Tiny particles that seed clouds can form from trace gases over open sea
2021-01-22
UPTON, NY - New results from an atmospheric study over the Eastern North Atlantic reveal that tiny aerosol particles that seed the formation of clouds can form out of next to nothingness over the open ocean. This "new particle formation" occurs when sunlight reacts with molecules of trace gases in the marine boundary layer, the atmosphere within about the first kilometer above Earth's surface. The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, will improve how aerosols and clouds are represented in models that describe Earth's climate so scientists can understand how the particles--and the processes that control them--might ...
Experts call for more pragmatic approach to higher education teaching
2021-01-22
Millions of students around the world could benefit if their educators adopted a more flexible and practical approach, say Swansea University experts.
After analysing the techniques current being used in higher education, the researchers are calling for a pragmatic and evidence-based approach instead.
Professor Phil Newton, director of learning and teaching at of Swansea University Medical School, said: "Higher education is how we train those who carry out important professional roles in our society. There are now more than 200 million students in HE worldwide and this number is likely to double again over the next decade.
"Given the size, impact, importance and cost of ...
A quarter of known bee species haven't appeared in public records since the 1990s
2021-01-22
Researchers at the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET) in Argentina have found that, since the 1990s, up to 25% of reported bee species are no longer being reported in global records, despite a large increase in the number of records available. While this does not mean that these species are all extinct, it might indicate that these species have become rare enough that no one is observing them in nature. The findings appear January 22 in the journal One Earth.
"With citizen science and the ability to share data, records are going up exponentially, but the number of species reported in these records is going down," says first ...
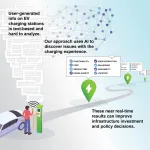
AI trained to read electric vehicle charging station reviews to find infrastructure gaps
2021-01-22
Although electric vehicles that reduce greenhouse gas emissions attract many drivers, the lack of confidence in charging services deters others. Building a reliable network of charging stations is difficult in part because it's challenging to aggregate data from independent station operators. But now, researchers reporting January 22 in the journal Patterns have developed an AI that can analyze user reviews of these stations, allowing it to accurately identify places where there are insufficient or out-of-service stations.
"We're spending billions ...
Genetic sequence for parasitic flowering plant Sapria
2021-01-22
On January 22 in Current Biology, a team of Harvard-led researchers presented the most complete genome yet assembled of one of the major Rafflesiaceae lineages, Sapria himalayana.
The species is found in Southeast Asia and its mottled red and white flower is about the size of a dinner plate. (It's more famous cousin, Rafflesia arnoldii, produces blossoms nearly three feet in diameter, the largest in the world.)
The genetic analysis revealed an astonishing degree of gene loss and surprising amounts of gene theft from its ancient and modern hosts. These findings bring unique perspectives into the number and kind of genes it takes to be an endoparasite (an organism that is completely dependent on its host for all nutrients), along ...
SARS-CoV-2 infection in children, their parents in southwest Germany
2021-01-22
What The Study Did: In this observational study, the spread of SARS-CoV-2 infection during a period of lockdown in southwest Germany was particularly low in children ages 1 to 10 years old. Overall, this large SARS-CoV-2 prevalence study in children is instructive for how ad hoc mass testing provides the basis for rational political decision-making in a pandemic setting.
Authors: Burkhard Tönshoff, M.D., of the University Children's Hospital in Heidelberg, Germany, and Klaus-Michael Debatin, M.D., of Ulm University Medical Center in Ulm, Germany, are the corresponding authors.
To ...
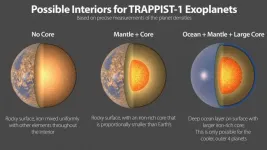
The seven rocky planets of TRAPPIST-1 seem to have very similar compositions
2021-01-22
A new international study led by astrophysicist Eric Agol from the University of Washington has measured the densities of the seven planets of the exoplanetary system TRAPPIST-1 with extreme precision, the values obtained indicating very similar compositions for all the planets. This fact makes the system even more remarkable and helps to better understand the nature of these fascinating worlds. This study has just been published in the Planetary Science Journal.
The TRAPPIST-1 system is home to the largest number of planets similar in size to our Earth ever found outside our solar system. Discovered in 2016 by a research team led by Michaël Gillon, astrophysicist at the University of Liège, the system offers an insight into the immense ...
Proteins unspool DNA so cells can take on unique properties
2021-01-22
ITHACA, NY - Biologists have long wondered how complex organisms contain a variety of dramatically different types of cells with specialized functions, even though all of those cells are genetically identical.
New research reveals how proteins, called "pioneer transcription factors," help turn on key genes that give cell types their unique properties and functions.
These pioneer factors, it turns out, help unspool tightly wound coils of DNA so that genetic blueprints in genes can be read and proteins that play roles in biological processes can be made.
The study in fruit flies, "Pioneer-like Factor GAF Cooperates with PBAP (SWI/SNF) and NURF (ISWI) to Regulate Transcription," was published Dec. 10 in the journal Genes & Development.
"We know pretty ...
Consenting for treatment in advance to reduce leaving the hospital against medical advice among patients with addiction - Experts debate pros and cons
2021-01-22
January 22, 2021 - Patients with substance use disorders (SUDs) being treated for serious medical conditions are more likely to leave the hospital against medical advice (AMA) than those without addiction. A special type of contract with healthcare providers might enable patients to consent in advance to life-saving medical care - even if they later refuse treatment, according to a commentary in the Journal of Addiction Medicine, the official journal of the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The Substance Use Advance Directive (SUAD) "has the potential to greatly improve the current state of treatment for life-threatening comorbid conditions in SUD patients through ...
Shift in caribou movements may be tied to human activity
2021-01-22
Human activities might have shifted the movement of caribou in and near the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, according to scientists with the University of Cincinnati.
Each year caribou take on one of nature's longest land migrations, trekking hundreds of miles across Alaska and Canada to find food and give birth in their preferred calving grounds.
A UC study published today in the journal Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution identified a shift in one herd's movements after the 1970s that coincided with changes in herd size and climate, and the construction of new roads and other energy infrastructure.
Researchers used isotope analysis of antlers shed by female caribou to track their historical patterns of movement over the landscape. Female caribou are unique among deer for growing ...
Lack of sleep, stress can lead to symptoms resembling concussion
2021-01-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study suggests that a lot of people might be going through life with symptoms that resemble concussion - a finding supporting researchers' argument that athletes recovering from a brain injury should be assessed and treated on a highly individualized basis.
In the national study, between 11% and 27% of healthy college athletes with no history of a recent concussion reported combinations of symptoms that met criteria for post-concussion syndrome (PCS) as defined by an international classification system. Among the nearly 31,000 student-athletes surveyed, three factors stood out as the most likely to predict ...
UMD researcher expands plant genome editing with newly engineered variant of CRISPR-Cas9
2021-01-22
Alongside Dennis vanEngelsdorp, associate professor at the University of Maryland (UMD) in Entomology named for the fifth year in a row for his work in honey bee and pollinator health, Yiping Qi, associate professor in Plant Science, represented the College of Agriculture & Natural Resources on the Web of Science 2020 list of Highly Cited Researchers for the first time. This list includes influential scientists based on the impact of their academic publications over the course of the year. In addition to this honor, Qi is already making waves in 2021 with a new high-profile publication in Nature Plants introducing SpRY, a newly engineered variant ...
New blueprint for more stable quantum computers
2021-01-22
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have put forward a detailed plan of how faster and better defined quantum bits - qubits - can be created. The central elements are magnetic atoms from the class of so-called rare-earth metals, which would be selectively implanted into the crystal lattice of a material. Each of these atoms represents one qubit. The researchers have demonstrated how these qubits can be activated, entangled, used as memory bits, and read out. They have now published their design concept and supporting calculations in the journal PRX Quantum.
On the way to quantum computers, an initial requirement is to create so-called quantum ...
Rediscovery of the 'extinct' Pinatubo volcano mouse
2021-01-22
In June 1991, Mount Pinatubo, a volcanic peak on the Philippine Island of Luzon, literally blew its top. It was the second-most powerful volcanic eruption of the 20th century, ten times stronger than Mount Saint Helens, and its effects were devastating. Lava and ash spewed into the surrounding environment in the Zambales Mountains, pooling in layers up to 600 feet thick in the valleys. Following the eruption, powerful typhoons and monsoon rains triggered landslides and ash flows that continued for many months. Eight hundred people lost their lives, and the lush forests that covered the mountain prior to the eruption were destroyed or severely damaged. In recent years, scientists returned to the region to survey the surviving mammal populations, and in a new paper in the ...
Massey researchers review geographic factors that affect HPV vaccination rates
2021-01-22
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection, with an estimated 79 million Americans currently infected with the virus, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If a high-risk HPV infection does not go away, it can lead to the development of a variety of cancers, including 91% of all cervical cancers, 70% of oropharyngeal cancers and cancers of the vulva, vagina, penis and anus.
HPV vaccination can significantly reduce the number of new cancer diagnoses linked to the virus, in addition to preventing a number of other health complications.
"Given ...
New maintenance treatment for acute myeloid leukemia prolongs the lives of patients
2021-01-22
Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the most common form of acute leukemia in adults, that has gone into remission following initial chemotherapy remain in remission longer and have improved overall survival when they are given a pill form of the cancer drug azacitidine as a maintenance treatment, according to a randomized, international phase 3 clinical trial for which Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian are trial sites. This is the first time a maintenance treatment for AML has shown such a strong benefit for patients, and it is already being adopted as part of standard care.
The results, which were published Dec. 24 in the New England Journal of Medicine, led to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's approval in September 2020 of oral ...
NIH-funded study examines mono, chronic fatigue syndrome in college students
2021-01-22
Many college students fully recover from infectious mononucleosis (which is almost always caused by Epstein-Barr virus) within 1-6 weeks, but some go on to develop chronic fatigue syndrome, also called myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME/CFS). A longitudinal study from DePaul University and Northwestern University followed 4,501 college students to examine risk factors that may trigger longer illness. The research appears in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases and was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Previous retrospective studies found that risk factors ...
Ageing dams pose growing threat: UN
2021-01-22
By 2050, most people on Earth will live downstream of tens of thousands of large dams built in the 20th century, many of them already operating at or beyond their design life, according to a UN University analysis.
The report, "Ageing water infrastructure: An emerging global risk," by UNU's Canadian-based Institute for Water, Environment and Health, says most of the 58,700 large dams worldwide were constructed between 1930 and 1970 with a design life of 50 to 100 years, adding that at 50 years a large concrete dam "would most probably begin to express signs of aging."
Ageing ...
Scientists improved eye tracking technology in VR systems
2021-01-22
The tracking of eye movement is one of the key elements of virtual and amplified reality technologies (VR/AR). A team from MSU together with a professor from RUDN University developed a mathematical model that helps accurately predict the next gaze fixation point and reduces the inaccuracy caused by blinking. The model would make VR/AR systems more realistic and sensitive to user actions. The results of the study were published in the SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers.
Foveated rendering is a basic technology of VR systems. When a person looks at something, their gaze is focused on the so-called foveated region, and everything else is covered by peripheral vision. Therefore, a computer has to render the images in the ...
Depression in new fathers connected to relationship insecurities
2021-01-22
Becoming a parent often brings great joy, but not always. Parenthood also entails challenges, stress and, for some people, it can trigger depression. A new study from Lund University in Sweden shows that male postnatal depression is more common in men who are insecure in their relationship with their partner.
Depression affects around 10-12 per cent of new mothers, and at least 8 per cent of new fathers. The figures are even higher when looking at depressive symptoms; as many as one in five new fathers experience troublesome symptoms, according to the new study conducted by Elia Psouni, registered psychologist and associate professor of ...
Potential combined drug therapy for lung cancer
2021-01-22
Most lung cancers are of a type called non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). This type of cancer is relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, so NSCLC therapies are usually based on drug treatment. Alectinib is a drug commonly used for treating patients with NSCLC. It addresses a gene rearrangement known as ALK that occurs in 3 to 5% of NSCLC patients (alectinib belongs to a class of drugs called ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors). It has been unclear, however, whether there is a correlation between the use of alectinib and the poorer prognosis in ALK-NSCLC patients in which secondary cancer mutations ...
Single atoms as a catalyst: Surprising effects ensue
2021-01-22
Metals such as gold or platinum are often used as catalysts. In the catalytic converters of vehicles, for example, platinum nanoparticles convert poisonous carbon monoxide into non-toxic CO2. Because platinum and other catalytically active metals are expensive and rare, the nanoparticles involved have been made smaller and smaller over time.
"Single-atom" catalysts are the logical end point of this downsizing: The metal is no longer present as particles, but as individual atoms that are anchored on the surface of a cheaper support material. Individual atoms can no longer be described using the rules developed from larger pieces of metal, so the rules used to predict which metals will ...
A study explores the alteration of the functional dynamics of the human brain associated with ageing
2021-01-22
Normal ageing causes disruptions in the brain that can lead to cognitive decline. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging studies have found significant age-related alterations in functional connectivity across various networks. However, most of the studies have focused primarily on static functional connectivity.
The authors of a recent study published in Cerebral Cortex based their research on the idea that studying the dynamics of resting-state brain activity across the whole-brain functional network can provide a better characterization of age-related changes.
The study was led by Gustavo Deco, director of the Center for Brain and Cognition (CBC) and ICREA research professor at the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), and Anira ...
Chimpanzee friends fight together to battle rivals
2021-01-22
Chimpanzees, one of the closest relatives of humans, cooperate on a group level - in combative disputes, they even cooperate with group members to whom they are not related. Those involved in fights with neighbouring groups put themselves at risk of serious injury or even death.
Within the context of the Tai Chimpanzee Project researchers observed three chimpanzee communities in Tai National Park in Cote d'Ivoire documenting social relationships, territory range and intergroup encounters amongst others. "We have been able to analyze almost 500 vocal and physical battles from the last 25 years with participation of at least one ...
Flowery diets help predatory insects help farmers keep pests in check
2021-01-22
Good news for the green transition: Flowery diets help predatory insects help farmers keep pests in check
Predatory insects have been shown to live longer when they have access to nectar and pollen, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Copenhagen. Thus, flowers don't just benefit insects, they help farmers farm sustainably. Predatory insects are skilled pest controllers whose hunting reduces the need for agricultural pesticides.
Until now, it was believed that predatory insects needed prey to survive. But in a systematic review conducted at the University ...
[1] ... [2709]
[2710]
[2711]
[2712]
[2713]
[2714]
[2715]
[2716]
2717
[2718]
[2719]
[2720]
[2721]
[2722]
[2723]
[2724]
[2725]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.