Highly efficient grid-scale electricity storage at fifth of cost
2021-01-22
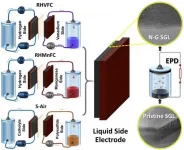
Researchers in WMG at the University of Warwick, in collaboration with Imperial College London, have found a way to enhance hybrid flow batteries and their commercial use. The new approach can store electricity in these batteries for very long durations for about a fifth the price of current technologies, with minimal location restraints and zero emissions.
The researchers enhanced three hybrid flow cells using nitrogen doped graphene (exposed to nitrogen plasma) in a binder-free electrophoresis technique (EPD).
Wind and solar power are increasingly popular sources for renewable energy. Unfortunately, intermittency issues keep them ...
Fungi strengthen plants to fend off aphids
2021-01-22
GREEN TRANSITION Researchers at the University of Copenhagen have demonstrated that unique fungi strengthen the "immune systems" of wheat and bean plants against aphids. Fungi enter and influence the amount of a plant's own defences, resulting in fewer aphids. The results could serve to reduce agricultural insecticide use and bring Denmark a step further along the path towards its green transition.
Wheat field
Certain fungi are able to establish a close rapport with plants that results in fewer insect infestations and thereby less damage to crops. Until now, it was unclear how these fungi could be used to reduce insect infestations.
"In order for us to really use fungi ...
Addressing the impact of structural racism on disparities in children with Type 1 diabetes
2021-01-22
PHILADELPHIA, PA (January 22, 2021) - Advancements in diabetes technology have improved quality of life and glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes. However, data show that a subset of children is being left behind. Those from low-income families and non-Hispanic Black (NHB) children are not experiencing benefits associated with technological advances, and are at higher risk for diabetes complications and adverse outcomes through ongoing poor glycemic control.
In an invited commentary to be published in the journal Diabetes Care, researchers describe how socioeconomic disparities ...
Novel target identified that could improve safety of therapy for pancreatic cancer
2021-01-22
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London, have identified a protein that may represent a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Using this protein as a target, the team successfully created a CAR T cell therapy - a type of immunotherapy - that killed pancreatic cancer cells in a pre-clinical model.
CAR T cell therapy is an immunotherapy that has shown great promise for the treatment of some blood cancers; however, the treatment of solid tumours using this therapy has proved very difficult. One barrier to success is toxicity in tissues other than the cancer because most of the proteins currently used to target CAR T cells to pancreatic cancer cells and other solid tumours are present in low levels on other normal tissues, ...
Reducing traps increases performance of organic photodetectors
2021-01-22
Organic photodetectors (OPDs) have a huge potential for applications in low-cost imaging, health monitoring and near infrared sensing. Yet, before industrially realizing these applications, the performance of these devices still needs to be improved.
Recent research on organic photodetectors based on donor-acceptor systems has resulted in narrow-band, flexible and biocompatible devices, of which the best reach external photovoltaic quantum efficiencies of close to 100%. However, the high noise in the off state produced by these devices limits their specific detectivity, severely reducing the performance, for example ...
University of Cincinnati student uses zebrafish to study spinal deformities
2021-01-22
Popular in aquariums all over the world, the zebrafish is native to South Asia. But here in a Cincinnati Children's laboratory, the freshwater variant plays a vital role in scientific discovery.
The iconic stripes are eye-catching but it's the transparency of zebrafish embryonic tissue which are most prized by researchers like Oriana Zinani, a fifth-year doctoral student in molecular developmental biology in the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine. The patterning of the zebrafish's spine gives the appearance of stripes; it is controlled by ...
New perspectives challenge the idea that saturated fats cause heart disease
2021-01-22
In science, sometimes a new perspective can turn our interpretation of the data upside-down, and necessitate a paradigm shift.
There has been, and continues to be, fierce disagreements in nutrition science as to what constitutes a healthy diet. A key controversy is the role of saturated fats in health and disease. Saturated fats are known to increase blood cholesterol levels, and increased blood cholesterol is often observed in people who develop cardiovascular disease.
It has been thought for more than half a century that saturated fats in the diet promote heart disease by increasing blood cholesterol. However, a new model explains why this so-called "diet-heart hypothesis", which ...
Highly functional membrane developed for producing freshwater from seawater
2021-01-22
Professor MATSUYAMA Hideto's research group at Kobe University's Research Center for Membrane and Film Technology has successfully developed a new desalination membrane. They achieved this by laminating a two-dimensional carbon material (*1) on to the surface of a porous polymer membrane (*2).
Desalination (*3) membranes are used to produce freshwater from seawater. In order to solve the worldwide issue of insufficient freshwater resources, researchers are striving to develop desalination membranes that are not only permeated by water faster than those currently in use but also remove salt efficiently, so that more effective, low-energy desalination systems can be implemented.
In this research study, graphene oxide (*4) nanosheets, which ...
Defects may help scientists understand the exotic physics of topology
2021-01-22
Real-world materials are usually messier than the idealized scenarios found in textbooks. Imperfections can add complications and even limit a material's usefulness. To get around this, scientists routinely strive to remove defects and dirt entirely, pushing materials closer to perfection. Now, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have turned this problem around and shown that for some materials defects could act as a probe for interesting physics, rather than a nuisance.
The team, led by professors Gaurav Bahl and Taylor Hughes, studied artificial materials, or metamaterials, which they engineered to include defects. The team used these customizable circuits as a proxy for studying exotic topological crystals, which are often ...
Making protein 'superfood' from marine algae
2021-01-22
Marine microalgae-based cellular agriculture is a promising new way to sustainably produce plant-based 'meat' and healthy 'superfoods' for the future.
Researchers at Flinders University's Centre for Marine Bioproducts Development (CMBD) in Australia are responding to growing interest from consumers looking for healthier, more environmentally friendly, sustainable and ethical alternatives to animal proteins.
Marine microalgae, single-cell photosynthetic organisms from the ocean could be the solution to the world's meat protein shortage, says CMBD director Flinders University Professor Wei Zhang, who is also co-leading a bid to establish a national Marine Bioproducts Cooperative Research Centre ...
Study recommends rugby league invests in young players' diets
2021-01-22
Young rugby league players could benefit from individualised nutrition plans to maximise performance and optimise recovery throughout their careers, according to QUT researchers.
The new study, published in the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, provides nutritional recommendations and considers potential supplements to improve players' physical capacity, health and recovery during the preparatory and competition phases of a season.
Lead researcher, Associate Professor Vince Kelly from QUT's Faculty of Health's Exercise and Nutrition Sciences, is a committee member of the National Rugby League Research Committee and has more than 20 years' experience in elite sport.
"Young players don't have the same access to dietary support as professional ...
Targeted coating improves graphene oxide membranes for nanofiltration
2021-01-22
Nanofiltration (NF) is an advanced technology for treating wastewater containing organic micropollutants (OMPs).
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a stable graphene oxide nanofiltration membrane with uniform pore size to remove OMPs.
The study was published in Chemical Engineering Journal on Jan. 20.
It proposes combining signal amplification strategy and defect chemistry to reduce membrane pore size distribution, thus offering a promising method for preparing highly ...
SUTD research team extends 4D printing to nanophotonics
2021-01-22
The Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and its research collaborators have successfully demonstrated the four-dimensional (4D) printing of shape memory polymers in submicron dimensions which are comparable to the wavelength of visible light. This novel development has allowed researchers to now explore new applications in the field of nanophotonics.
4D printing enables 3D printed structures to change its configurations over time and is used in a wide variety of fields such as soft robotics, flexible electronics, and medical devices.
Different materials such as hydrogels, liquid crystal elastomers and magnetic nanoparticles embedded resists ...
New variety of paintbrush lily developed by a novel plant tissue culture technique
2021-01-22
Scientists at Hokkaido University and Chiba University have developed simultaneous triploid and hexaploid varieties of Haemanthus albiflos by the application of endosperm culture, thus extending the use of this technique.
In plants, the number of chromosome sets in cells (ploidy) affects a large number of desirable characteristics. In general, the greater the number of chromosome sets, the more like the plant is to have larger flowers, larger fruits, be more disease resistant, and so on. Hence, particularly in agriculture and horticulture, the development of polyploid plants continues to receive much attention.
Scientists from Hokkaido University and Chiba University have successfully developed triploid (3 chromosome sets) ...
A large number of gray whales are starving and dying in the eastern North Pacific
2021-01-22
It's mid-January 2021, and the first gray whales from the eastern North Pacific population have started to arrive in the breeding lagoons in Baja California, Mexico. Since the start of their southbound migration from their high latitude feeding grounds, several sightings of emaciated gray whales have already been reported along their migration route.
This has raised concern among scientists that the unusual mortality event (UME, an unexpected phenomenon during which a significant number of a marine mammal population dies), that started in January 2019, and which so far has resulted in 378 confirmed ...
ACSL1 as a main catalyst of CoA conjugation of propionic acid-class NSAIDs in liver
2021-01-22
Kanazawa, Japan - Liver injury is a rare side effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which are frequently used for daily pain control. This toxicity has been regarded as a "black box" and is mainly managed by an empirical approach, but there is not a clear understanding of the mechanism. Now, researchers from Japan have found that a bit of attention to the types and frequencies of NSAIDs could help people avoid liver injury.
In a study published recently in Biochemical Pharmacology, researchers from Kanazawa University have revealed that specific NSAIDs, including ibuprofen, are metabolized by one of the acyl-CoA synthetases, ACSL1, in a manner that can have toxic effects.
NSAIDs containing a specific chemical group, carboxylic acid, can form "conjugates" with ...
Pancreatic β cell-derived exosomal miR-29 family enhances hepatic glucose output
2021-01-22
In a new study published in Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, Chen-Yu Zhang's group at Nanjing University, School of Life Sciences, and Antonio Vidal-Puig's group at University of Cambridge report that pancreatic β cells secrete miR-29 family members (miR-29s) via exosomes in response to high levels of free fatty acids (FFAs). Theses β cell-derived exosomal miR-29s regulate glucose homeostasis through their manipulations on glucose output in liver.
Previously, Chen-Yu Zhang's group identified extracellular miRNA as a new form of cell-to-cell communication. They are among the first that reported the selective secretion of miRNAs under different physiological or pathological states; also, the uptake and function of secreted miRNAs in recipient cells. In the past decade, intensive ...
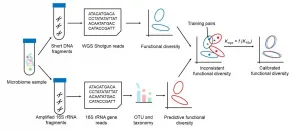
Meta-Apo supports cheaper, quicker microbiome functional assessment
2021-01-22
A new algorithm may reduce the need for expensive, time-consuming whole-genome sequencing computations to understand how a microbiome functions. A team led by JING Gongchao of the Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and SU Xiaoquan of Qingdao University, published their approach, called Meta-Apo, on Jan. 6 in BMC Genomics.
Researchers routinely sequence samples of microbial communities found on human skin, in human guts, and in the environment to understand what genes they contain with the ultimate goal of understanding ...
Cargo delivery by polymers
2021-01-22
Degradable, bio-based polymers offer options for chemical recycling, and they can be a tool to store and release useful molecules. Scientists have developed a class of sugar-based polymers that are degradable through acid hydrolysis. The researchers also integrated "cargo" molecules in the polymer, which are designed to split off after polymer degradation. Degradable, cargo-bearing polymers are important for medical and sensor applications, says the study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Most plastics resist natural degradation processes. Consequently, increasing contamination of the environment with plastics has led to a call for degradable plastics. Such materials can be subjected to chemical recycling processes, in which chemical reactions break up polymer bonds. ...
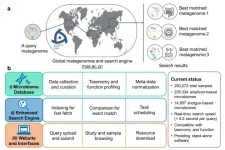
Microbiome Search Engine 2 helps researchers explore microbiome space
2021-01-22
Metagenomics - the study of genetic material from an environmental sample - is growing as species evolve or are discovered across the globe. To correlate the newly developed microbiomes with existing data sets, a team of researchers based in China has developed the Microbiome Search Engine 2 (MSE 2). It was published on Jan. 19 in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Here, we introduce MSE 2, a microbiome database platform for searching query microbiomes in the global metagenome data space based on taxonomic or functional similarity of the whole microbiome," ...
Research shows preference for male children is declining in Bangladesh
2021-01-22
Research from the University of Kent has demonstrated a decline in 'son preference' by women of childbearing age in Bangladesh. However, the study also shows that fertility decisions are still influenced according to son preference.
The paper, 'Is son preference disappearing from Bangladesh?', surveyed a nationally representative sample of Bangladeshi women of childbearing age, born between 1975 and 1994, to assess how son preference is evolving.
The term 'son preference' refers to any situation where parents value sons over daughters and make resulting choices accordingly, which can have a strong economic and demographic impact.
The study finds that among women of childbearing age in ...
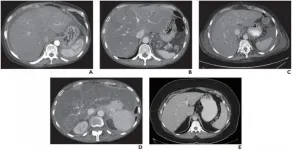
CT identifies patients with high-risk nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
2021-01-22
Leesburg, VA, January 22, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) and multiple CT findings can identify patients with high-risk nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)--advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis, that is--though the presence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) remains elusive on CT.
"Subjective assessment of multiple morphologic and separately quantified parameters by trained readers and a simple quantitative three-parameter model combining two CT features, liver surface nodularity (LSN) and liver segmental volume ratio (LSVR), and a clinical score (FIB-4) showed good association with presence of advanced fibrosis," wrote first author Meghan G. Lubner from the department of radiology at the University of Wisconsin School ...
Magnetic waves explain mystery of Sun's outer layer
2021-01-22
The Sun's extremely hot outer layer, the corona, has a very different chemical composition from the cooler inner layers, but the reason for this has puzzled scientists for decades.
One explanation is that, in the middle layer (the chromosphere), magnetic waves exert a force that separates the Sun's plasma into different components, so that only the ion particles are transported into the corona, while leaving neutral particles behind (thus leading to a build-up of elements such as iron, silicon and magnesium in the outer atmosphere).
Now, in a new study published ...
Patients of Asian and black backgrounds more likely to die from COVID, large study reveals
2021-01-22
Patients of Asian and black backgrounds suffered disproportionate rates of premature death from COVID-19, according to a study of 1,737 patients by Queen Mary University of London and Barts Health NHS Trust.
The study, published in BMJ Open, is one of the most comprehensive studies exploring COVID-19 outcomes in black, Asian and minority ethnic populations so far reported, from one of the largest and most diverse UK hospital COVID-19 cohorts, representing a majority ethnically diverse population (only 35.2 per cent of patients identified as White ethnicity).
The work resulted from a new interdisciplinary collaboration between intensive care physicians and HIV physicians. The researchers looked at data from all patients ...
Geoscientists reconstruct 6.5 million years of sea level stands
2021-01-22
TAMPA, Fla. (January 22, 2021)- The pressing concern posed by rising sea levels has created a critical need for scientists to precisely predict how quickly the oceans will rise in coming centuries. To gain insight into future ice sheet stability and sea-level rise, new research from an international team led by University of South Florida geoscientists is drawing on evidence from past interglacial periods when Earth's climate was warmer than today.
Using deposits in the caves of the Mediterranean island of Mallorca, known as phreatic overgrowths ...
[1] ... [2710]
[2711]
[2712]
[2713]
[2714]
[2715]
[2716]
[2717]
2718
[2719]
[2720]
[2721]
[2722]
[2723]
[2724]
[2725]
[2726]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.