New blueprint for more stable quantum computers
2021-01-22
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have put forward a detailed plan of how faster and better defined quantum bits - qubits - can be created. The central elements are magnetic atoms from the class of so-called rare-earth metals, which would be selectively implanted into the crystal lattice of a material. Each of these atoms represents one qubit. The researchers have demonstrated how these qubits can be activated, entangled, used as memory bits, and read out. They have now published their design concept and supporting calculations in the journal PRX Quantum.
On the way to quantum computers, an initial requirement is to create so-called quantum ...
Rediscovery of the 'extinct' Pinatubo volcano mouse
2021-01-22
In June 1991, Mount Pinatubo, a volcanic peak on the Philippine Island of Luzon, literally blew its top. It was the second-most powerful volcanic eruption of the 20th century, ten times stronger than Mount Saint Helens, and its effects were devastating. Lava and ash spewed into the surrounding environment in the Zambales Mountains, pooling in layers up to 600 feet thick in the valleys. Following the eruption, powerful typhoons and monsoon rains triggered landslides and ash flows that continued for many months. Eight hundred people lost their lives, and the lush forests that covered the mountain prior to the eruption were destroyed or severely damaged. In recent years, scientists returned to the region to survey the surviving mammal populations, and in a new paper in the ...
Massey researchers review geographic factors that affect HPV vaccination rates
2021-01-22
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection, with an estimated 79 million Americans currently infected with the virus, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If a high-risk HPV infection does not go away, it can lead to the development of a variety of cancers, including 91% of all cervical cancers, 70% of oropharyngeal cancers and cancers of the vulva, vagina, penis and anus.
HPV vaccination can significantly reduce the number of new cancer diagnoses linked to the virus, in addition to preventing a number of other health complications.
"Given ...
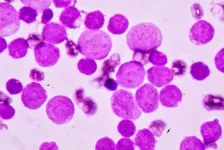
New maintenance treatment for acute myeloid leukemia prolongs the lives of patients
2021-01-22
Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the most common form of acute leukemia in adults, that has gone into remission following initial chemotherapy remain in remission longer and have improved overall survival when they are given a pill form of the cancer drug azacitidine as a maintenance treatment, according to a randomized, international phase 3 clinical trial for which Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian are trial sites. This is the first time a maintenance treatment for AML has shown such a strong benefit for patients, and it is already being adopted as part of standard care.
The results, which were published Dec. 24 in the New England Journal of Medicine, led to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's approval in September 2020 of oral ...
NIH-funded study examines mono, chronic fatigue syndrome in college students
2021-01-22
Many college students fully recover from infectious mononucleosis (which is almost always caused by Epstein-Barr virus) within 1-6 weeks, but some go on to develop chronic fatigue syndrome, also called myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME/CFS). A longitudinal study from DePaul University and Northwestern University followed 4,501 college students to examine risk factors that may trigger longer illness. The research appears in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases and was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Previous retrospective studies found that risk factors ...
Ageing dams pose growing threat: UN
2021-01-22
By 2050, most people on Earth will live downstream of tens of thousands of large dams built in the 20th century, many of them already operating at or beyond their design life, according to a UN University analysis.
The report, "Ageing water infrastructure: An emerging global risk," by UNU's Canadian-based Institute for Water, Environment and Health, says most of the 58,700 large dams worldwide were constructed between 1930 and 1970 with a design life of 50 to 100 years, adding that at 50 years a large concrete dam "would most probably begin to express signs of aging."
Ageing ...
Scientists improved eye tracking technology in VR systems
2021-01-22
The tracking of eye movement is one of the key elements of virtual and amplified reality technologies (VR/AR). A team from MSU together with a professor from RUDN University developed a mathematical model that helps accurately predict the next gaze fixation point and reduces the inaccuracy caused by blinking. The model would make VR/AR systems more realistic and sensitive to user actions. The results of the study were published in the SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers.
Foveated rendering is a basic technology of VR systems. When a person looks at something, their gaze is focused on the so-called foveated region, and everything else is covered by peripheral vision. Therefore, a computer has to render the images in the ...
Depression in new fathers connected to relationship insecurities
2021-01-22
Becoming a parent often brings great joy, but not always. Parenthood also entails challenges, stress and, for some people, it can trigger depression. A new study from Lund University in Sweden shows that male postnatal depression is more common in men who are insecure in their relationship with their partner.
Depression affects around 10-12 per cent of new mothers, and at least 8 per cent of new fathers. The figures are even higher when looking at depressive symptoms; as many as one in five new fathers experience troublesome symptoms, according to the new study conducted by Elia Psouni, registered psychologist and associate professor of ...
Potential combined drug therapy for lung cancer
2021-01-22
Most lung cancers are of a type called non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). This type of cancer is relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, so NSCLC therapies are usually based on drug treatment. Alectinib is a drug commonly used for treating patients with NSCLC. It addresses a gene rearrangement known as ALK that occurs in 3 to 5% of NSCLC patients (alectinib belongs to a class of drugs called ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors). It has been unclear, however, whether there is a correlation between the use of alectinib and the poorer prognosis in ALK-NSCLC patients in which secondary cancer mutations ...
Single atoms as a catalyst: Surprising effects ensue
2021-01-22
Metals such as gold or platinum are often used as catalysts. In the catalytic converters of vehicles, for example, platinum nanoparticles convert poisonous carbon monoxide into non-toxic CO2. Because platinum and other catalytically active metals are expensive and rare, the nanoparticles involved have been made smaller and smaller over time.
"Single-atom" catalysts are the logical end point of this downsizing: The metal is no longer present as particles, but as individual atoms that are anchored on the surface of a cheaper support material. Individual atoms can no longer be described using the rules developed from larger pieces of metal, so the rules used to predict which metals will ...
A study explores the alteration of the functional dynamics of the human brain associated with ageing
2021-01-22
Normal ageing causes disruptions in the brain that can lead to cognitive decline. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging studies have found significant age-related alterations in functional connectivity across various networks. However, most of the studies have focused primarily on static functional connectivity.
The authors of a recent study published in Cerebral Cortex based their research on the idea that studying the dynamics of resting-state brain activity across the whole-brain functional network can provide a better characterization of age-related changes.
The study was led by Gustavo Deco, director of the Center for Brain and Cognition (CBC) and ICREA research professor at the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), and Anira ...
Chimpanzee friends fight together to battle rivals
2021-01-22
Chimpanzees, one of the closest relatives of humans, cooperate on a group level - in combative disputes, they even cooperate with group members to whom they are not related. Those involved in fights with neighbouring groups put themselves at risk of serious injury or even death.
Within the context of the Tai Chimpanzee Project researchers observed three chimpanzee communities in Tai National Park in Cote d'Ivoire documenting social relationships, territory range and intergroup encounters amongst others. "We have been able to analyze almost 500 vocal and physical battles from the last 25 years with participation of at least one ...
Flowery diets help predatory insects help farmers keep pests in check
2021-01-22
Good news for the green transition: Flowery diets help predatory insects help farmers keep pests in check
Predatory insects have been shown to live longer when they have access to nectar and pollen, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Copenhagen. Thus, flowers don't just benefit insects, they help farmers farm sustainably. Predatory insects are skilled pest controllers whose hunting reduces the need for agricultural pesticides.
Until now, it was believed that predatory insects needed prey to survive. But in a systematic review conducted at the University ...
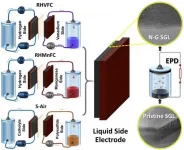
Highly efficient grid-scale electricity storage at fifth of cost
2021-01-22
Researchers in WMG at the University of Warwick, in collaboration with Imperial College London, have found a way to enhance hybrid flow batteries and their commercial use. The new approach can store electricity in these batteries for very long durations for about a fifth the price of current technologies, with minimal location restraints and zero emissions.
The researchers enhanced three hybrid flow cells using nitrogen doped graphene (exposed to nitrogen plasma) in a binder-free electrophoresis technique (EPD).
Wind and solar power are increasingly popular sources for renewable energy. Unfortunately, intermittency issues keep them ...
Fungi strengthen plants to fend off aphids
2021-01-22
GREEN TRANSITION Researchers at the University of Copenhagen have demonstrated that unique fungi strengthen the "immune systems" of wheat and bean plants against aphids. Fungi enter and influence the amount of a plant's own defences, resulting in fewer aphids. The results could serve to reduce agricultural insecticide use and bring Denmark a step further along the path towards its green transition.
Wheat field
Certain fungi are able to establish a close rapport with plants that results in fewer insect infestations and thereby less damage to crops. Until now, it was unclear how these fungi could be used to reduce insect infestations.
"In order for us to really use fungi ...
Addressing the impact of structural racism on disparities in children with Type 1 diabetes
2021-01-22
PHILADELPHIA, PA (January 22, 2021) - Advancements in diabetes technology have improved quality of life and glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes. However, data show that a subset of children is being left behind. Those from low-income families and non-Hispanic Black (NHB) children are not experiencing benefits associated with technological advances, and are at higher risk for diabetes complications and adverse outcomes through ongoing poor glycemic control.
In an invited commentary to be published in the journal Diabetes Care, researchers describe how socioeconomic disparities ...
Novel target identified that could improve safety of therapy for pancreatic cancer
2021-01-22
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London, have identified a protein that may represent a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Using this protein as a target, the team successfully created a CAR T cell therapy - a type of immunotherapy - that killed pancreatic cancer cells in a pre-clinical model.
CAR T cell therapy is an immunotherapy that has shown great promise for the treatment of some blood cancers; however, the treatment of solid tumours using this therapy has proved very difficult. One barrier to success is toxicity in tissues other than the cancer because most of the proteins currently used to target CAR T cells to pancreatic cancer cells and other solid tumours are present in low levels on other normal tissues, ...
Reducing traps increases performance of organic photodetectors
2021-01-22
Organic photodetectors (OPDs) have a huge potential for applications in low-cost imaging, health monitoring and near infrared sensing. Yet, before industrially realizing these applications, the performance of these devices still needs to be improved.
Recent research on organic photodetectors based on donor-acceptor systems has resulted in narrow-band, flexible and biocompatible devices, of which the best reach external photovoltaic quantum efficiencies of close to 100%. However, the high noise in the off state produced by these devices limits their specific detectivity, severely reducing the performance, for example ...
University of Cincinnati student uses zebrafish to study spinal deformities
2021-01-22
Popular in aquariums all over the world, the zebrafish is native to South Asia. But here in a Cincinnati Children's laboratory, the freshwater variant plays a vital role in scientific discovery.
The iconic stripes are eye-catching but it's the transparency of zebrafish embryonic tissue which are most prized by researchers like Oriana Zinani, a fifth-year doctoral student in molecular developmental biology in the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine. The patterning of the zebrafish's spine gives the appearance of stripes; it is controlled by ...
New perspectives challenge the idea that saturated fats cause heart disease
2021-01-22
In science, sometimes a new perspective can turn our interpretation of the data upside-down, and necessitate a paradigm shift.
There has been, and continues to be, fierce disagreements in nutrition science as to what constitutes a healthy diet. A key controversy is the role of saturated fats in health and disease. Saturated fats are known to increase blood cholesterol levels, and increased blood cholesterol is often observed in people who develop cardiovascular disease.
It has been thought for more than half a century that saturated fats in the diet promote heart disease by increasing blood cholesterol. However, a new model explains why this so-called "diet-heart hypothesis", which ...
Highly functional membrane developed for producing freshwater from seawater
2021-01-22
Professor MATSUYAMA Hideto's research group at Kobe University's Research Center for Membrane and Film Technology has successfully developed a new desalination membrane. They achieved this by laminating a two-dimensional carbon material (*1) on to the surface of a porous polymer membrane (*2).
Desalination (*3) membranes are used to produce freshwater from seawater. In order to solve the worldwide issue of insufficient freshwater resources, researchers are striving to develop desalination membranes that are not only permeated by water faster than those currently in use but also remove salt efficiently, so that more effective, low-energy desalination systems can be implemented.
In this research study, graphene oxide (*4) nanosheets, which ...
Defects may help scientists understand the exotic physics of topology
2021-01-22
Real-world materials are usually messier than the idealized scenarios found in textbooks. Imperfections can add complications and even limit a material's usefulness. To get around this, scientists routinely strive to remove defects and dirt entirely, pushing materials closer to perfection. Now, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have turned this problem around and shown that for some materials defects could act as a probe for interesting physics, rather than a nuisance.
The team, led by professors Gaurav Bahl and Taylor Hughes, studied artificial materials, or metamaterials, which they engineered to include defects. The team used these customizable circuits as a proxy for studying exotic topological crystals, which are often ...
Making protein 'superfood' from marine algae
2021-01-22
Marine microalgae-based cellular agriculture is a promising new way to sustainably produce plant-based 'meat' and healthy 'superfoods' for the future.
Researchers at Flinders University's Centre for Marine Bioproducts Development (CMBD) in Australia are responding to growing interest from consumers looking for healthier, more environmentally friendly, sustainable and ethical alternatives to animal proteins.
Marine microalgae, single-cell photosynthetic organisms from the ocean could be the solution to the world's meat protein shortage, says CMBD director Flinders University Professor Wei Zhang, who is also co-leading a bid to establish a national Marine Bioproducts Cooperative Research Centre ...
Study recommends rugby league invests in young players' diets
2021-01-22
Young rugby league players could benefit from individualised nutrition plans to maximise performance and optimise recovery throughout their careers, according to QUT researchers.
The new study, published in the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, provides nutritional recommendations and considers potential supplements to improve players' physical capacity, health and recovery during the preparatory and competition phases of a season.
Lead researcher, Associate Professor Vince Kelly from QUT's Faculty of Health's Exercise and Nutrition Sciences, is a committee member of the National Rugby League Research Committee and has more than 20 years' experience in elite sport.
"Young players don't have the same access to dietary support as professional ...
Targeted coating improves graphene oxide membranes for nanofiltration
2021-01-22
Nanofiltration (NF) is an advanced technology for treating wastewater containing organic micropollutants (OMPs).
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a stable graphene oxide nanofiltration membrane with uniform pore size to remove OMPs.
The study was published in Chemical Engineering Journal on Jan. 20.
It proposes combining signal amplification strategy and defect chemistry to reduce membrane pore size distribution, thus offering a promising method for preparing highly ...
[1] ... [2722]
[2723]
[2724]
[2725]
[2726]
[2727]
[2728]
[2729]
2730
[2731]
[2732]
[2733]
[2734]
[2735]
[2736]
[2737]
[2738]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.