(Press-News.org) AMHERST, Mass. - A new study led by biologist R. Thomas Zoeller of the University of Massachusetts Amherst provides "the strongest evidence to date" that endocrine disrupting chemicals such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) found in flame retardant cloth, paint, adhesives and electrical transformers, can interfere with thyroid hormone action in pregnant women and may travel across the placenta to affect the fetus.
Results appeared in an early online edition and in the December print edition of the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. The paper was also honored this week as an "extramural paper of the month" by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences.
Zoeller says, "As endocrine-disrupting chemicals, PCBs interfere with the way the thyroid hormone functions, but they don't actually change the amount of the hormone found in the body. Although these effects are largely invisible in scientific studies that only judge thyroid activity by measuring hormone levels, they may be having a real impact on infants' brain development."
Although endocrine-disrupting PCBs were banned in the United States in 1979, they are still released into the environment from disposal sites or products manufactured before the ban. Most people have been exposed to low levels of PCBs, Zoeller points out.
In this prospective birth cohort study, he and colleagues looked at the effects of low-dose chemical exposure in 164 pregnant women. Tissue from their placentas, the uterine structure that provides oxygen and nutrients to the fetus, was analyzed for a specific enzyme, CYP1A1, which changes endocrine-disrupting chemicals into a form that can interfere directly with the body's thyroid hormone receptors.
This work was a collaboration between scientists in the biology department at UMass Amherst and physician scientists led by Larissa Takser at the University of Sherbrooke, Québec, who collected placental tissue from a large epidemiological study. Biochemistry and experimental work conducted at Zoeller's UMass Amherst laboratory over the past decade provided the framework for the analyses. "This led us to predict specific molecular events that might be occurring in the placenta," he notes, "and as best as we can tell right now, we were correct."
Zoeller and colleagues found that in pregnancies where the placenta contained higher levels of CYP1A1, it also showed signs of thyroid disruption. Levels of two thyroid-regulated genes tended to be higher in these pregnancies, although the mother's overall thyroid hormone levels did not change.
"Whatever is happening in the placenta likely reflects what is happening in the fetus," says Zoeller. "To truly understand how endocrine-disrupting chemicals may be affecting pregnancies, the findings show we need to study not only hormone levels, but hormone activity at the cellular level."
The effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals may be particularly insidious in people who smoke, Zoeller said. The enzyme CYP1A1 is supposed to clean the blood, and the body produces more of this enzyme when it is exposed to cigarette smoke. The researchers found pregnant women who smoked tended to have higher levels of the enzyme in the placental tissue.
INFORMATION:
In addition to Zoeller, other authors at UMass Amherst are Thomas Luke Wadzinski, Katherine Geromini, Judy McKinley Brewer and Ruby Bansal, with Nadia Abdelouahab and Marie-France Langlois in addition to Takser at the University of Sherbrooke.
BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA -- Those formerly silent walls can "talk" now: Researchers have demonstrated a simple optical technique by which audio information can be extracted from high-speed video recordings. The method uses an image-matching process based on vibration from sound waves, and is reported in an article appearing in the November issue of the journal Optical Engineering, published by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics.
"One of the intriguing aspects of the paper is the ability to recover spoken words from a video of objects in the room," ...
In what is believed to be the first interview-style qualitative study of its kind among health care providers in the trenches, a team led by a Johns Hopkins geriatrician has further documented barriers to better care of older adults as they are transferred from hospital to rehabilitation center to home, and too often back again.
Using comments and concerns drawn from in-depth interviews of 18 physicians and two home health care agency administrators -- all experienced in trying to coordinate care of older adults -- the researchers created a framework for evaluating what ...
VIDEO:
A bat lands on the rewarded object in complete darkness (movie taken in IR). The movie shows that the bat has a general knowledge of the location of the object,...
Click here for more information.
In a discovery that overturns conventional wisdom about bats, researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on December 4 have found that Old World fruit bats--long classified as "non-echolocating"--actually do use a rudimentary form of echolocation. Perhaps ...
A new study shows that increasing sugar in the diet of male fruit flies for just 1 or 2 days before mating can cause obesity in their offspring through alterations that affect gene expression in the embryo. There is also evidence that a similar system regulates obesity susceptibility in mice and humans. The research, which is published online December 4 in the Cell Press journal Cell, provides insights into how certain metabolic traits are inherited and may help investigators determine whether they can be altered.
Research has shown that various factors that are passed ...
New Caledonian crows--well known for their impressive stick-wielding abilities--show preferences when it comes to holding their tools on the left or the right sides of their beaks, in much the same way that people are left- or right-handed. Now researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on December 4 suggest that those bill preferences allow each bird to keep the tip of its tool in view of the eye on the opposite side of its head. Crows aren't so much left- or right-beaked as they are left- or right-eyed.
"If you were holding a brush in your mouth ...
Blood cancers are more common in men than in women, but it has not been clear why this is the case. A study published by Cell Press December 4th in Cell Stem Cell provides an explanation, revealing that female sex hormones called estrogens regulate the survival, proliferation, and self-renewal of stem cells that give rise to blood cancers. Moreover, findings in mice with blood neoplasms--the excessive production of certain blood cells--suggest that a drug called tamoxifen, which targets estrogen receptors and is approved for the treatment of breast cancer, may also be a ...
In a breakthrough study to be published on the December 4th issue of the prestigious scientific journal Cell, a research team led by Miguel Soares at the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC; Portugal) discovered that specific bacterial components in the human gut microbiota can trigger a natural defense mechanism that is highly protective against malaria transmission.
Over the past few years, the scientific community became aware that humans live under a continuous symbiotic relationship with a vast community of bacteria and other microbes that reside in the gut. ...
This discovery has a potential application in the treatment of certain blood disorders for which there is currently no cure. The study was led by Dr. Simón Méndez-Ferrer of the CNIC, working in partnership with the laboratories of Doctors Jürg Schwaller and Radek Skoda of the University Hospital in Basel (Switzerland). The study's authors have demonstrated in mice that tamoxifen, a drug already approved and widely used for the treatment of breast cancer, blocks the symptoms and the progression of a specific group of blood disorders known as myeloproliferative ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- In a study in the journal Neuron, scientists describe a new high data-rate, low-power wireless brain sensor. The technology is designed to enable neuroscience research that cannot be accomplished with current sensors that tether subjects with cabled connections.
Experiments in the paper confirm that new capability. The results show that the technology transmitted rich, neuroscientifically meaningful signals from animal models as they slept and woke or exercised.
"We view this as a platform device for tapping into the richness of ...
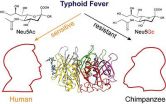
The bacterium Salmonella Typhi causes typhoid fever in humans, but leaves other mammals unaffected. Researchers at University of California, San Diego and Yale University Schools of Medicine now offer one explanation -- CMAH, an enzyme that humans lack. Without this enzyme, a toxin deployed by the bacteria is much better able to bind and enter human cells, making us sick. The study is published in the Dec. 4 issue of Cell.
In most mammals (including our closest evolutionary cousins, the great apes), the CMAH enzyme reconfigures the sugar molecules found on these animals' ...