Saturn's tilt caused by its moons
2021-01-21
Rather like David versus Goliath, it appears that Saturn's tilt may in fact be caused by its moons. This is the conclusion of recent work carried out by scientists from the CNRS, Sorbonne University and the University of Pisa, which shows that the current tilt of Saturn's rotation axis is caused by the migration of its satellites, and especially by that of its largest moon, Titan.
Recent observations have shown that Titan and the other moons are gradually moving away from Saturn much faster than astronomers had previously estimated. By incorporating this increased migration rate into their calculations, the researchers concluded that ...
Balancing brain cell activity
2021-01-21
To process information in our brains, nerve cells produce brief electrical impulses, called action potentials, triggered from one highly specialized region. Research from the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, together with researchers from Heidelberg University and the University of Göttingen in Germany, now show that the electrical trigger sites surprisingly change with experience; they are either becoming smaller with increasing number of experiences and, vice versa, they grow larger when less input arrives in the brain. The results were published in Nature Communications.
Exploring the environment
Rodents learn about their environment by moving their highly sensitive whiskers, with which they touch ...
Early humans used chopping tools to break animal bones and consume the bone marrow
2021-01-21
Researchers from the Sonia and Marco Nadler Institute of Archaeology at Tel Aviv University unraveled the function of flint tools known as 'chopping tools', found at the prehistoric site of Revadim, east of Ashdod. Applying advanced research methods, they examined use-wear traces on 53 chopping tools, as well as organic residues found on some of the tools. They also made and used replicas of the tools, with methods of experimental archaeology. The researchers concluded that tools of this type, found at numerous sites in Africa, Europe and Asia, were used by prehistoric humans at Revadim to neatly break open bones of medium-size animals such as fallow deer, gazelles and ...
Sunbathing after menopause may be harmful
2021-01-21
UV-radiation can affect hormone levels of postmenopausal women negatively and this may contribute to several health issues.
The concentration of oestrogens in the blood affects a woman's health in many ways. For example, oestrogens contribute to a strong bone structure and help wounds heal more quickly:
"When a woman reaches menopause, we see the levels of oestrogens decline and an increase of other hormones, called gonadotropins", says Kai Triebner at the University of Bergen.
For several years, he has studied the hormonal balance of women in relation to menopause: What effects changing hormone levels ...
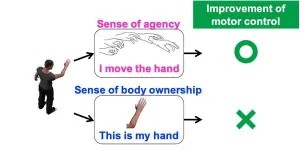
Using VR training to boost our sense of agency and improve motor control
2021-01-21
With Japan's society rapidly aging, there has been a sharp increase in patients who experience motor dysfunctions. Rehabilitation is key to overcoming such ailments.
A researcher from Tohoku University has developed a new virtual reality (VR) based method that can benefit rehabilitation and sports training by increasing bodily awareness and?improving motor control.
His research was published in the Journal Scientific Report.
Not only can we see and touch our body, but we can sense it too. Our body is constantly firing off information to our brains that tell us where our limbs are in real-time. This process makes us aware of our body and gives us ownership over it. Meanwhile, our ability to control ...
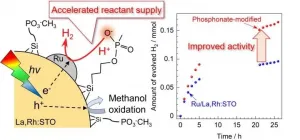
Boosted photocatalysis for hydrogen evolution: Reactant supply thru phosphonate groups
2021-01-21
Water splitting research for solar hydrogen production has focused on physical processes inside the semiconductor, such as light absorption, charge separation, and chemical processes on the surface that are highly complex and rely on the development of new materials. However, processes inside the solution had yet to be thoroughly explored.
One recent approach to improve photocatalytic hydrogen production was proposed by loading phosphonate groups on the surface of the visible-light-responsive photocatalyst lanthanum and rhodium-doped strontium titanate (La,Rh:STO) with a silane coupling agent. The phosphonate functional group functions as a mediator of proton supply (i.e., promotes the supply of reactants) and improves hydrogen production activity.
There have been ...
Cartilage matrix as natural biomaterial for cartilage regeneration
2021-01-21
Just a few millimetres thick, articular cartilage plays a crucial role in our musculoskeletal system, since it is responsible for smooth (in the truest sense of the word) movement. However, the downside of its particular structure is that even minor injuries do not regenerate. Timely treatment of cartilage damage is therefore essential. Biomaterials are often used to support the cells, their distribution and protection. In most cases, this treatment significantly improves the patient's clinical symptoms but fails to fully restore the cartilage to its original state. The working group led by Sylvia Nürnberger (MedUni Vienna's Department of Orthopedics and Trauma Surgery) ...
Brazilian dam collapse could have been predicted with right monitoring technology
2021-01-21
One of Brazil's worst environmental disasters - a dam collapse that also killed more than 200 people - could have been foreseen with the right monitoring technology, according to a new study by the University of Nottingham and Durham University.
The high-profile catastrophe took place on 25 January 2019 at a tailings dam near the Córrego do Feijão iron ore mine, close to the town of Brumadinho, in Minas Gerais state, south-east Brazil.
When the dam collapsed, it caused a torrent of sludge to cover surrounding land; taking lives, destroying homes and livelihoods and polluting rivers with toxic material.
Owned by Vale, Brazil's largest mining company, the tailings dam was ...
Researchers develop a new approach to detect pancreatic cancer
2021-01-21
A protein found commonly in human blood might help with the detection of hard-to-diagnose pancreatic tumours. Researchers at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), the Alfried Krupp Hospital in Essen and the University of Witten/Herdecke have developed approach using the protein's structure and its function as a proxy for this. In a first study in ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science, the team shows how its method can also be used to differentiate between benign and malignant tumours.
Pancreatic cancer is particularly insidious: "It remains asymptomatic for a long time, which leads to very late diagnoses and therefore a low chance of treating it successfully," says Dr Marcos Gelos from the Alfried Krupp Hospital and Witten/Herdecke University who ...
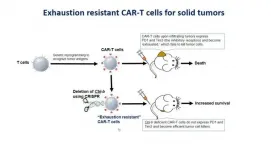
Reviving exhausted immune cells to fight cancer
2021-01-21
DALLAS - Jan. 19, 2021 - Eliminating a single gene can turn exhausted cancer-fighting immune cells known as CD8+ T cells back into refreshed soldiers that can continue to battle malignant tumors, a new study led by UT Southwestern researchers suggests. The findings, published online this week in the Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer, could offer a new way to harness the body's immune system to attack cancers.
In 2017, the Food and Drug Administration approved treatments involving chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells, which consist of immune cells known as T cells that ...
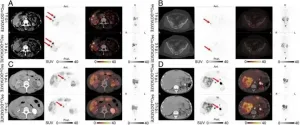
Expanded PET imaging time window adds flexibility for neuroendocrine tumor patients
2021-01-21
Reston, Virginia--The imaging time window of 64Cu-DOTATATE positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) for patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms can be expanded from one hour to three hours post-injection, according to new research published in the January issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine. In a head-to-head comparison of scans performed at the two time intervals, there were no significant differences in the number of lesions detected, and tumor-to-normal tissue ratios remained high in all key organs.
Previous research has demonstrated that 64Cu-DOTATATE PET imaging at one hour post-injection provides excellent lesion detection in patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms. "Given the long half-life and excellent image resolution of 64Cu-DOTATATE, ...
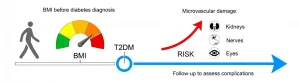
Type 2 Diabetes: New Evidence Underlines the Role of Obesity in Late Complications
2021-01-21
Successful weight loss is considered to be an integral part of the therapy for type 2 diabetes. Nevertheless, studies keep appearing that question the importance of losing weight. However, new data from a large-scale observational study carried out at DIfE in cooperation with the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) support the current recommendations of physicians. The findings, published in the journal Diabetologia, suggest that obesity and weight gain can lead to vascular disorders, the leading cause of disease and death for people with type 2 diabetes.
A close look at vascular disorders
Weight plays a crucial role in the development of type 2 diabetes. However, ...
New eco-friendly way to make ammonia could be boon for agriculture, hydrogen economy
2021-01-21
Chemical engineers at UNSW Sydney have found a way to make 'green' ammonia from air, water and renewable electricity that does not require the high temperatures, high pressure and huge infrastructure currently needed to produce this essential compound.
And the new production method - demonstrated in a laboratory-based proof of concept - also has the potential to play a role in the global transition towards a hydrogen economy, where ammonia is increasingly seen as a solution to the problem of storing and transporting hydrogen energy.
In a paper published today in Energy and Environmental Science, the authors from UNSW and University of Sydney say that ammonia synthesis was one of the critical achievements of the 20th century. When used in fertilisers ...
Could lab-grown plant tissue ease the environmental toll of logging and agriculture?
2021-01-21
It takes a lot to make a wooden table. Grow a tree, cut it down, transport it, mill it ... you get the point. It's a decades-long process. Luis Fernando Velásquez-García suggests a simpler solution: "If you want a table, then you should just grow a table."
Researchers in Velásquez-García's group have proposed a way to grow certain plant tissues, such as wood and fiber, in a lab. Still in its early stages, the idea is akin in some ways to cultured meat -- an opportunity to streamline the production of biomaterials. The team demonstrated the concept by growing structures made of wood-like cells from an initial sample of cells extracted from zinnia leaves.
While that's still ...
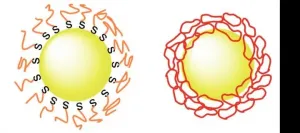
Gold nanoparticles more stable by putting rings on them
2021-01-21
Hokkaido University scientists have found a way to prevent gold nanoparticles from clumping, which could help towards their use as an anti-cancer therapy.
Attaching ring-shaped synthetic compounds to gold nanoparticles helps them retain their essential light-absorbing properties, Hokkaido University researchers report in the journal Nature Communications.
Metal nanoparticles have unique light-absorbing properties, making them interesting for a wide range of optical, electronic and biomedical applications. For example, if delivered to a tumour, they could react with applied light to kill cancerous tissue. A problem with this approach, though, is that they easily clump together in solution, losing their ability to absorb light. ...
COVID-19, influenza and suicide fuel increase in deaths among ICE detainees
2021-01-21
Thirty-five people have died in the custody of U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) since April 2018, with a seven-fold increase in deaths even as the average daily population decreased by nearly a third between 2019 and 2020, a new USC study shows.
"Potentially preventable causes of death -- including COVID-19 infection, influenza and suicide -- are responsible for at least half of recent deaths," said researcher Sophie Terp, an assistant professor of clinical emergency medicine at the Keck School of Medicine of USC and a clinical scholar at the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy and ...
Fish sex organs boosted under high-CO2
2021-01-21
Research from the University of Adelaide has found that some species of fish will have higher reproductive capacity because of larger sex organs, under the more acidic oceans of the future.
Published in PLOS Biology, the researchers say that far from the negative effects expected under the elevated CO2 levels in our oceans predicted for the end of the century, these fish capitalise on changes to the underwater ecosystems to produce more sperm and eggs. They also look after them better, enhancing the chances of reproductive success.
"The warming oceans absorb about one-third of the additional CO2 being released into the atmosphere from carbon emissions, causing the oceans to acidify," says lead author Professor Ivan Nagelkerken from the University's Environment ...
Immunology - Functionality of immune cells in early life
2021-01-21
Dendritic cells are a vital component of the innate immune system, which constitutes the body's first line of defense against infectious agents and tumor cells. Their job is to activate the T-cell arm of the adaptive immune system, which confers specific and long-lasting protection against bacterial and viral infections. Dendritic cells engulf and degrade proteins that signal the presence of invasive pathogens. The resulting fragments (antigens) are displayed on their surfaces. T cells bearing the appropriate receptors are then activated to seek out and eliminate the pathogen. Newborns and young children ...
School-made lunch 'better' for children
2021-01-21
Packing a lunchbox with fruit, sandwiches, and snacks is common practice for most Australian families. But what if there was another way?
Flinders University researchers investigating the pros and cons of school-provided lunches say uniform delivery of lunchtime food at school could be a solution to better childhood nutrition and learning in Australia.
Flinders Caring Futures Institute deputy director Professor Rebecca Golley says universal school-provided lunch models - a common practice in other countries such as the UK - would involve all children in the ...
New technique to fast-track pain research
2021-01-21
Scientists have for the first time established a sensory neuron model able to mass-reproduce two key sensory neuron types involved in pain sensation, enabling the easy generation of large numbers of the cells to fast-track chronic pain research.
In research applications usually sensory neurons need to be isolated from animals. They represent a wide variety of different cell types, making it difficult to collect and isolate large quantities of pain sensing neurons.
Using a new technique, researchers at Flinders University have found a way to reproduce millions of the cells, providing ample resources for the simultaneous testing of thousands of samples or potential drug libraries.
"Our ...
How clicks on a job platform can reveal bias
2021-01-21
Education, professional skills and experience are the essential criteria for filling a position - or at least that is the expectation. The reality often looks different, as numerous studies have shown. When deciding whether to hire a candidate or not, gender, origin or ethnicity sometimes also play an important role; factors that say little about a candidate's suitability for a job.
This type of discrimination violates the principle of equal opportunities. For those affected, this may have long-term disadvantages, such as longer unemployment or lower wages. This is why it is crucial to understand who is discriminated against, and why. The study conducted by Dominik Hangartner (Public Policy Group), Daniel Kopp and Michael Siegenthaler (both KOF Swiss Economic Institute) ...
How cells 'eat' their own fluid components
2021-01-21
Autophagy is a fundamental cellular process by which cells capture and degrade their own dysfunctional or superfluous components for degradation and recycling. Recent research has revealed that phase separated droplets have a range of important functions in cells. An international collaboration between German, Norwegian, and Japanese researchers has unravelled the mechanisms underpinning both how these droplets are captured through autophagy, as well as how droplets can serve as a platform from which structures facilitating cytosolic autophagy arise.
Two worlds meet
Autophagy[1], a critical intracellular ...
Common pesticides stop bees and flies from getting a good night's sleep
2021-01-21
Just like us, many insects need a decent night's sleep to function properly, but this might not be possible if they have been exposed to neonicotinoid insecticides, the most common form of insecticide used worldwide, suggests research by academics at the University of Bristol.
Two studies by scientists at Bristol's Schools of Physiology, Pharmacology and Neuroscience and Biological Sciences have shown these insecticides affect the amount of sleep taken by both bumblebees and fruit flies, which may help us understand why insect pollinators are vanishing from the wild.
Dr Kiah Tasman, Teaching Associate in the School of Physiology, ...
Study pins down number of Americans with most common form of lupus
2021-01-21
Just over 200,000 Americans suffer from systemic lupus erythematosus, or SLE, a condition in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues, especially joints and skin, a new study shows.
Led by a researcher at NYU Grossman School of the Medicine, the study provides the first national estimate of how widespread the autoimmune disease is since the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) set up a half dozen state registries to track the illness more than a decade ago. SLE affects mostly women, can be fatal, and often involves debilitating flare-ups of fatigue and pain that keep nearly ...
Patients in cancer remission at high risk for severe COVID-19 illness
2021-01-21
PHILADELPHIA--Patients with inactive cancer and not currently undergoing treatments also face a significantly higher risk of severe illness from COVID-19, a new study from Penn Medicine published online today in JNCI Cancer Spectrum shows. Past reports have established an increased risk of severe disease and death for sick or hospitalized cancer patients with COVID-19 compared to patients without cancer, but less is known about patients in the general population.
The findings underscore the importance of COVID-19 mitigation, like social distancing and mask wearing, and vaccinations for all patients, not just those recently diagnosed or with active disease.
"Patients who have cancer need to be careful ...
[1] ... [2719]
[2720]
[2721]
[2722]
[2723]
[2724]
[2725]
[2726]
2727
[2728]
[2729]
[2730]
[2731]
[2732]
[2733]
[2734]
[2735]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.