Consent forms design influences patient willingness to share personal health information
2021-01-12
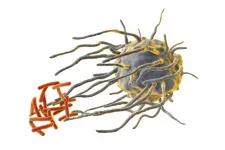
Patients are sometimes asked to share their personal health information for research purposes. Informed consent and trust are critical components in a patient's decision to participate in research. Researchers at the University of Florida conducted a three-arm randomized controlled trial to compare the effects on patient experiences of three electronic consent (e-consent) designs that asked them to share PHI for research purposes. Participants were randomized to a standard e-consent form (standard); an e-consent that contained standard information plus hyperlinks to additional interactive details (interactive); or an e-consent that contained standard information, interactive hyperlinks, and factual ...
No-till practices in vulnerable areas significantly reduce soil erosion
2021-01-12
URBANA, Ill. - Soil erosion is a major challenge in agricultural production. It affects soil quality and carries nutrient sediments that pollute waterways. While soil erosion is a naturally occurring process, agricultural activities such as conventional tilling exacerbate it. Farmers implementing no-till practices can significantly reduce soil erosion rates, a new University of Illinois study shows.
Completely shifting to no-till would reduce soil loss and sediment yield by more than 70%, says Sanghyun Lee, doctoral student in the Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering at U of I and lead author on the study, published in Journal of Environmental Management.
But even a partial change in tilling practices could have significant results, he adds.
"If we ...
New study examines medical practice patterns over time
2021-01-12
Harmful medical practices, like inappropriate prescribing of opioids and racial and income-based discrimination in clinical settings, can vary across medical practices and individuals. Patients may find that even common primary care health services, like getting a chest x-rays or a referral to a heart or lung specialist, can differ widely depending on your doctor or clinic location. These variations in medical practice can have serious consequences for the quality, equity and cost of one's health care; however, it's unclear whether these disparities can be attributed to individual differences, from one ...
Researchers speed up analysis of Arctic ice and snow data through AI
2021-01-12
Researchers at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) have developed a technique to more quickly analyze extensive data from Arctic ice sheets in order to gain insight and useful knowledge on patterns and trends. Over the years, vast amounts of data have been collected about the Arctic and Antarctic ice. These data are essential for scientists and policymakers seeking to understand climate change and the current trend of melting. Masoud Yari, research assistant professor, and Maryam Rahnemoonfar, associate professor of information systems, have utilized new AI technology to develop a fully automatic technique to analyze ice data, published in the Journal ...
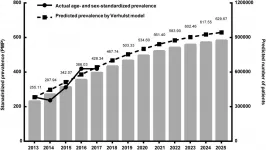
Prevalence of patients receiving dialysis in China may exceed 800,000 by 2025
2021-01-12
Study published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD) projects that prevalence of patients receiving dialysis in China will increase from 384.4 patients per million (PPM) in 2017 to 629.7 PMP in 2025 with a predicted 874,373 patients receiving dialysis in 2025.
The national prevalence of dialysis in China has not been well studied due to its large population and limited resources. Insurance claims data provide a unique opportunity to understand the burden of kidney failure and have been used to characterize dialysis patients in the ...
Metabolism may play role in recurrent major depression
2021-01-12
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, in collaboration with Dutch scientists, have found that certain metabolites -- small molecules produced by the process of metabolism -- may be predictive indicators for persons at risk for recurrent major depressive disorder.
The findings were published in the January 11, 2021 online issue of Translational Psychiatry.
"This is evidence for a mitochondrial nexus at the heart of depression," said senior author Robert K. Naviaux, MD, PhD, professor of medicine, pediatrics and pathology at UC San Diego School of Medicine. "It's a small study, but it is the first to show the potential of using metabolic ...
CDC report: removing unnecessary medical barriers to contraception
2021-01-12
New Rochelle, NY, January 12, 2021--The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is committed to removing unnecessary medical barriers to contraception use by people with certain characteristics or medical conditions. The CDC is celebrating the 10th anniversary of the release of its U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use (MEC), with an exclusive article published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women's Health. Click here to read the article now.
The CDC has updated the MEC recommendations over the past decade based on new evidence. It has collaborated with national partners to disseminate and implement the guidelines and has conducted surveys of health ...
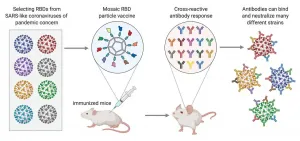
Nanoparticle immunization technology could protect against many strains of coronaviruses
2021-01-12
The SARS-CoV-2 virus that is causing the COVID-19 pandemic is just one of many different viruses in the coronavirus family. Many of these are circulating in populations of animals like bats and have the potential to "jump" into the human population, just as SARS-CoV-2 did. Researchers in the laboratory of Pamela Björkman, the David Baltimore Professor of Biology and Bioengineering, are working on developing vaccines for a wide range of related coronaviruses, with the aim of preventing future pandemics.
Now, led by graduate student Alex Cohen, a Caltech ...
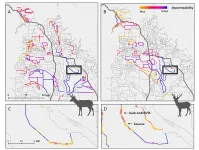
New study reveals how fences hinder migratory wildlife in the West
2021-01-12
Berkeley -- Each year, thousands of migratory mule deer and pronghorn antelope journey northwest from their winter homes in the Green River Basin, a grassland valley in western Wyoming, to their summer homes in the mountainous landscape near Grand Teton National Park.
But to reach their destination, these ungulates must successfully navigate the more than 6,000 kilometers (3,728 miles) of fencing that crisscrosses the region. That's enough distance to span nearly twice the length of the U.S.-Mexico border.
In a new study, wildlife biologists at the University of California, Berkeley, combined GPS location data of tagged mule deer and pronghorn with satellite imagery of ...
Hunters and busybodies: Researchers use Wikipedia to measure different types of curiosity
2021-01-12
Curiosity has been found to play a role in our learning and emotional well-being, but due to the open-ended nature of how curiosity is actually practiced, measuring it is challenging. Psychological studies have attempted to gauge participants' curiosity through their engagement in specific activities, such as asking questions, playing trivia games, and gossiping. However, such methods focus on quantifying a person's curiosity rather than understanding the different ways it can be expressed.
Efforts to better understand what curiosity actually looks like for different people have underappreciated roots in the field of philosophy. Varying styles have been described with loose ...
Beating the 'billion-dollar bug' is a shared burden
2021-01-12
A lurking threat that has stymied US corn growers for decades is now returning to the forefront: western corn rootworm. Sometimes referred to as the "billion-dollar bug," the species' tiny larvae chew through the roots of corn plants, causing devastating yield losses. In 2003, farmers began planting a genetically engineered variety of corn known as "Bt," which produces a protein toxic to the pest species - but by 2009, the billion-dollar bug had already evolved adaptations for resistance to the toxin.
A new study suggests that slowing the resurgence of western corn rootworm may require a larger-scale strategy than previously thought. The findings, ...
Mechanisms in the kidney that control magnesium and calcium levels discovered
2021-01-12
BOSTON - While investigating the underlying causes of a rare skin disorder, a researcher at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) discovered a previously unknown mechanism in the kidneys that is important for regulating levels of magnesium and calcium in the blood.
The discovery, described in the journal Cell Reports, highlights the role of a previously little-studied gene called KCTD1. The gene directs production of a protein that regulates the kidney's ability to reabsorb magnesium and calcium from urine and return it to the bloodstream.
A genetic mutation causing the loss of KCTD1 results in defects in nephrons, ...
'Old Faithful' cosmic eruption shows black hole ripping at star
2021-01-12
You've heard of Old Faithful, the Yellowstone National Park geyser that erupts every hour or two, a geological phenomenon on a nearly predictable schedule.
Now, an international group of scientists who study space have discovered an astronomical "Old Faithful" - an eruption of light flashing about once every 114 days on a nearly predictable schedule. The researchers believe it is a tidal disruption event, a phenomenon that happens when a star gets so close to a black hole that the black hole "rips" away pieces of the star, causing the flare.
The team made the discovery using data from NASA and from a network of telescopes operated by The Ohio State University.
Their findings, presented today at the Astronomical Society's annual meeting and accepted for publication ...
New method helps pocket-sized DNA sequencer achieve near-perfect accuracy
2021-01-12
Researchers have found a simple way to eliminate almost all sequencing errors produced by a widely used portable DNA sequencer, potentially enabling scientists working outside the lab to study and track microorganisms like the SARS-CoV-2 virus more efficiently.
Using special molecular tags, the team was able to reduce the five-to-15 per cent error rate of Oxford Nanopore Technologies' MinION device to less than 0.005 per cent -- even when sequencing many long stretches of DNA at a time.
"The MinION has revolutionized the field of genomics by freeing DNA sequencing from the confines of large laboratories," says Ryan Ziels, an ...
Gene-editing produces tenfold increase in superbug slaying antibiotics
2021-01-12
Scientists have used gene-editing advances to achieve a tenfold increase in the production of super-bug targeting formicamycin antibiotics.
The John Innes Centre researchers used the technology to create a new strain of Streptomyces formicae bacteria which over-produces the medically promising molecules.
Discovered within the last ten years, formicamycins have great potential because, under laboratory conditions, superbugs like MRSA do not become resistant to them.
However, Streptomyces formicae only produce the antibiotics in small quantities. This has made it difficult to scale up ...
DNA in water used to uncover genes of invasive fish
2021-01-12
ITHACA, NY - Invasive round goby fish have impacted fisheries in the Great Lakes and the Finger Lakes by competing with native species and eating the eggs of some species of game fish.
But the camouflaged bottom dwellers can be difficult to find and collect - especially when they first enter a new body of water and their numbers are low and they might be easier to remove.
In a proof-of-principle study, Cornell researchers describe a new technique in which they analyzed environmental DNA - or eDNA - from water samples in Cayuga Lake to gather nuanced information about the presence of these invasive fish.
The study, "Nuclear eDNA Estimates Population Allele Frequencies and Abundance in Experimental Mesocosms and Field Samples," was ...
First-degree relative with kidney disease increases disease risk by three-fold
2021-01-12
In a large population-based family study, family history of kidney disease was strongly associated with increased risk of chronic kidney disease.
In this large population-based family study recently published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases, researchers investigated the familial aggregation of CKD by comparing the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in individuals with an affected first-degree relative to that in the general population. Participants with an affected first-degree relative were observed to have a threefold higher risk of CKD compared to that in the general population, independent of BMI, hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, history of cardiovascular disease (CVD), and smoking status. ...
Is the COVID-19 vaccine safe for nursing mothers?
2021-01-12
New Rochelle, NY, January 12, 2021--The Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine (ABM) does not recommend cessation of breastfeeding for individuals who are vaccinated against COVID-19. In a new statement, the ABM suggests that lactating women discuss the risks and benefits of vaccination with their health care provider, within the context of their risk of contracting COVID-19 and of developing severe disease, according to the peer-reviewed journal Breastfeeding Medicine. Click here to read the ABM statement now.
This is a challenging topic because the vaccine trials excluded lactating women. Thus, there are no clinical data regarding the safety ...
Killing cancer by unleashing the body's own immune system
2021-01-12
The body's immune system is the first line of defense against infections like bacteria, viruses or cancers. Some cancers, however, have developed the art of molecular deception to avoid destruction by the body's immune system. However, a University of Missouri researcher might have found a new way to help the body's immune system get past that deception and destroy the cancer.
"Normally, your body's immune cells are constantly on patrol to identify and destroy foreign entities in the body," said Yves Chabu, an assistant professor in the Division of Biological Sciences. "Normal cells put up a 'don't-eat-me' molecular ...
New process evaluates patients for elective surgeries following COVID-19
2021-01-12
Acknowledging that COVID-19 may be here to stay, Oregon Health & Science University has laid out a series of steps to prepare patients for elective surgery following their illness.
The evaluation, outlined in a commentary published in the journal Perioperative Medicine, is believed to be the first published protocol laying out a COVID-era path forward in American medicine.
"We think this is groundbreaking," said senior author Avital O'Glasser, M.D., associate professor of medicine (hospital medicine) in the OHSU School of Medicine. "We are hoping other clinics and surgical centers can use this to keep their patients safe."
The work started around Memorial Day, when OHSU clinicians began to see an increasing number of patients ...
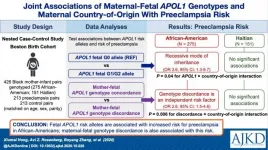
Fetal-maternal discordance in APOL1 genotype contributes to preeclampsia risk
2021-01-12
Fetal APOL1 kidney risk alleles are associated with increased risk for preeclampsia in African Americans and maternal fetal genotype discordance is also associated with this risk.
Preeclampsia, characterized by increased blood pressure after 20 weeks of pregnancy, as well as other abnormalities (e.g., protein in the urine), is dangerous to mothers and their infants. Previous studies found that individuals with African ancestry may carry APOL1 genetic variants that increase risk for chronic kidney disease. This study published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD) found that fetal high-risk APOL1 genotypes and maternal-fetal APOL1 genotype discordance independently contribute to preeclampsia risk in African-American mothers. This ...
Immune system killer cells controlled by circadian rhythms
2021-01-12
TROY, N.Y. -- An analysis of an exhaustive dataset on cells essential to the mammalian immune system shows that our ability to fight disease may rely more heavily on daily circadian cycles than previously assumed.
Malfunctions in circadian rhythms, the process that keeps our bodies in tune with the day/night cycles, are increasingly associated with diabetes, cancer, Alzheimer's, and many other diseases. An investigation published today in Genome Research shows that the activity of macrophages -- cells within us that seek and destroy intruders like bacteria -- may time daily changes in their responses to pathogens and stress through the circadian control of metabolism.
In this study, ...
Boomerang performance is on par with internal employees who never left the firm, new paper finds
2021-01-12
Organizations seeking to fill internal roles traditionally have two options: promote from within or hire externally. Internal promotions benefit from being vetted talent who possess firm-specific skills while outside hires harbor external knowledge that can infuse an organization with new energy. Though this dichotomy is often accepted as unavoidable, there is a third option: boomerang employees.
Boomerang employees are those who return to an organization after an amicable absence. Whether the absence was for personal or professional reasons, their return provides unique value to an ...
Most distant quasar discovered sheds light on how black holes grow
2021-01-12
A team of astronomers led by the University of Arizona has observed a luminous quasar 13.03 billion light-years from Earth - the most distant quasar discovered to date. Dating back to 670 million years after the Big Bang, when the universe was only 5% its current age, the quasar hosts a supermassive black hole equivalent to the combined mass of 1.6 billion suns.
In addition to being the most distant - and by extension, earliest - quasar known, the object is the first of its kind to show evidence of an outflowing wind of super-heated gas escaping from the surroundings of the black hole at a fifth of the speed of light. In ...
Quasar discovery sets new distance record
2021-01-12
An international team of astronomers has discovered the most distant quasar yet found -- a cosmic monster more than 13 billion light-years from Earth powered by a supermassive black hole more than 1.6 billion times more massive than the Sun and more than 1,000 times brighter than our entire Milky Way Galaxy.
The quasar, called J0313-1806, is seen as it was when the Universe was only 670 million years old and is providing astronomers with valuable insight on how massive galaxies -- and the supermassive black holes at their cores -- formed in the early Universe. The scientists presented their findings to the American Astronomical Society's meeting, now underway virtually, and in a paper accepted to ...
[1] ... [2757]
[2758]
[2759]
[2760]
[2761]
[2762]
[2763]
[2764]
2765
[2766]
[2767]
[2768]
[2769]
[2770]
[2771]
[2772]
[2773]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.