The world's first integrated quantum communication network
2021-01-06
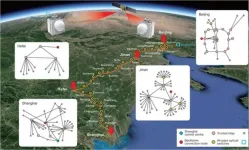
Chinese scientists have established the world's first integrated quantum communication network, combining over 700 optical fibers on the ground with two ground-to-satellite links to achieve quantum key distribution over a total distance of 4,600 kilometers for users across the country. The team, led by Jianwei Pan, Yuao Chen, Chengzhi Peng from the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei, reported in Nature their latest advances towards the global, practical application of such a network for future communications.
Unlike conventional encryption, quantum communication is considered ...
It's getting hot in here: Warming world will fry power plant production in coming years
2021-01-06
SYRACUSE, N.Y. - There's no doubt the Earth's temperatures are going up. According to a December report by the World Meteorological Organization, 2020 is on track to be one of the three hottest years on record, already within the warmest decade to date. During the year's hottest months, many people rely on electricity-generated cooling systems to remain comfortable. But the power plants that keep air conditioners pushing out cold air could soon be in a vicious cycle in a warming world-not able to keep up with growing demands on hotter days and driving up greenhouse gas emissions ...
New evidence: Effects of Huntington's disease mutation may begin in childhood
2021-01-06
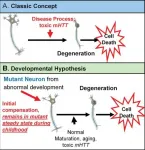
Amsterdam, NL, January 6, 2021 - There is growing evidence to support the hypothesis that there is a neurodevelopmental component to the late-onset neurodegeneration occurring in the brain of huntingtin gene (HTT gene) mutation carriers, and that this increased susceptibility to brain cell death begins during childhood. Experts discuss the evidence that the HTT gene mutation affects brain and body growth based on a unique study of children at risk for HD, the Kids-HD study, in a review paper and accompanying research article published in the Journal of Huntington's Disease.
The classic concept is that Huntington's disease is caused by toxic mutant huntingtin (mHTT) acting over time on mature brain cells. However, there is growing evidence for an alternative ...
Mighty morphing 3D printing
2021-01-06
Engineers at the University of Maryland (UMD) have created a new shape-changing or "morphing" 3D printing nozzle that was featured as a Frontispiece in the January 5th issue of the journal Advanced Materials Technologies.
The team's morphing nozzle offers researchers new means for 3D printing "fiber-filled composites" - materials made up of short fibers that boost special properties over traditional 3D-printed parts, such as enhancing part strength or electrical conductivity. The challenge is that these properties are based on the directions or "orientations" of the short fibers, which has been difficult to control during the 3D printing process, until now.
"When 3D printing with the morphing nozzle, the power lies on ...
Study: Black Americans, women, conservatives more hesitant to trust COVID-19 vaccine
2021-01-06
A survey of approximately 5,000 Americans suggests that 31.1 percent of the U.S. public does not intend to get the COVID-19 vaccine once it becomes available to them - and the likelihood of vaccine refusal is highest among Black Americans, women and conservatives.
Timothy Callaghan, assistant professor at the Texas A&M University School of Public Health, led the study with the aim of better understanding the intentions of the American public regarding vaccines. The results were recently published in Social Science and Medicine.
According to the study, survey respondents answered a series of questions about their behaviors and attitudes about COVID-19, including why or why not they intend to pursue vaccination. Women are 71 percent ...
Surrey unveils breakthrough manufacturing process of ultra-thin sensor for smart contact lenses
2021-01-06
In a paper published by the journal Matter, engineers from the University of Surrey together with partners from Harvard University, University of Science and Technology of China, UK National Physical Laboratory, George Washington University and Zhejiang University Ningbo Research Institute report on how they have developed a breakthrough sensor system and manufacturing process.
The global team of engineers reveal that the new contact lens sensor system contains a photodetector for receiving optical information, a temperature sensor for diagnosing potential corneal disease and a glucose sensor ...
Guinea baboons grunt with an accent
2021-01-06
Musical masterworks as the Queen of the Night's Aria from Mozart's The Magic Flute, are examples of the sounds trained human voices can produce. The precondition for vocal virtuosity as well as for any spoken word is vocal learning, the ability to imitate auditory input. Some songbirds and bats can do this, but humans excel. We can acquire new languages into old age. To shed light on the evolution of vocal learning, a team led by Julia Fischer from the German Primate Center (DPZ) - Leibniz Institute for Primate Research has analyzed the sound structures of Guinea baboons and was ...
New paper describes use of geographic monitoring for early COVID cluster detection
2021-01-06
CLEVELAND - In a new paper, researchers describe their development of a near-real time spatial assessment of COVID-19 cases to help guide local medical responses to clusters of outbreaks of the virus at the local level.
The paper, entitled "Geographic monitoring for early disease detection (GeoMEDD)," appeared in the Dec. 10 issue of Nature Scientific Reports and comes from researchers at Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) School of Medicine, University Hospitals (UH) Cleveland Medical Center, and Texas A & M University.
While developing a tracking system during the beginning stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, ...
Israel can expect a major earthquake of 6.5 on the Richter scale in the coming years
2021-01-06
A first-of-its-kind study conducted under the bed of the Dead Sea reveals that a devastating earthquake measuring 6.5 on the Richter scale is expected to hit our region in the coming years. The study showed that an earthquake of this magnitude occurs in the land of Israel on an average cycle of between 130 and 150 years, but there have been cases in history where the lull between one earthquake and another was only a few decades long.
The last earthquake with a magnitude of 6.5 on the Richter scale was felt in the Dead Sea valley in 1927, when hundreds of people were injured in Amman, Jerusalem, Bethlehem and even Jaffa. Now, in the wake of the findings ...
Gut microbe may promote breast cancers
2021-01-06
A microbe found in the colon and commonly associated with the development of colitis and colon cancer also may play a role in the development of some breast cancers, according to new research from investigators with the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and its Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy. Breast tissue cells exposed to this toxin retain a long-term memory, increasing the risk for disease.
In a series of laboratory experiments, researchers discovered that when enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis (ETBF) was introduced to the guts or breast ducts of mice, it always induced growth and metastatic progression of tumor cells. A description of the work is published in the January 6 issue of the journal Cancer Discovery.
While microbes are known to be present in ...
Advancing the study of T cells to improve immunotherapy
2021-01-06
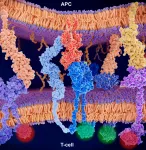
DALLAS - Jan. 6, 2020 - UT Southwestern scientists have developed a new method to study the molecular characteristics of T cells, critical immune cells that recognize and attack invaders in the body such as viruses, bacteria, and cancer.
The approach, described today in the journal Nature Methods, enables researchers to more easily analyze the roles of T cell receptors (TCRs) - the molecules on the surfaces of T cells that are responsible for recognizing pathogens.
"This could lead to a better understanding of how T cells work as well as new ways to harness T cells to fight disease," ...
Long-term study finds dozens of new genetic markers associated with lifetime bone growth
2021-01-06
Philadelphia, January 6, 2021 - A multidisciplinary team of researchers led by Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) has discovered several genetic markers associated with bone mineral accrual, which could ultimately help identify causes of eventual osteoporosis earlier in life through genetic testing. The findings, which were made possible by following a group of children over several years, were published online by the journal Genome Biology.
Osteoporosis is widely considered a disease of old age. However, the accrual of bone density early in life is critical for achieving optimal bone mass in adulthood ...
A prognostic Alzheimer's disease blood test in the symptom-free stage
2021-01-06
Using a blood test, a German-Dutch research team has predicted the risk of Alzheimer's disease in people who were clinically diagnosed as not having Alzheimer's disease but who perceived themselves as cognitively impaired (Subjective Cognitive Declined, SCD). The researchers analyzed blood samples from an SCD cohort supervised at the Alzheimer Center Amsterdam. Using a test developed at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) called the Immuno-Infrared Sensor, they identified all 22 subjects at study entry who developed Alzheimer's dementia, thus the clinical symptoms, within six years. The test ...
Why we use our smartphone at cafés
2021-01-06
Maybe you're like us. We're the folks who are on our smartphones almost all the time, even when we're with others. We know it annoys a lot of people, but we do it anyway. Why?
Researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) have looked at why people in cafés pull out their phones, and how this affects café life. Three main reasons they identified are: to delay or pause a conversation (interaction suspension); to get out of a conversation (deliberately shielding interaction); and to share something with others (accessing shareables).
But what does that actually mean?
The smartphone is the world's most ubiquitous personal tech gizmo. ...
How can we help victims of torture?
2021-01-06
Post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD, affects many people who are exposed to extreme situations, such as torture. Recent research suggests that chronic pain may make it more difficult to treat trauma.
"Trauma-focused therapy is effective for many patients with PTSD, enabling them to talk through the trauma they experienced", according to Iselin Solerød Dibaj, a psychologist at Oslo University Hospital.
However, not everyone benefits equally from this form of therapy.
"Torture victims who struggle with both chronic pain and PTSD unfortunately often reap less benefit from ordinary treatment," says Dibaj.
The Red Cross estimates that between 10 000 and 35 000 people with a refugee background who have come to Norway have experienced torture, reflecting ...
Businesses stand to benefit from sustainable restructuring
2021-01-06
The Earth is populated by an increasing number of people who demand more and more products, which is simply not viable in the long run. Our planet does not have unlimited resources. Emissions are harming the environment in various ways.
More companies thus need to switch to more sustainable production, sometimes due to pressure from consumers, but often resulting from new rules imposed by the authorities.
But this kind of change can't ever pay off - or can it?
A new study by a research group from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) has reviewed 100 articles on how sustainably oriented innovation affects companies' competitiveness.
"The ...
Detecting CRISPR/Cas gene doping
2021-01-06
All athletes want to be at the top of their game when they compete, but some resort to nefarious approaches to achieve peak muscle growth, speed and agility. Recent developments in gene editing technology could tempt athletes to change their DNA to get an edge. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Analytical Chemistry demonstrate first steps toward detecting this type of doping both in human plasma and in live mice.
The gene editing method called CRISPR/Cas is a popular way for scientists to precisely change the DNA in many organisms, and it recently gained even more attention when key developers of the method were awarded the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. With this method, researchers add an RNA molecule and a protein into cells. The RNA molecule guides the protein to the appropriate ...
A better pen-and-ink system for drawing flexible circuits
2021-01-06
Conductive ink is a great tool for printing flexible electronic circuits on surfaces. But these inks can be costly, they do not work on some materials, and devices to apply them can plug up. Now, scientists report in ACS Applied Electronic Materials that they have developed inexpensive conductive inks for clog-free ballpoint pens that can allow users to "write" circuits almost anywhere -- even on human skin.
Flexible electronics are widely used in applications such as biosensors, electronic skin and energy storage. Recent advances to produce such devices include pens ...
How Earth's oddest mammal got to be so bizarre
2021-01-06
Often considered the world's oddest mammal, Australia's beaver-like, duck-billed platypus exhibits an array of bizarre characteristics: it lays eggs instead of giving birth to live babies, sweats milk, has venomous spurs and is even equipped with 10 sex chromosomes. Now, an international team of researchers led by University of Copenhagen has conducted a unique mapping of the platypus genome and found answers regarding the origins of a few of its stranger features.
It lays eggs, but nurses, it is toothless, has a venomous spur, has webbed feet, fur that glows and has 10 sex chromosomes. Ever since Europeans discovered the platypus in Australia during ...
Researchers turn coal powder into graphite in microwave oven
2021-01-06
Using copper foil, glass containers and a conventional household microwave oven, University of Wyoming researchers have demonstrated that pulverized coal powder can be converted into higher-value nano-graphite.
The discovery is another step forward in the effort to find alternative uses for Wyoming's Powder River Basin coal, at a time when demand for coal to generate electricity is declining due to concerns about climate change.
In a paper published in the journal Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects, the UW researchers report that they created an environment in a microwave oven to successfully convert raw coal powder into nano-graphite, which is ...
'Sniffing out' fruity thiols in hoppy beers
2021-01-06
Hoppy beers such as pale ales are becoming increasingly popular. One reason is their pleasant fruity aroma that partially stems from compounds called thiols. Brewers have been looking for an accurate way to track thiols in beer, but current methods typically are not sensitive enough or require use of potentially harmful substances. Now, researchers in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry present an automated, solvent-less process to assess thiols at very low concentrations.
Thiols, along with other compounds such as terpenes and esters, contribute to the enjoyable odors in "hop-forward" beer styles. Although very small amounts ...
New research finds ginger counters certain autoimmune diseases in mice
2021-01-06
Naturopathic medicine, or herbal medicine, is all the rage, especially among young people. But how much of this is supported by science?
Ginger is known to have anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects, making it a popular herbal supplement to treat inflammatory diseases.
And according to a Michigan Medicine led END ...
HKUST researchers discover a novel mechanism of recruiting ARF family proteins to specific subcellul
2021-01-06
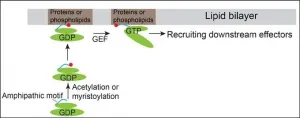
The small GTPases of the ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) family are key initiators of various physiological processes including secretion, endocytosis, phagocytosis and signal transduction. Arf family proteins function to mediate recruitment of cytosolic effectors to specific subcellular compartments. This process facilitates Arf effectors to perform cargo recognition, lipid modification or other cellular functions. Blocking the activities of Arf family proteins inhibits secretion of important molecules from the cell and also inhibits cellular uptake of nutrients. Defects in Arfs or their regulatory proteins are related to various inherited diseases, including X-linked intellectual disability (XLID), Joubert syndrome, Bardet-Biedl syndrome and cilia dysfunction. Thus, studying molecular ...
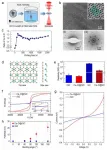
2D CaCl crystals with +1 calcium ions displaying unexpected metallicity and ferromagnetism
2021-01-06
Calcium ions are presented in rocks, bones, shells, biominerals, geological deposits, ocean sediments, and many other important materials. Calcium ions also play major roles in the retention of carbon dioxide in natural waters, water hardness, signal transduction and tissue generation. As one of the alkaline earth metals, the calcium atom has two valence electrons according to the octet rule. Up to now, the only known valence state of calcium ions under ambient conditions is +2, and the corresponding crystals with calcium ions are insulating.
By using cryo-electron ...
New review says the ineffective 'learning styles' theory persists in education
2021-01-06
A new review by Swansea University reveals there is widespread belief, around the world, in a teaching method that is not only ineffective but may actually be harmful to learners.
For decades educators have been advised to match their teaching to the supposed 'learning styles' of students. There are more than 70 different classification systems, but the most well-known (VARK) sees individuals being categorised as visual, auditory, read-write or kinesthetic learners.
However, a new paper by Professor Phil Newton, of Swansea University Medical School, highlights that this ineffective approach is still believed by teachers and calls for a more evidence-based approach to teacher-training.
He explained that various reviews, carried out since the mid-2000s, have concluded there is no ...
[1] ... [2764]
[2765]
[2766]
[2767]
[2768]
[2769]
[2770]
[2771]
2772
[2773]
[2774]
[2775]
[2776]
[2777]
[2778]
[2779]
[2780]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.