Could "Power Walking" fuel the energy revolution? India is ready to step up
2021-01-19
India has an energy problem. It currently relies heavily on coal and consumer demand is expected to double by 2040, making its green energy targets look out of reach. Part of the solution could come from harvesting energy from footsteps, say Hari Anand and Binod Kumar Singh from the University of Petroleum and Energy Studies in Dehradun, India. Their new study, published in the De Gruyter journal Energy Harvesting and Systems, shows that Indian attitudes towards power generated through piezoelectric tiles are overwhelmingly positive.
Cities like Delhi and Mumbai are famously crowded, especially at railway stations, temples and big commercial buildings. This led researchers to wonder whether piezoelectric tiles, which produce ...
Scientists present novel approach for monitoring freshwater health
2021-01-19
Researchers have used the world's smallest, smartphone-sized DNA sequencing device to monitor hundreds of different bacteria in a river ecosystem.
Writing in the journal eLife, the interdisciplinary team from the University of Cambridge, UK, provide practical and analytical guidelines for using the device, called the MinION (from Oxford Nanopore Technologies), to monitor freshwater health. Their guidelines promise a significantly more cost-effective and simple approach to this work outside the lab, compared to existing methods.
Rowers and swimmers in Cambridge are regularly affected by waterborne infections such as Weil's disease, sometimes leading to public closures of the city's iconic waterways. Monitoring the microbial species in freshwater ...
Automakers delay recalls to minimize stock penalties, avoid being the first safety issue in news
2021-01-19
Whether consciously or unconsciously, automotive firms time their product recalls to minimize stock price penalties, resulting in unnecessary delays and clusters of subsequent recalls by other companies, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame.
An initial recall by one firm prompts clusters of additional recalls in close proximity by competitor firms, according to "Hiding in the Herd: The Product Recall Clustering Phenomenon," forthcoming in Manufacturing and Service Operations Management from Kaitlin Wowak, assistant professor of IT, analytics, and operations at Notre Dame's Mendoza College of Business.
According to the study, "Automobile recalls seem to be announced after inexplicable delays. Toyota's unintended acceleration recall and General ...
Mental health conditions alarmingly high among children with autism
2021-01-19
Nearly 78 per cent of children with autism have at least one mental health condition and nearly half have two mental health conditions or more, according to a new U.S. study from the University of British Columbia's department of psychology and the AJ Drexel Autism Institute at Drexel University (Pennsylvania).
The study also found mental health conditions present in 44.8 per cent of pre-school age children with autism. The scope of the issue among that age group had not previously been established using a large, population-based sample.
By contrast, the study found that only 14.1 per cent of youth without autism (ages 3-17) had mental health conditions.
It is the first research since 2008 to examine the prevalence of mental health conditions among children with autism at a population ...
ALS study reveals a unique population
2021-01-19
Malta, a sovereign microstate in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, has no shortage of sunny beaches, honey-bricked villages and rugged countryside. Beyond its Mediterranean charm, Malta is home to a geographically and culturally isolated population whose unique genetic makeup, makes this island nation a goldmine for genetics research.
Four years ago, the University of Malta set up a national ALS Registry and Biobank to identify patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and collect data on their residence, occupation, lifestyle and environmental exposures. Blood samples ...
Online courses reinforce inequalities
2021-01-19
With the global student community taking online courses as a result of the anti-Covid-19 measures, a study led by the University of Geneva (UNIGE) reveals that online courses deepen inequalities between gifted and less gifted students by 5%. The results of the study, which was based on data collected in 2016-2017 prior to the anti-Covid lockdown initiatives, are published in the Journal of the European Economic Association. They indicate that this learning gap between different student profiles is mainly due to their behaviour and motivation. The study gives higher education establishments worldwide practical ways to deal with lockdown or the chronic lack of space in lecture theatres, including via co-educational ...
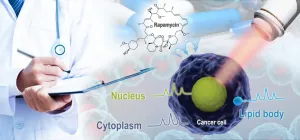
Single-cell test can reveal precisely how drugs kill cancer cells
2021-01-19
Cancer cells are smart when it comes to anti-cancer drugs, evolving and becoming resistant to even the strongest chemotherapies over time. To combat this evasive behavior, researchers have developed a method named D2O-probed CANcer Susceptibility Test Ramanometry (D2O-CANST-R) to see, at single-cell/organelle level, how pharmaceuticals induce cancer cell death and how cancer cells adapt.
The research, conducted by the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), was published on Jan. 12 in Analytical Chemistry, ...
Prenatal BPA exposure may contribute to the male bias of autism spectrum disorder
2021-01-19
A new study by researchers from Chulalongkorn University, Tohoku University, and The George Washington University is the first to identify autism candidate genes that may be responsible for the sex-specific effects of bisphenol A (BPA) on the brain. It suggests BPA may serve as an environmental factor that contributes to the prevalence of male bias in autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
The research was published in the journal Scientific Reports.
BPA is widely used in many products in our daily life and abundant in micro/nanoplastics found in the environment, ...
Ultra-small nanomedicines which stably deliver oligonucleotides to refractory cancers
2021-01-19
Summary
Ultra-small nanomedicines of approximately 18 nm were fabricated by dynamic ion-pairing between Y-shaped block copolymers and nucleic acid drugs, such as siRNA and antisense drugs.
Chemically modified and double-stranded oligonucleotides dramatically enhanced the stability of the ultra-small nanomedicines in the blood circulation.
The ultra-small size allows for high permeability in cancer tissues by slipping through the cracks in tumor vasculatures and stromal tissues.
Clinical trials and preclinical studies using the developed ultra-small nanomedicines are proceeding for cancer therapy.
Published in the website of Journal of Controlled Release on January 6.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.01.001
Main body
January 19, 2021 - Kawasaki in ...
How drain flies dodge a washout
2021-01-19
The survival of pesky little flies in showers and other wet areas around the house, impervious to water droplets that may be larger than they are, comes down to more than quick reflexes. The insects have evolved a unique coating of hairs that allows them to shrug off water droplets of almost any size, KAUST researchers have shown.
Sigurdur Thoroddsen, who leads the high-speed fluids imaging laboratory at KAUST, couldn't help but take a professional interest in the small drain flies that made a home in his shower and never seemed to wash away. Thoroddsen's research focuses on multiphase flow and dynamics at air-liquid interfaces -- an environment where drain flies have found a niche, despite some risky physics.
Insects are so small that the surface tension of ...
Solar activity reconstructed over a millennium
2021-01-19
What goes on in the sun can only be observed indirectly. Sunspots, for instance, reveal the degree of solar activity - the more sunspots are visible on the surface of the sun, the more active is our central star deep inside. Even though sunspots have been known since antiquity, they have only been documented in detail since the invention of the telescope around 400 years ago. Thanks to that, we now know that the number of spots varies in regular eleven-year cycles and that, moreover, there are long-lasting periods of strong and weak solar activity, which is also reflected in the climate on Earth.
However, how solar activity developed before the start of systematic records has so far been ...
New biodegradable polyurethane foams are developed from wheat straw
2021-01-19
Every year around 734 million tons of wheat straw are produced worldwide, a large amount of waste, which is cheap and has had no well-defined use until now. Recently, the RNM-271 Chemical Engineering and FQM-383 NANOVAL Organic Chemistry research groups at the University of Córdoba have been able to give a new use to this agricultural excess material, by using it as the foundation in order to manufacture polyurethane foams.
Also known as foam rubber, this plastic material, often manufactured from petroleum by-products, is extremely versatile within the industry and has multiple uses in the construction and automobile sectors as a sealant as well as ...
Clocking electron movements inside an atom
2021-01-19
An international consortium of scientists, initiated by Reinhard Kienberger, Professor of Laser and X-ray Physics at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), several years ago, has made significant measurements in the femtosecond range at the U.S. Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC).
However, on these miniscule timescales, it is extremely difficult to synchronize the X-ray pulse that sparks a reaction in the sample on the one hand and the laser pulse which 'observes' it on the other. This problem is called timing jitter, and it is a major hurdle in ongoing ...
New method heals skeletal injuries with synthetic bone
2021-01-19
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden, in collaboration with colleagues in Dresden, Germany, have developed a way of combining a bone substitute and drugs to regenerate bone and heal severe fractures in the thigh or shin bone. The study, published in the research journal Science Advances, was conducted on rats, but the researchers think that the method in various combinations will soon be commonplace in clinical settings.
"The drugs and materials we used in the study for the regeneration of bone are already approved. We simply packaged them in a new combination. Therefore, there are no real obstacles to already using the method in clinical studies for certain major bone defects that are difficult to resolve in patients. But we want to ...
A sea of rubbish: ocean floor landfills
2021-01-19
The Messina Strait, a submarine bridge separating the island of Sicily from the Italian Peninsula, is the area with the largest marine litter density worldwide -more than a million objects per square kilometre in some parts-, as reported in a new review paper published in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
Also, over the next thirty years, the volume of rubbish in the sea could surpass three billion metric tons (Mt), as cited in the study, whose corresponding authors are the experts Miquel Canals, from the Faculty of Earth Sciences of the University of Barcelona, and Georg Hanke from the European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC), where ...
Rescuers at risk: emergency personnel face trauma and post traumatic stress symptoms
2021-01-19
A new study in Frontiers in Psychiatry has for the first time, demonstrated differences in the prevalence of post-traumatic stress symptoms (PTSS) in different groups of rescue workers and emergency personnel, including firefighters, police officers and psychiatric nurses. The researchers showed that the varying experiences and circumstances these workers encounter, such as handling aggressive people, working with families or dealing with deaths and suicide, are tied to varying levels of PTSS and suicidal thoughts, with emergency department staff and psychiatric nurses showing the highest levels of PTSS and suicidal thoughts out of the emergency professions studied. The findings highlight the urgent need for bespoke training and counselling services ...
Aphids suck: Invasive aphid found on Danish apple trees
2021-01-19
INSECTS The spirea aphid, Aphis spiraecola, an invasive pest, has been discovered for the first time in Denmark by University of Copenhagen researchers. The extent of its current distribution remains unknown, but in time, it could prove to be a troublesome pest for Danish apple growers.
Aphis
Whether the discovery of this aphid in Denmark is an isolated incident, or if the species has made itself at home due to a milder climate, remains unknown to the researchers. Closer investigation is needed. Photo: UCPH/Uni.Budapest
In a collaboration with colleagues at the University of Budapest, University of Copenhagen researchers have analysed and compared a number of samples of green aphids from apples around ...
Psychological well-being declined during second wave of the pandemic - especially for men
2021-01-19
The psychological well-being of both men and women declined when Denmark closed down during the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic in the spring of 2020 - with women being hit the hardest. But during the second wave, it is the other way round in terms of gender: The psychological well-being of men and women is generally low, but it has fallen most in men.
This is shown in a survey conducted by Søren Dinesen Østergaard, among others. He is professor at the Department of Clinical Medicine and affiliated with the Department of Affective Disorders at Aarhus University Hospital - Psychiatry in Denmark.
The survey is the latest of three assessments of Danes' psychological well-being ...
Improving long-term climate calculations
2021-01-19
Climate researchers have found a simple but efficient way to improve estimations of ultimate global warming from complex climate models. The finding is relevant for the evaluation and comparison of climate models and thus for accurate projections of future climate change - especially beyond the year 2100. The study is published in Geophysical Research Letters by Dr. Robbin Bastiaansen and colleagues at the Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Research Utrecht, Utrecht University, The Netherlands. The work is part of the European TiPES project coordinated by the University of Copenhagen, Denmark.
Complex climate models are rarely used to simulate the effect of global warming for a given amount of CO2 beyond a couple of centuries into the future. ...
Broadening horizons for people with quadriplegia
2021-01-19
A system that uses flexible, breathable magnetic skin allows people with severe quadriplegia to move around and choose their surroundings. Developed by KAUST researchers, the high-tech system relies on the user's facial expressions to accomplish a wide variety of tasks, from moving down the street to using an elevator.
There are a wide variety of assistive technologies for people with quadriplegia, but most systems are not suitable for patients with severe quadriplegia as they often rely on head or neck movements to work. For these patients, the options are limited to camera, tongue control, voice-assistant and neural detector systems. But these either offer a limited range of gestures or are not compatible with outdoor applications. Some also require invasive attachments or ...
Naltrexone use decreases the risk of hospitalization in persons with alcohol use disorder
2021-01-19
Naltrexone, used either alone or together with disulfiram or acamprosate, is associated with a decreased risk of hospitalization due to alcohol use disorder (AUD) when compared with non-use of AUD drugs, a new register-based study shows. The same associations were noticed for hospitalization due to any cause. Disulfiram use and polytherapy with two or more drugs indicated for AUD was associated with a decreased risk of hospitalization due to alcohol-related somatic causes. None of the studied medications were associated with mortality or work disability (sickness absence or disability pension). The study was published in Addiction.
Benzodiazepine use linked to harmful effects
As benzodiazepine use is common among persons with AUD, the ...
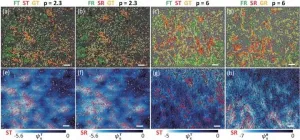
What stops flows in glassy materials?
2021-01-19
Various glass materials have been essential to the development of modern civilization due to their advantageous properties. Specifically, glasses have a liquid-like disordered structure but solid-like mechanical properties. This leads to one of the central mysteries of glasses: "Why don't glasses flow like liquids?" This question is so important that it was selected by the journal Science in 2005 as one of 125 key, unanswered scientific questions, and one of 11 unsolved important physical issues.
We can hardly observe the movements of atoms at a ~0.1 nanometer length scale and a ~1 ...
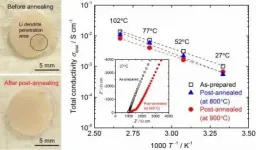
Healing ceramic electrolyte degraded by Li dendrite
2021-01-19
Overview:
A research team in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology and the Department of Chemistry at University of Calgary has investigated the effect of post-annealing for healing Li garnet solid electrolyte degraded by the growth of Li dendrites. The ionic conductivity of the annealed solid electrolyte was slightly lower than that of the electrolyte before annealing but was retained above 10?4 S cm?1 at room temperature. The electrochemical results obtained indicate the possibility of reusing the solid electrolyte degraded by the growth of Li dendrites in another all-solid-state Li battery.
Details:
A ...
Proposing a new drug to treat tuberculosis utilizing state-of-the-art computer simulations
2021-01-19
Overview:
The research team of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at the Toyohashi University of Technology and the Institute of Food Biotechnology and Genomics at the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine have proposed a new drug to treat tuberculosis (TB), utilizing the state-of-the-art molecular simulations. This drug may inhibit the cell division of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) and suppress its growth. In addition, because this drug acts on the enzymes secreted by M. tuberculosis instead of acting on M. tuberculosis itself, M. tuberculosis ...
Sensei RNA: Iron fist in a velvet glove
2021-01-19
"The real voyage of discovery consists not in seeking new landscapes, but in having new eyes."
Scientists would vouch for this statement because scientific pursuit has the habit of offering chance discoveries if we think about things differently.
In the lab of Arati Ramesh at the NCBS, the team loves to spy on the structure and sequence of Ribonucleic acids (RNAs; molecules that decrypt an organism's genetic code into protein messages). During one such instance, graduate students in Arati's lab were peering at a family of nickel and cobalt (NiCo RNAs) sensing bacterial RNAs that have a clover leaf-like structure. ...
[1] ... [2726]
[2727]
[2728]
[2729]
[2730]
[2731]
[2732]
[2733]
2734
[2735]
[2736]
[2737]
[2738]
[2739]
[2740]
[2741]
[2742]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.