experts predict. In the meantime, thousands of Americans are hospitalized and die from COVID-19 each ...
How to get more electric cars on the road
2021-01-21
A new study from researchers at MIT uncovers the kinds of infrastructure improvements that would make the biggest difference in increasing the number of electric cars on the road, a key step toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions from transportation.
The researchers found that installing charging stations on residential streets, rather than just in central locations such as shopping malls, could have an outsized benefit. They also found that adding on high-speed charging stations along highways and making supplementary vehicles more easily available to people who need to travel beyond the single-charge range of their electric vehicles could greatly increase the vehicle electrification potential.
The findings are reported today in the journal Nature Energy, in a paper by MIT associate ...
New study: nine out of ten US infants experience gut microbiome deficiency
2021-01-21
DAVIS, Calif., January 21, 2020 - A new peer-reviewed study reveals that the vast majority of U.S. infants may be suffering from a substantial deficiency in an important bacterium key to breast milk utilization and immune system development, as well as protection against gut pathogens linked to common newborn conditions such as colic and diaper rash.
According to the study published today in END ...
Snake sex chromosomes say less about sex and more about survival
2021-01-21
Sex-specific chromosomes are a dangerous place to be, if you're a gene. Because these chromosomes -- Y chromosomes, in humans -- do not have a matching chromosome with which to exchange genetic information, they are prone to losing non-essential genes left and right in a process called genetic decay.
Now, a new study from research scientist Daniel Winston Bellott in the lab of Whitehead Institute Member David Page broadens our understanding of what makes a gene able to survive on a sex-specific chromosome by looking at one especially slithery branch of the evolutionary tree: snakes.
Comparing surviving genes on snake ...
Scientists make pivotal discovery on mechanism of Epstein-Barr virus latent infection
2021-01-21
PHILADELPHIA -- (Jan. 21, 2021) -- Researchers at The Wistar Institute have discovered a new enzymatic function of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) protein EBNA1, a critical factor in EBV's ability to transform human cells and cause cancer. Published in Cell, this study provides new indications for inhibiting EBNA1 function, opening up fresh avenues for development of therapies to treat EBV-associated cancers.
EBV establishes life-long, latent infection in B lymphocytes, which can contribute to development of different cancer types, including Burkitt's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 (EBNA1) serves as an attractive therapeutic ...
Survey: Frequent reports of missed medical care in US adults during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic
2021-01-21
Two out of five individuals delayed or missed medical care in the early phase of the pandemic--from March through mid-July 2020--according to a new survey from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The survey of 1,337 U.S. adults found that 544, or 41 percent, delayed or missed medical care during the survey period. Among the 1,055 individuals who reported needing medical care, 29 percent (307 respondents), indicated fear of transmission of COVID-19 as the main reason. Seven percent (75 respondents) reported financial concerns as the main reason for delaying ...
Detailed tumour profiling
2021-01-21
Researchers from the University Hospitals in Zurich and Basel, ETH Zurich, University of Zurich and the pharmaceutical company Roche have set out to improve cancer diagnostics by developing a platform of state-of-the-art molecular biology methods. The "Tumor Profiler" project aims to derive the comprehensive molecular profile of tumours in cancer patients, which has the potential to predict the efficacy of a host of new cancer medications. It will therefore make it possible to offer treating physicians personalised and improved therapy recommendations.
Three years ago, the researchers began a large-scale clinical study involving ...
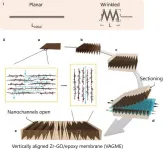
Researchers develop new graphene nanochannel water filters
2021-01-21
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- When sheets of two-dimensional nanomaterials like graphene are stacked on top of each other, tiny gaps form between the sheets that have a wide variety of potential uses. In research published in the journal Nature Communications, a team of Brown University researchers has found a way to orient those gaps, called nanochannels, in a way that makes them more useful for filtering water and other liquids of nanoscale contaminants.
"In the last decade, a whole field has sprung up to study these spaces that form between 2-D nanomaterials," said Robert Hurt, a professor in Brown's School of Engineering and coauthor of the ...
When a story is breaking, AI can help consumers identify fake news
2021-01-21
TROY, N.Y. -- Warnings about misinformation are now regularly posted on Twitter, Facebook, and other social media platforms, but not all of these cautions are created equal. New research from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute shows that artificial intelligence can help form accurate news assessments -- but only when a news story is first emerging.
These findings were recently published in Computers in Human Behavior Reports by an interdisciplinary team of Rensselaer researchers. They found that AI-driven interventions are generally ineffective when used to flag issues with stories on frequently covered ...
Squeezing a rock-star material could make it stable enough for solar cells
2021-01-21
Among the materials known as perovskites, one of the most exciting is a material that can convert sunlight to electricity as efficiently as today's commercial silicon solar cells and has the potential for being much cheaper and easier to manufacture.
There's just one problem: Of the four possible atomic configurations, or phases, this material can take, three are efficient but unstable at room temperature and in ordinary environments, and they quickly revert to the fourth phase, which is completely useless for solar applications.
Now scientists at Stanford ...
OSU researchers prove fish-friendly detection method more sensitive than electrofishing
2021-01-21
Delivering a minor electric shock into a stream to reveal any fish lurking nearby may be the gold standard for detecting fish populations, but it's not much fun for the trout.
Scientists at Oregon State University have found that sampling stream water for evidence of the presence of various species using environmental DNA, known as eDNA, can be more accurate than electrofishing, without disrupting the fish.
"It's revolutionizing the way we do fish ecology work," said Brooke Penaluna, a research fish biologist with the U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service who also has an appointment in OSU's Department ...
'Aging well' greatly affected by hopes and fears for later life, OSU study finds
2021-01-21
If you believe you are capable of becoming the healthy, engaged person you want to be in old age, you are much more likely to experience that outcome, a recent Oregon State University study shows.
"How we think about who we're going to be in old age is very predictive of exactly how we will be," said Shelbie Turner, a doctoral student in OSU's College of Public Health and Human Sciences and co-author on the study.
Previous studies on aging have found that how people thought about themselves at age 50 predicted a wide range of future health outcomes up to 40 years later -- cardiovascular events, memory, balance, will to live, hospitalizations; even mortality.
"Previous ...
COVID-19 infection in immunodeficient patient cured by infusing convalescent plasma
2021-01-21
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - A 72-year-old woman was hospitalized with severe COVID-19 disease, 33 days after the onset of symptoms. She was suffering a prolonged deteriorating illness, with severe pneumonia and a high risk of death, and she was unable to mount her own immune defense against the SARS-CoV-2 virus because of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, which compromises normal immunoglobulin production.
But when physicians at the University of Alabama at Birmingham recommended a single intravenous infusion of convalescent blood plasma from her son-in-law -- who had recovered from COVID-19 disease ...
Adaptive optics with cascading corrective elements
2021-01-21
Microscopy is the workhorse of contemporary life science research, enabling morphological and chemical inspection of living tissue with ever-increasing spatial and temporal resolution. Even though modern microscopes are genuine marvels of engineering, minute deviations from ideal imaging conditions will still lead to optical aberrations that rapidly degrade imaging quality. A mismatch between the refractive indices of the sample and its immersion medium, deviations in the thickness of sample holders or cover glasses, the effects of aging on the instrument--such deviations ...
[1] ... [2725]
[2726]
[2727]
[2728]
[2729]
[2730]
[2731]
[2732]
2733
[2734]
[2735]
[2736]
[2737]
[2738]
[2739]
[2740]
[2741]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.