New study on the role of monocytes in sarcoidosis
2021-01-21
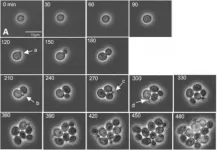
The cause of the inflammatory lung disease sarcoidosis is unknown. In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have investigated whether a type of immune cell called a monocyte could be a key player in sarcoidosis pathogenesis and explain why some patients develop more severe and chronic disease than others. The study, which is published in The European Respiratory Journal, opens new possibilities for future diagnostic and therapeutic methods.
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that in 90 percent of cases affects the lungs, but can also attack the heart, skin and lymph system. The cause of the disease is not yet established, and there is currently ...
Pioneering new technique could revolutionise super-resolution imaging systems
2021-01-21
Scientists have developed a pioneering new technique that could revolutionise the accuracy, precision and clarity of super-resolution imaging systems.
A team of scientists, led by Dr Christian Soeller from the University of Exeter's Living Systems Institute, which champions interdisciplinary research and is a hub for new high-resolution measurement techniques, has developed a new way to improve the very fine, molecular imaging of biological samples.
The new method builds upon the success of an existing super-resolution imaging technique called DNA-PAINT ...
Seeds transfer their microbes to the next generation
2021-01-21
Scientists have been pondering if the microbiome of plants is due to nature or nurture. Research at Stockholm University, published in Environmental Microbiology, showed that oak acorns contain a large diversity of microbes, and that oak seedlings inherit their microbiome from these acorns.
"The idea that seeds can be the link between the microbes in the mother tree and its offspring has frequently been discussed, but this is the first time someone proves the transmission route from the seed to the leaves and roots of emerging plants", says Ahmed Abdelfattah, researcher at the Department of Ecology Environment and Plant ...
Turbulence model could help design aircraft capable of handling extreme scenarios
2021-01-21
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- In 2018, passengers onboard a flight to Australia experienced a terrifying 10-second nosedive when a vortex trailing their plane crossed into the wake of another flight. The collision of these vortices, the airline suspected, created violent turbulence that led to a free fall.
To help design aircraft that can better maneuver in extreme situations, Purdue University researchers have developed a modeling approach that simulates the entire process of a vortex collision at a reduced computational time. This physics knowledge could then be incorporated into engineering design codes so that the aircraft ...
Hair aging differs by race, ethnicity
2021-01-21
(Boston)--While aging is an unavoidable biological process with many influencing factors that results in visible changes to the hair, there is limited literature examining the characteristics of hair aging across the races. Now a new study describes the unique characteristics of hair aging among different ethnicities that the authors hope will aid in a culturally sensitive approach when making recommendations to prevent hair damage during one's life-time.
Among the findings: hair-graying onset varies with race, with the average age for Caucasians being mid-30s, that for Asians being late 30s, and ...
Addiction researchers recount creating virtual recovery meetings during pandemic
2021-01-21
LAWRENCE -- The COVID-19 pandemic has created new perils and challenges for people experiencing substance use disorders and addictive behaviors. Social distancing and isolation can trigger loneliness, anxiety and depression. These circumstances have put some "recreational users" at risk for developing addictions and caused some in recovery from addictions to relapse.
At the same time, the pandemic has made it nearly impossible for mutual-help (e.g., AA, NA) recovery groups to gather in person, forcing a scramble to provide remote support through platforms like Zoom.
Now, researchers at the Cofrin Logan Center for Addiction Research and ...
Strange colon discovery explains racial disparities in colorectal cancer
2021-01-21
The colons of African-Americans and people of European descent age differently, new research reveals, helping explain racial disparities in colorectal cancer - the cancer that killed beloved "Black Panther" star Chadwick Boseman at only 43.
Scientists led by UVA Health's Li Li, MD, PhD; Graham Casey, PhD; and Matt Devall, PhD, of the Center for Public Health Genomics, found that one side of the colon ages biologically faster than the other in both African-Americans and people of European descent. In African-Americans, however, the right side ages significantly faster, explaining why African-Americans are more likely to develop cancerous lesions on the right side and why they are more likely to suffer colorectal cancer at a younger age, ...
Vegan diet significantly remodels metabolism in young children
2021-01-21
The study concludes that vegan diet has a broad effect on children's metabolism. Serum biomarker levels for vitamins A and D, cholesterol forms and essential amino acids were significantly lower in children on vegan diet compared to age-adjusted omnivores. In addition, docosahexaenoic acid is absent from vegan diet. The results were recently published in a high-profile international scientific journal EMBO Molecular Medicine.
Vegan diets gain popularity especially among young adults, and through choices of the families vegan diet is becoming more common in young children, too. The motives behind choosing a vegan lifestyle are ecological, ethical and health-related: vegan ...
SHEA releases COVID-19 research agenda identifying gaps in knowledge
2021-01-21
ARLINGTON, Va. (Jan. 21, 2021) -- A new research agenda developed by 40 leading experts in healthcare epidemiology and infectious diseases defines the critical areas of study to inform clinical practice, policy, and prevention strategies for COVID-19 and future pandemics. "COVID-19 Research Agenda for Healthcare Epidemiology," published today in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, identifies the gaps in the understanding of the epidemiology, transmission, and individual as well as public health consequences of viral diseases that were revealed through some of the worst phases of the ...
New, simplified genetic test effectively screens for hereditary cancers
2021-01-21
Philadelphia, January 21, 2021 - Researchers have developed a new integrated genetic/epigenetic DNA-sequencing protocol known as MultiMMR that can identify the presence and cause of mismatch repair (MMR) deficiency in a single test from a small sample of DNA in colon, endometrial, and other cancers. This alternative to complex, multi-step testing workflows can also determine causes of MMR deficiency often missed by current clinical tests. Their results are presented in the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by Elsevier.
MMR genes monitor and repair errors that can occur in normal cell replication and recombination. In some inherited and acquired cancers, one or more of the MMR genes are deactivated. "The impact of ...
Embedded counseling services can improve accessibility for students, MU study finds
2021-01-21
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Kerry Karaffa is the first MU Counseling Center psychologist to be embedded specifically within the University of Missouri College of Veterinary Medicine, where he provides tailored counseling services for professional students training to become veterinarians. He is also aware that veterinarians are at increased risk for mental health concerns and suicidality compared to the general public due to the stressful demands of the job.
To help universities better serve students dealing with high levels of stress and anxiety, Karaffa conducted a research study in which he developed and distributed a survey to other counselors specifically embedded in veterinary ...
Modified pain management strategy reduces opioid exposure to trauma patients, study shows
2021-01-21
A pain management regimen comprised mostly of over-the-counter medication reduced opioid exposure in trauma patients while achieving equal levels of pain control, according to a new study by physician-researchers at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth.)
Results of the study, which was conducted at the Red Duke Trauma Institute at Memorial Hermann-Texas Medical Center, were published today in the Journal of American College of Surgeons.
"The research shows us that seriously injured people with acute pain can effectively be treated with an opioid-minimizing strategy," ...
Dynamic, personalized treatment approach may improve outcomes in gastroesophageal cancers
2021-01-21
A phase 2 clinical trial providing personalized treatments based on the genetic profile of metastatic tumors in gastroesophageal cancers has found that using customized treatment approaches, and adapting them over time as tumors become resistant, led to higher rates of survival compared to historical controls. The final results were published online on Jan. 21 in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Advances in technology have made it possible for scientists and physicians to use information about the genetic makeup of a cancerous tumor to inform cancer treatment, but genetic heterogeneity ...
Study updates breast cancer risk estimates for women with no family history
2021-01-21
ROCHESTER, Minnesota -- A new multi-institution study led by Fergus Couch, Ph.D., a Mayo Clinic pathologist, provides more accurate estimates of breast cancer risk for U.S. women who harbor inherited mutations in breast cancer predisposition genes. The findings of the CARRIERS Consortium study, which were published Wednesday, Jan. 20 in the New England Journal of Medicine, may allow health care providers to better assess the risk of breast cancer in women ? many of whom have no family history of breast cancer ? and provide more appropriate risk management strategies.
"Traditionally, genetic testing of inherited breast cancer genes has focused on women at high risk who have a strong family history of breast cancer or those who were diagnosed at an early ...
Study defines small-cell lung cancer subtypes and distinct therapeutic vulnerabilities for each type
2021-01-21
HOUSTON -- Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed the first comprehensive framework to classify small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) into four unique subtypes, based on gene expression, and have identified potential therapeutic targets for each type in a study published today in Cancer Cell.
SCLC is known for rapid, aggressive growth and resistance to treatment, which leads to poor outcomes. While recent advances in immunotherapy and targeted therapy have improved survival for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), progress for SCLC has been limited.
"For decades, small-cell lung cancer has been treated as a single disease because the tumors all ...
'Attitude of gratitude' keeps older people in Japan feeling hopeful as they age
2021-01-21
Older people in Japan have an "attitude of gratitude" which keeps them feeling hopeful despite the challenges of aging, a new study says.
Feeling thankful and grateful for the care and support they have had during their life helps pensioners in the country to be more optimistic, even when they experienced difficulties and were anxious about getting older, an expert found.
Dr Iza Kavedžija, from the University of Exeter, observed people in their 80s and 90s in the course of long-term ethnographic fieldwork in a merchant neighbourhood in the city of Osaka. Her research is published in the journal Anthropology and Aging.
Dr Kavedžija found many members of ...
Message in a bottle: Info-rich bubbles respond to antibiotics
2021-01-21
Once regarded as merely cast-off waste products of cellular life, bacterial membrane vesicles (MVs) have since become an exciting new avenue of research, due to the wealth of biological information they carry to other bacteria as well as other cell types.
These tiny particles, produced by most bacteria, can bud off from outer cellular membranes, traveling along cell surfaces and occasionally migrating into intercellular spaces.Luis Cisneros is a researcher in the Biodesign Center for Biocomputing, Security and Society, and the BEYOND Center for Fundamental Concepts in Science, at Arizona state University.
In a new study, Luis H. Cisneros and his colleagues describe ...
The physics behind tumor growth
2021-01-21
DURHAM, N.C. -- Researchers at Duke University have developed a predictive theory for tumor growth that approaches the subject from a new point of view. Rather than focusing on the biological mechanisms of cellular growth, the researchers instead use thermodynamics and the physical space the tumor is expanding into to predict its evolution from a single cell to a complex cancerous mass.
The results appeared Jan. 15 in the journal Biosystems.
"When scientists think about cancer, the first thing that comes to mind is biology, and they tend to overlook the physical reality of ...
Indigenous lands: A haven for wildlife
2021-01-21
Indigenous peoples' lands may harbour a significant proportion of threatened and endangered species globally, according to University of Queensland-led research.
UQ's Dr Chris O'Bryan and his team conducted the first comprehensive analysis of land mammal composition across mapped Indigenous lands.
"These lands cover more than one-quarter of the Earth, of which a significant proportion is still free from industrial-level human impacts," Dr O'Bryan said.
"As a result, Indigenous peoples and their lands are crucial for the long-term persistence of the planet's biodiversity and ecosystem services.
"Despite this, we know relatively little about what animals, including highly imperilled species, may reside in or depend on these lands."
The team overlayed maps of Indigenous ...
Astronomers estimate Titan's largest sea is 1,000-feet deep
2021-01-21
ITHACA, N.Y. - Far below the gaseous atmospheric shroud on Saturn's largest moon, Titan, lies Kraken Mare, a sea of liquid methane. Cornell University astronomers have estimated that sea to be at least 1,000-feet deep near its center - enough room for a potential robotic submarine to explore.
After sifting through data from one of the final Titan flybys of the Cassini mission, the researchers detailed their findings in "The Bathymetry of Moray Sinus at Titan's Kraken Mare," which published in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
"The depth and composition of each of Titan's seas had already been measured, ...
CRISPR technology to cure sickle cell disease at UIC
2021-01-21
University of Illinois Chicago is one of the U.S. sites participating in clinical trials to cure severe red blood congenital diseases such as sickle cell anemia or Thalassemia by safely modifying the DNA of patients' blood cells.
The first cases treated with this approach were recently published in an article co-authored by Dr. Damiano Rondelli, the Michael Reese Professor of Hematology at the UIC College of Medicine. The article reports two patients have been cured of beta thalassemia and sickle cell disease after their own genes were edited with CRISPR-Cas9 technology. The two researchers ...
Treating moms with postpartum depression helps their babies' brains
2021-01-21
New research from McMaster University has found that psychiatric help for mothers with postpartum depression results in healthy changes in the brains of their babies.
The study, published in the journal Depression and Anxiety this week, found treating mothers who had postpartum depression with cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) not only helped the moms, but resulted in adaptive changes in the brains and behaviour of their infants.
More specifically, after the mothers' treatment, their infants showed healthy changes in their nervous and cardiovascular systems, and they were observed to better regulate their behaviours and emotions by both mothers and fathers.
"In fact, we found that after their moms were treated that their infant's ...
The immune system mounts a lasting defense after recovery from COVID-19
2021-01-21
As the number of people who have fought off SARS-CoV-2 climbs ever higher, a critical question has grown in importance: How long will their immunity to the novel coronavirus last? A new Rockefeller study offers an encouraging answer, suggesting that those who recover from COVID-19 are protected against the virus for at least six months, and likely much longer.
The findings, published in Nature, provide the strongest evidence yet that the immune system "remembers" the virus and, remarkably, continues to improve the quality of antibodies even after the infection has waned. Antibodies produced ...
Drug-delivery microcapsules tagged with zirconium-89 can be tracked by PET imaging
2021-01-21
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - University of Alabama at Birmingham polymer and radionuclide chemists report what they say "may represent a major step forward in microcapsule drug delivery systems."
The UAB microcapsules -- labeled with radioactive zirconium-89 -- are the first example of hollow polymer capsules capable of long-term, multiday positron emission tomography, or PET, imaging in vivo. In previous work, UAB researchers showed that the hollow capsules could be filled with a potent dose of the cancer drug doxorubicin, which could then be released by therapeutic ultrasound that ruptures the microcapsules.
PET imaging with zirconium-89 -- which has a half-life of 3.3 days -- allowed the capsules to be traced in test mice up to seven days. The major ...
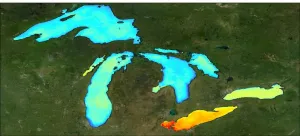
World's largest lakes reveal climate change trends
2021-01-21
NASA-funded research on the 11 largest freshwater lakes in the world coupled field and satellite observations to provide a new understanding of how large bodies of water fix carbon, as well as how a changing climate and lakes interact.
Scientists at the Michigan Tech Research Institute (MTRI) studied the five Laurentian Great Lakes bordering the U.S. and Canada; the three African Great Lakes, Tanganyika, Victoria and Malawi; Lake Baikal in Russia; and Great Bear and Great Slave lakes in Canada.
These 11 lakes hold more than 50% of the surface freshwater that millions of people and countless other creatures rely on, underscoring the importance of understanding how they are being altered by climate change and other factors.
The two Canadian lakes ...
[1] ... [2714]
[2715]
[2716]
[2717]
[2718]
[2719]
[2720]
[2721]
2722
[2723]
[2724]
[2725]
[2726]
[2727]
[2728]
[2729]
[2730]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.