Using solar energy and agriculture to limit climate change, assist rural communities
2021-01-05
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Co-developing land for both solar photovoltaic power and agriculture could provide 20% of total electricity generation in the United States with an investment of less than 1% of the annual U.S. budget, a new paper by Oregon State University researchers found.
Wide-scale installation of agrivoltaic systems could lead to an annual reduction of 330,000 tons of carbon dioxide emissions in the U.S - the equivalent of 75,000 cars off the road per year - and the creation of more than 100,000 jobs in rural communities, while minimally impacting crop yield, the researchers say.
"Agrivoltaics provide a rare chance for true synergy: more food, more energy, lower water demand, lower carbon emissions, and more prosperous rural communities," said Chad Higgins, an associate ...
Mid-term clinical trial results show similar outcomes in promising cell therapies for CLI
2021-01-05
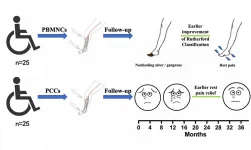
Durham, NC - Mid-term results of the first clinical trial designed specifically to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of two cell therapies that are showing early promise in treating angiitis-induced critical limb ischemia were released today in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine. The study, by researchers at Zhongshan Hospital/Fudan University in Shanghai, compared how transplantation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells fared versus transplantation of purified CD34+ cells in treating this condition.
It revealed both therapies yielded satisfactory results and provided evidence for ...
Researchers uncover a potential treatment for an aggressive form of lung cancer
2021-01-05
DALLAS - Jan. 5, 2021 - Researchers at the Children's Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI) have discovered a new metabolic vulnerability in a highly aggressive form of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). These findings could pave the way for new treatments for patients with mutations in two key genes - KRAS and LKB1. Patients whose tumors contain both of these mutations, known as KL tumors, have poor outcomes and usually do not respond to immunotherapy.
"We used to think that most tumors rely on the same handful of metabolic pathways to grow, but we've learned over the last decade that this is an oversimplification. Instead, different tumor subclasses have particular metabolic needs arising from mutations ...
COVID-19 news from Annals of Internal Medicine
2021-01-05
Trio of articles suggest that a single dose of vaccine, even if less effective than two doses, may have greater population benefit.
Three articles published today in Annals of Internal Medicine discuss the most effective vaccination strategy for maximum impact against the COVID-19 pandemic. The articles are accompanied by an editorial from Thomas J. Bollyky, JD, Director of Global Health Program, Council on Foreign Relations. Mr. Bollyky can be reached through Lauran Potter at lpotter@cfr.org. The full text of his editorial is available here: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-8280.
Speed Versus Efficacy: Quantifying Potential Tradeoffs in COVID-19 Vaccine Deployment https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-7866.
Researchers from Yale School of Public ...
Ibrutinib with rituximab in previously untreated CLL: indication of added benefit over FCR
2021-01-05
The combination of ibrutinib plus rituximab is approved for the treatment of adults with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL). In an early benefit assessment, the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) now examined which advantages and disadvantages this drug combination has for the patients. For patients who could also be treated with the chemo-immunotherapy FCR, the assessment found an indication of a major added benefit in comparison with this appropriate comparator therapy. No study data are available for patients for whom FCR or other chemo-immunotherapy is not an option due to their poorer general health. An added benefit is therefore ...
Rare footage captured of jaguar killing ocelot at waterhole
2021-01-05
PULLMAN, Wash. - In what may be a sign of climate-change-induced conflict, researchers have captured rare photographic evidence of a jaguar killing another predatory wild cat at an isolated waterhole in Guatemala.
In the footage, a male jaguar arrives near the waterhole and apparently lies in wait for an hour. It lets a potentially dangerous prey animal, a large tapir, pass by, but when the ocelot stops to drink, the jaguar pounces and carries off the smaller predator.
The event, detailed in a recent study published in the journal Biotropica, was captured in the Maya Biosphere Reserve in March 2019, a dry month in a drought year for the tropical forest, by wildlife ecologists from Washington State University ...
New clues why gold standard treatment for bipolar disorder doesn't work for majority of patients
2021-01-05
LA JOLLA--(January 5, 2021) Lithium is considered the gold standard for treating bipolar disorder (BD), but nearly 70 percent of people with BD don't respond to it. This leaves them at risk for debilitating, potentially life-threatening mood swings. Researchers at the Salk Institute have found that the culprit may lie in gene activity--or lack of it.
A new study led by Salk Professor and President Rusty Gage, which published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry on January 4, 2021, shows that decreased activation of a gene called LEF1 disrupts ordinary ...
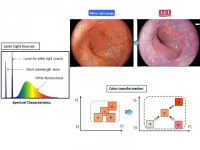
Viewing upper gastrointestinal cancers in a new light
2021-01-05
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) describe an endoscopic modality for detecting upper gastrointestinal tract neoplasms by Linked Color Imaging that innovatively mixes light of different wavelengths to better depict mucosal changes
Tokyo, Japan - Recently there have been significant advances on several fronts in the ongoing war against cancer of the alimentary tract. Now, Japanese researchers report the development of another weapon: Linked Color Imaging (LCI), a novel endoscopic technique that improves detection of cancer by viewing the upper digestive tract mucosa under illumination that combines specific wavelengths of light to intensify subtle color variations indicative of neoplastic change.
Upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy ...
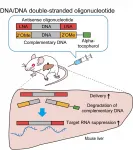
Making therapeutic sense of antisense oligonucleotides
2021-01-05
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and Ionis Pharmaceuticals, USA, report a modification wherein replacing the RNA strand of a heteroduplex oligonucleotide with DNA may enhance the efficacy of antisense oligonucleotide-based drugs
Tokyo, Japan - Antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) hold great promise for pharmacotherapy. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and Ionis Pharmaceuticals, advancing their earlier work on a heteroduplex oligonucleotide (HDO) model, have demonstrated augmentation of ASO-based ...
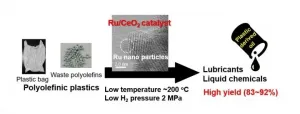
Catalyst transforms plastic waste to valuable ingredients at low temperature
2021-01-05
For the first time, researchers have used a novel catalyst process to recycle a type of plastic found in everything from grocery bags and food packaging to toys and electronics into liquid fuels and wax.
The team published their results on Dec. 10 in Applied Catalysis B: Environmental.
"Plastics are essential materials for our life because they bring safety and hygiene to our society," said paper co-authors Masazumi Tamura, associate professor in the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis in the Advanced Research Institute for Natural Science and Technology in Osaka City University, and Keiichi Tomishige, professor in the Graduate School of Engineering in Tohoku University. "However, the growth of the global ...
Dental experts discover biological imbalance is the link between gum and kidney disease
2021-01-05
An imbalance of the body's oxygen producing free radicals and its antioxidant cells could be the reason why gum disease and chronic kidney disease affect each other, a new study led by the University of Birmingham has found.
Periodontitis - or gum disease - is a common, inflammatory disease which causes bleeding gums, wobbly or drifting teeth and can eventually result in tooth loss.
Previous studies have shown a link between the severe oral inflammation caused by gum disease and chronic kidney disease (CKD) which demonstrated that those with worse inflammation of the gums have worse kidney function.
Previous research also showed that patients with CKD and periodontitis experience ...
Looking forwards rather than backwards safeguards wellbeing during Covid-19 lockdowns
2021-01-05
Practicing gratitude and looking to the future will help safeguard our mental wellbeing during Covid-19 lockdowns, a new study in the Journal of Positive Psychology reports.
In the first study of its kind, researchers from the University of Surrey investigated the effectiveness of three psychological interventions -- nostalgia, a sentimentality for the past; gratitude, recognising the good things currently in our life; and best possible self, thinking about positive elements of the future -- and how they each affect wellbeing during lockdowns.
Personal characteristics such as emotion regulation (the ability to respond ...
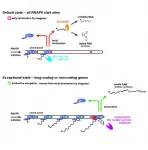
Integrator: A guardian of the human transcriptome
2021-01-05
In a joint collaboration, Danish and German researchers have characterized a cellular activity that protects our cells from potentially toxic by-products of gene expression. This activity is central for the ability of multicellular organisms to uphold a robust evolutionary 'reservoir' of gene products.
Manufacturing processes need quality control systems in order to ensure proper assembly of functional products. Moreover, space-consuming, and perhaps even toxic, by-products of such processes need to be properly discarded or recycled by efficient waste handling systems.
By analogy, transcription of our genome is an imperfect process that produces large quantities of non-functional and potentially harmful transcripts both from within and ...
New imaging method reveals if antibiotics reach bacteria hiding in tissues
2021-01-05
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and the University of Western Australia have developed a new imaging method to see where antibiotics have reached bacteria within tissues. The method could be used to help develop more effective antibiotic treatments, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
During bacterial infections like tuberculosis, bacteria enter human cells, which poses a challenge for treatment, as antibiotics must reach and enter all infected cells in order to be effective. If researchers could select for or develop more effective antibiotics based on where they reach, this may reduce the length of treatment ...
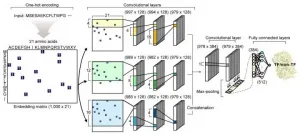
DeepTFactor predicts transcription factors
2021-01-05
A joint research team from KAIST and UCSD has developed a deep neural network named DeepTFactor that predicts transcription factors from protein sequences. DeepTFactor will serve as a useful tool for understanding the regulatory systems of organisms, accelerating the use of deep learning for solving biological problems.
A transcription factor is a protein that specifically binds to DNA sequences to control the transcription initiation. Analyzing transcriptional regulation enables the understanding of how organisms control gene expression in response to genetic or environmental changes. In this regard, finding the transcription factor of an organism is the first step in the analysis ...
Neither liquid nor solid
2021-01-05
While glass is a truly ubiquitous material that we use on a daily basis, it also represents a major scientific conundrum. Contrary to what one might expect, the true nature of glass remains something of a mystery, with scientific inquiry into its chemical and physical properties still underway. In chemistry and physics, the term glass itself is a mutable concept: It includes the substance we know as window glass, but it may also refer to a range of other materials with properties that can be explained by reference to glass-like behaviour, including, for instance, ...
Impurities boost performance of organic solar cells
2021-01-05
Sunlight offers a potential solution in the search for an energy source that does not harm the planet, but this depends on finding a way to efficiently turn electromagnetic energy into electricity. Researchers from KAUST have shown how a known herbicide can improve this conversion in organic devices.
While solar cells have traditionally been made from inorganic materials such as silicon, organic materials are starting to break through as an alternative because they are light, flexible and relatively inexpensive to make, even offering the possibility for ...
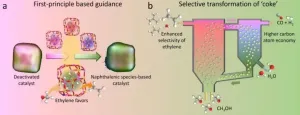
Researchers regenerate deactivated catalyst in methanol-to-olefins process
2021-01-05
MTO process, which was first commercialized in 2010, is a catalytic process converting methanol, which is typically made from coal, natural gas, biomass, and CO2, over SAPO-34 zeolite catalyst. It's becoming one of the main streams for producing light olefins, including ethylene and propylene, from non-oil resources.
One of the major challenges in MTO is the rapid deactivation of zeolite catalyst due to the coke deposition.
In industrial practices, a fluidized bed reactor-regenerator configuration is normally used in order to maintain the continuous operation, in ...
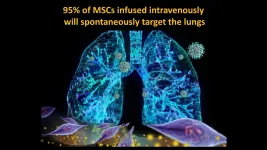
UC-MSC infusion helps repair COVID-19 damage in severe cases
2021-01-05
Dr. Camilo Ricordi, director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, and his team of international collaborators are reporting the results of a groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the most severe COVID-19 patients. Dr. Ricordi's peer-reviewed paper has just been published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine (SCTM) January 2021.
The clinical trial, authorized by the FDA last ...
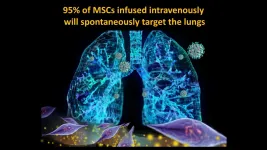
UC-MSC transfusion helps repair COVID-19 damage in severe cases
2021-01-05
Dr. Camilo Ricordi, director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, and his team of international collaborators are reporting the results of a groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the most severe COVID-19 patients. Dr. Ricordi's peer-reviewed paper has just been published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine (SCTM) January 2021.
The clinical trial, authorized by the FDA last April, was initiated by The Cure Alliance, a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization of research scientists founded ten years ago by Dr. Ricordi for scientists ...
A plant's way to its favorite food
2021-01-05
Like any other plant, Arabidopsis thaliana or mouse-ear cress, needs nitrogen to survive and thrive. But, like maize, beans and sugar beet, it prefers nitrogen in the form of nitrate, growing better on nitrate rich soil. Whereas, pine and rice for example preferentially grow on ammonium nutrition, another form of the key macronutrient nitrogen. If the concentration or the availability of the different forms of nitrogen fluctuate, plants have to adapt quickly. "One of the most important questions is, what is the role of plant hormones in adaptation to the nitrogen availability? How do the machineries within a plant cope with their changing environment?" asks Eva Benková, developmental biologist and Professor at the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria.
Finding the balance
In ...
University of Miami leads groundbreaking trial for COVID-19 treatment
2021-01-05
University of Miami Miller School of Medicine researchers led a unique and groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cell infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the severest COVID-19 patients, according to results published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine in January 2021.
The study's senior author, Camillo Ricordi, M.D., director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, said treating COVID-19 with mesenchymal stem cells makes sense.
Results: treatment group vs. ...
3D-printed smart gel changes shape when exposed to light
2021-01-05
Inspired by the color-changing skin of cuttlefish, octopuses and squids, Rutgers engineers have created a 3D-printed smart gel that changes shape when exposed to light, becomes "artificial muscle" and may lead to new military camouflage, soft robotics and flexible displays.
The engineers also developed a 3D-printed stretchy material that can reveal colors when light changes, according to their study in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Their invention is modeled after the amazing ability of cephalopods such as cuttlefish, octopuses and squids to change the color and texture of their soft skin for camouflage and communication. This is achieved by the ...
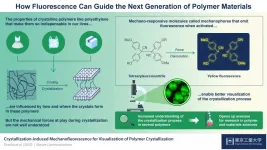
Mechanophores: Making polymer crystallization processes crystal clear
2021-01-05
In modern times, manufacturers produce highly specialized materials for a wide array of uses, called polymers. Polymers have a variety of purposes owing to their versatile properties, ranging from being used in construction due to their high tensile strength and resistance to manufacturing plastic bags that require more lightweight, flexible materials, such as nylon or polyethene.
These differences between the properties of different polymers stems from their internal structure. Polymers are made up of long chains of smaller sub-units, called "monomers." Crystallization occurs when crystalline polymers are melted, then cooled down slowly, which enables the chains to organize themselves into neatly arranged ...
Uncovering how grasslands changed our climate
2021-01-05
Grasslands are managed worldwide to support livestock production, while remaining natural or semi-natural ones provide critical services that contribute to the wellbeing of both people and the planet. Human activities are however causing grasslands to become a source of greenhouse gas emissions rather than a carbon sink. A new study uncovered how grasslands used by humans have changed our climate over the last centuries.
Grasslands are the most extensive terrestrial biome on Earth and are critically important for animal forage, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. They absorb and release carbon dioxide (CO2), and emit methane (CH4) from grazing livestock and nitrous oxide (N2O) from soils, especially when manure or ...
[1] ... [2768]
[2769]
[2770]
[2771]
[2772]
[2773]
[2774]
[2775]
2776
[2777]
[2778]
[2779]
[2780]
[2781]
[2782]
[2783]
[2784]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.