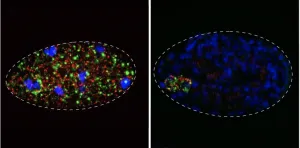
Patterns in primordial germ cell migration
2021-01-07
Whenever an organism develops and forms organs, a tumour creates metastases or the immune system becomes active in inflammation, cells migrate within the body. As they do, they interact with surrounding tissues which influence their function. The migrating cells react to biochemical signals, as well as to biophysical properties of their environment, for example whether a tissue is soft or stiff. Gaining detailed knowledge about such processes provides scientists with a basis for understanding medical conditions and developing treatment approaches.
A team of biologists and mathematicians at the Universities of Münster and Erlangen-Nürnberg has now developed a new method for analysing cell migration ...
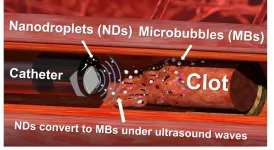
Nanodroplets and ultrasound 'drills' prove effective at tackling tough blood clots
2021-01-07
Engineering researchers have developed a new technique for eliminating particularly tough blood clots, using engineered nanodroplets and an ultrasound "drill" to break up the clots from the inside out. The technique has not yet gone through clinical testing. In vitro testing has shown promising results.
Specifically, the new approach is designed to treat retracted blood clots, which form over extended periods of time and are especially dense. These clots are particularly difficult to treat because they are less porous than other clots, making it hard for drugs ...
How medical schools can transform curriculums to undo racial biases
2021-01-07
PHILADELPHIA - Medical school curriculums may misuse race and play a role in perpetuating physician bias, a team led by Penn Medicine researchers found in an analysis of curriculum from the preclinical phase of medical education. In a perspective piece published Tuesday in the New England Journal of Medicine, the researchers identified five key categories in which curriculum misrepresented race in class discussions, presentations, and assessments. The authors recommend that rather than oversimplifying conversations about how race affects diseases' prevalence, diagnosis, and treatment, medical school faculty must widen the lens to "impart an adequate and accurate understanding of the complexity ...
Researchers create comprehensive database of head and neck cancers
2021-01-07
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In what is believed to be the most comprehensive molecular characterization to date of the most common type of head and neck cancer, researchers from the Johns Hopkins departments of END ...
Power, water and climate
2021-01-07
As the planet continues to warm, the twin challenges of diminishing water supply and growing energy demand will intensify. But water and energy are inextricably linked. For instance, nearly a fifth of California's energy goes toward water-related activities, while more than a tenth of the state's electricity comes from hydropower. As society tries to adapt to one challenge, it needs to ensure it doesn't worsen the other.
To this end, researchers from UC Santa Barbara, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and UC Berkeley have developed a framework to evaluate how different climate adaptations may impact this water-energy nexus. Their research appears in the open access journal Environmental Research Letters.
"Electricity and water systems are linked in many ...
Intelligence deficit: Conclusion from the mouse to the human being
2021-01-07
Impaired intelligence, movement disorders and developmental delays are typical for a group of rare diseases that belong to GPI anchor deficiencies. Researchers from the University of Bonn and the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics used genetic engineering methods to create a mouse that mimics these patients very well. Studies in this animal model suggest that in GPI anchor deficiencies, a gene mutation impairs the transmission of stimuli at the synapses in the brain. This may explain the impairments associated with the disease. The results are now published ...
IU research findings could reduce treatment-related complication for blood cancer patients
2021-01-07
INDIANAPOLIS-- Researchers at the Indiana University Melvin and Bren Simon Comprehensive Cancer Center published promising findings today in the New England Journal of Medicine on preventing a common complication to lifesaving blood stem cell transplantation in leukemia.
Sherif Farag, MD, PhD, found that using a drug approved for Type 2 diabetes reduces the risk of acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), one of the most serious complications of blood stem cell transplantation. GVHD occurs in more than 30 percent of patients and can lead to severe side effects and potentially fatal results. Farag is ...
Chemists invent shape-shifting nanomaterial with biomedical potential
2021-01-07
Chemists have developed a nanomaterial that they can trigger to shape shift -- from flat sheets to tubes and back to sheets again -- in a controllable fashion. The Journal of the American Chemical Society published a description of the nanomaterial, which was developed at Emory University and holds potential for a range of biomedical applications, from controlled-release drug delivery to tissue engineering.
The nanomaterial, which in sheet form is 10,000 times thinner than the width of a human hair, is made of synthetic collagen. Naturally occurring collagen is the most abundant protein in humans, making the new material intrinsically biocompatible.
"No one has previously made collagen ...
COVID-19 and dental and dental hygiene students' career plans
2021-01-07
Alexandria, Va., USA -- The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted dental education and training. The study "COVID-19 and Dental and Dental Hygiene Students' Career Plans," published in the JDR Clinical & Translational Research (JDR CTR), examined the short-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on dental hygiene and dental students' career intentions.
An anonymous online survey was emailed to dental and dental hygiene students enrolled at Virginia Commonwealth University School of Dentistry, Richmond, USA. The survey consisted of 81 questions that covered a wide range of topics including demographics, anticipated educational debt, career plans post-graduation, ...
Paper: Emotionally appealing ads may not always help consumer memory
2021-01-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- In almost all successful advertising campaigns, an appeal to emotion sparks a call-to-action that motivates viewers to become consumers. But according to research from a University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign expert who studies consumer information-processing and memory, emotionally arousing advertisements may not always help improve consumers' immediate memory.
A new paper co-written by Hayden Noel, a clinical associate professor of business administration at the Gies College of Business at Illinois, finds that an ad's emotional arousal can have a negative effect on immediate ...
Stem cell therapy corrects skull, brain function in mouse model of childhood disorder
2021-01-07
Using stem cells to regenerate parts of the skull, scientists corrected skull shape and reversed learning and memory deficits in young mice with craniosynostosis, a condition estimated to affect 1 in every 2,500 infants born in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The only current therapy is complex surgery within the first year of life, but skull defects often return afterward. The study, supported by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR), could pave the way for more effective and less invasive therapies for children with craniosynostosis. ...
Archaeology: sharing leftover meat may have contributed to early dog domestication
2021-01-07
Humans feeding leftover lean meat to wolves during harsh winters may have had a role in the early domestication of dogs, towards the end of the last ice age (14,000 to 29,000 years ago), according to a study published in Scientific Reports.
Maria Lahtinen and colleagues used simple energy content calculations to estimate how much energy would have been left over by humans from the meat of species they may have hunted 14,000 to 29,000 years that were also typical wolf prey species, such as horses, moose and deer. The authors hypothesized that if wolves and humans had hunted the same animals during harsh winters, humans would have killed wolves to reduce competition rather than domesticate them. With the exception of Mustelids such as weasels, ...
Selfish elements turn embryos into a battlefield
2021-01-07
"Nature red in tooth and claw" - The battle to survive is fought down to the level of our genes. Toxin-antidote elements are gene pairs that spread in populations by killing non-carriers. Now, research by the Burga lab at IMBA and the Kruglyak lab at the University of California, Los Angeles shows that these elements are more common in nature than first thought and have evolved a wide range of mechanisms to force their inheritance and propagate in populations - a parasite within the genome.
Originally described in the model nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, toxin-antidote elements consist of two linked genes, a toxin and its antidote. While the toxin is loaded into eggs by mothers, only embryos that inherit the element express the antidote. Thus, the ...
NHGRI proposes an action agenda for building a diverse genomics workforce
2021-01-07
The National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) within the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has released a new action agenda for a diverse genomics workforce. This ambitious set of goals, objectives, and implementation strategies details NHGRI's plans for enhancing the diversity of the genomics workforce by 2030.
"To reach its full potential, the field of genomics requires a workforce that better reflects the diversity of the U.S. population," NHGRI Director Eric Green, M.D., Ph.D., said. "Fostering an appropriately diverse genomics workforce of the future requires an immediate and substantial commitment ...
Noncognitive skills -- distinct from cognitive abilities -- are important to success across the life
2021-01-07
Noncognitive skills and cognitive abilities are both important contributors to educational attainment -- the number of years of formal schooling that a person completes -- and lead to success across the life course, according to a new study from an international team led by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, the University of Texas at Austin, and Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam. The research provides evidence for the idea that inheriting genes that affect things other than cognitive ability are important for understanding differences in people's life outcomes. Until now there had been questions about what these noncognitive skills are and how much they really matter for life outcomes. The new findings are published ...
SARS-CoV-2 transmission from people without COVID-19 symptoms
2021-01-07
What The Study Did: Under a range of assumptions of presymptomatic transmission and transmission from individuals with infection who never develop symptoms, the model presented here estimated that more than half of transmission comes from asymptomatic individuals.
Author: Jay C. Butler, M.D., of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35057)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and ...
Examining association of age, household dysfunction, outcomes in early adulthood
2021-01-07
What The Study Did: Population data from Denmark were used to examine whether age at exposure to negative experiences in childhood and adolescence (parents' unemployment, incarceration, mental disorders, death and divorce, and the child's foster care experiences) was associated with outcomes in early adulthood.
Author: Signe Hald Andersen, Ph.D., of the Rockwool Foundation Research Unit in Copenhagen, Denmark, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.32769)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Adapting to COVID-19 with outdoor intraocular pressure monitoring
2021-01-07
What The Study Did: To adapt to broader public health initiatives around COVID-19, researchers developed a drive-through intraocular pressure (IOP) screening clinic to minimize COVID-19 exposure for patients and clinicians by measuring eye pressure in the unconventional setting of a clinic parking lot.
Authors: Miel Sundararajan, M.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2020.6073)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article ...
Speech recognition changes after cochlear implant
2021-01-07
What The Study Did: Researchers compared changes in preoperative aided speech recognition with postoperative speech recognition among individuals who received cochlear implants.
Authors: Theodore R. McRackan, M.D., M.S.C.R., of the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5094)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please ...
Virtual care at cancer center during COVID-19
2021-01-07
What The Study Did: The outcomes of a cancer center-wide virtual care program launched in response to the COVID-19 pandemic were examined in this study.
Authors: Alejandro Berlin, M.D., M.Sc., of the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.6982)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict ...
Assessment of duplicate evidence in systematic reviews of imaging findings of children with COVID-19
2021-01-07
What The Study Did:This cross-sectional study maps a coronavirus research question to illustrate the overlap and shortcomings of the evidence syntheses in this area.
Author: Giordano Pérez-Gaxiola, M.D., M.Sc., of Sinaloa Pediatric Hospital's Cochrane Associate Centre in Culiacan, Mexico, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.32769)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
Mount Sinai researchers identify and characterize 3 molecular subtypes of Alzheimer's
2021-01-07
(New York, NY - January 6, 2021) - Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have identified three major molecular subtypes of Alzheimer's disease (AD) using data from RNA sequencing. The study advances our understanding of the mechanisms of AD and could pave the way for developing novel, personalized therapeutics.
The work was funded by the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and published in Science Advances on January 6, 2021.
RNA is a genetic molecule similar to DNA that encodes the instructions for making proteins. RNA sequencing is a technology that reveals the presence and quantity of RNA in a biological sample such as a brain slice.
Alzheimer's ...
Unusual sex chromosomes of platypus, emu and duck
2021-01-07
Sex chromosomes are presumed to originate from a pair of identical ancestral chromosomes by acquiring a male- or a female-determining gene on one chromosome. To prevent the sex-determining gene from appearing in the opposite sex, recombination is suppressed on sex chromosomes. This leads to the degeneration of Y chromosome (or the W chromosome in case of birds) and the morphological difference of sex chromosomes between sexes. For example, the human Y chromosome bears only less than 50 genes, while the human X chromosome still maintains over 1500 genes from the autosomal ancestor. This process occurred independently in birds, in ...
High-flux table-top source for femtosecond hard X-ray pulses
2021-01-07
Femtosecond hard X-ray pulses are an important tool for unraveling structure changes of condensed matter on atomic length and time scales. A novel laser-driven X-ray source provides femtosecond copper Kα pulses at a 1 kHz repetition rate with an unprecedented flux of some 10^12 X-ray photons per second.
Elementary processes in physics, chemistry, and biology are connected with changes of the atomic or molecular structure on a femtosecond time scale (1 femtosecond (fs) = 10^-15 seconds). Ultrafast X-ray methods hold strong potential for following structure changes in space and time and generate 'movies' of the motions of electrons, atoms and molecules. This perspective has ...
How to mitigate the impact of a lockdown on mental health
2021-01-07
The Covid-19 pandemic is impacting people's mental health. But what helps and hinders people in getting through a lockdown? A new study led by researchers at the University of Basel addressed this question using data from 78 countries across the world. The results hint at the pivots and hinges on which the individual's psyche rests in the pandemic.
At the outset of the Covid-19 pandemic, little was known about the impact of population-wide governmental lockdowns. What was known was taken from restricted quarantines of small groups of people. "On the one hand, such drastic changes to daily routines can be detrimental to mental health," explains Professor ...
[1] ... [2772]
[2773]
[2774]
[2775]
[2776]
[2777]
[2778]
[2779]
2780
[2781]
[2782]
[2783]
[2784]
[2785]
[2786]
[2787]
[2788]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.