Teen marijuana use down despite greater availability
2015-09-15
Marijuana use among American high school students is significantly lower today than it was 15 years ago, despite the legalization in many states of marijuana for medical purposes, a move toward decriminalization of the drug and the approval of its recreational use in a handful of places, new research suggests.
The Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health researchers say, however, that marijuana use is significantly greater than the use of other illegal drugs, with 40 percent of teens in 2013 saying they had ever smoked marijuana. That number was down from 47 percent ...
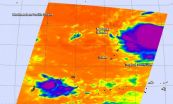
NASA gets infrared view of new Tropical Storm 20W
2015-09-15
The twentieth tropical depression of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean formed early on September 14 and became a tropical storm the next day, triggering a tropical storm watch. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the low pressure area as it was consolidating and saw powerful thunderstorms circling the center.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite gathers data in infrared light that provides information about temperatures. The colder the cloud top temperature, the higher the storms are in the troposphere (because the higher ...
Beta-blockers promote heart muscle cell survival following a heart attack, York U study
2015-09-15
TORONTO, Sept. 15, 2015 - A commonly prescribed drug for heart disease may do more good than previously thought. Researchers at York University have found that beta-blockers may prevent further cell death following a heart attack and that could lead to better longer term patient outcomes.
Human hearts are unable to regenerate. When cardiac muscle cells die during and immediately after a heart attack, there is no way to bring the organ back to full health, which contributes to the progression towards eventual heart failure.
Preventing the cells from dying in the first ...
Scientists report earlier date of shift in human ancestors' diet
2015-09-15
Millions of years ago, our primate ancestors turned from trees and shrubs to search for food on the ground. In human evolution, that has made all the difference.
The shift toward a grass-based diet marked a significant step toward the diverse eating habits that became a key human characteristic, and would have made these early humans more mobile and adaptable to their environment.
New evidence just published by a research team led by a Johns Hopkins University scientist shows that this significant shift took place about 400,000 years earlier than experts previously ...
Skin microbiome influences common sexually transmitted disease
2015-09-15
Washington, DC - September 15, 2015 - For years, researchers have known that the human skin is home to a diverse community of microorganisms, collectively known as the skin microbiome. Now a new study has shown that individuals with a particular skin microbiome can effectively clear bacteria that cause chancroid, a sexually transmitted disease common in the developing world that has been linked to enhanced HIV transmission. The study, published in the September 15th issue of mBio, is the first prospective study to show that the skin microbiome can influence the outcomes ...
Dealing with climate change and local beliefs in Africa
2015-09-15
Experts should take note of local knowledge and beliefs when making plans about how to help people in vulnerable regions cope with the impacts of climate change. This will ensure that such interventions are money well spent, and are not culturally insensitive, advises Conor Murphy of Ireland's Maynooth University. Together with an interdisciplinary research team from universities in Malawi, Zambia and Ireland he interviewed community members in rural Malawi and Zambia to assess how well they are able to adapt to the way they produce food within the context of shifting belief ...
Whole-body PET scan with new imaging agent can locate hidden blood clots
2015-09-15
A novel radiopharmaceutical probe developed at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has the potential of providing physicians with information that could save the lives of patients with ischemic stroke or pulmonary embolism - conditions caused when important blood vessels are blocked by a clot that has traveled from another part of the body. In a report that will appear in the October issue of the journal Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology and has been published online, the MGH team describes using this new probe to conduct full-body scans in an animal model. ...
Hookah tobacco smoking seems to be increasing in both prevalence and frequency
2015-09-15
PITTSBURGH, Sept. 15, 2015 - Nearly 1 in 5 recently surveyed high school seniors report having smoked tobacco from a hookah in the past year, and more than a third of them reported smoking hookahs often enough to be considered regular users, an analysis led by the University of Pittsburgh Center for Research on Media, Technology, and Health (CRMTH) revealed.
The findings, published online and scheduled for a coming print issue of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, add to evidence that hookah use among adolescents is increasing in both prevalence and frequency. ...
NYU researchers document self-reported use of new synthetic drugs by teens/young adults
2015-09-15
In recent years, there has been an increase in emergence and use of a variety of new drugs, so-called "novel psychoactive substances" (NPS) in the US and worldwide. However, there is little published survey data estimating the prevalence of use in the US. Media reports about use of new drugs such as "Spice" ("synthetic marijuana") and "bath salts" such as "Flakka" are now common, yet very few health surveys ask about use of such drugs.
A new study, published in Drug and Alcohol Dependence by researchers affiliated with New York University's Center for Drug Use and HIV ...
Are early childhood educators undervalued?
2015-09-15
Montreal, September 15, 2015 -- With the federal election around the corner, child care has become a major ballot issue. While every party has its own idea of how best to offset the costs of raising children, no one is looking at how we perceive and value those who provide the education and care.
Concordia researcher Sandra Chang-Kredl wants that to change. In a paper recently published in the Journal of Media & Cultural Studies, she writes that "invariably, the focus of the debate is on the children's needs, the parents' needs and society's needs. The educator is rarely ...
How much water does US fracking really use?
2015-09-15
DURHAM, N.C. -- Energy companies used nearly 250 billion gallons of water to extract unconventional shale gas and oil from hydraulically fractured wells in the United States between 2005 and 2014, a new Duke University study finds.
During the same period, the fracked wells generated about 210 billion gallons of wastewater.
Large though those numbers seem, the study calculates that the water used in fracking makes up less than 1 percent of total industrial water use nationwide.
While fracking an unconventional shale gas or oil well takes much more water than drilling ...
Link between air pollution and increased deaths from heart disease affirmed
2015-09-15
In what is believed to be the largest, most detailed study of its kind in the United States, scientists at NYU Langone Medical Center and elsewhere have confirmed that tiny chemical particles in the air we breathe are linked to an overall increase in risk of death.
The researchers say this kind of air pollution involves particles so small they are invisible to the human eye (at less than one ten-thousandth of an inch in diameter, or no more than 2.5 micrometers across).
In a report on the findings, published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives online Sept. ...
Best candidates for fetal spina bifida surgery may be identified through brain scans
2015-09-15
Fetuses with enlarged ventricles--the fluid-filled cavities inside the brain--may be less likely than other fetuses to benefit from surgery in the womb to treat spina bifida, according to a study co-authored by researchers at UCSF Benioff Children's Hospital San Francisco.
The researchers found that fetuses with enlarged ventricles were more likely to require a second surgery to relieve a life-threatening build-up of pressure within the brain. Given the risks that fetal surgery poses for mother and newborn, the findings indicate that in these cases, it may be better ...
Researchers develop 'instruction manual' for futuristic metallic glass
2015-09-15
Sydney, Australia -- Creating futuristic, next generation materials called 'metallic glass' that are ultra-strong and ultra-flexible will become easier and cheaper, based on UNSW Australia research that can predict for the first time which combinations of metals will best form these useful materials.
Just like something from science fiction - think of the Liquid-Metal Man robot assassin (T-1000) in the Terminator films - these materials behave more like glass or plastic than metal.
While still being metals, they become as malleable as chewing gum when heated and can ...
Virus in cattle linked to human breast cancer
2015-09-15
BERKELEY -- A new study by University of California, Berkeley, researchers establishes for the first time a link between infection with the bovine leukemia virus and human breast cancer.
In the study, published this month in the journal PLOS ONE and available online, researchers analyzed breast tissue from 239 women, comparing samples from women who had breast cancer with women who had no history of the disease for the presence of bovine leukemia virus (BLV). They found that 59 percent of breast cancer samples had evidence of exposure to BLV, as determined by the presence ...
Social media data could contribute to conservation science
2015-09-15
Planning conservation actions requires up-to-date information on
Biodiversity is diminishing at unprecedented rates, and quick decisions are needed in what and where to protect.
"The decisions should be based on comprehensive information, but scientists do not have enough resources to collect more data and effectively monitor all species and habitats that need protection. As human are the main driving force of global change, conservation also needs information on human presence and behaviour" says Enrico Di Minin, a researcher in conservation science at the Department ...
Study finds growing public support in the USA and Canada for smokefree outdoor laws
2015-09-15
A new study has found increasing support in the United States and Canada for smokefree laws for outdoor areas, especially in playgrounds and school grounds.
The collaborative study between the University of Otago, New Zealand and University of Alberta, Canada, provides new and some unexpected insights for health promotion in North America. A key finding is that most residents welcome smokefree laws. Support was strongest for smokefree playgrounds and school grounds, but there was also majority support for a range of other smokefree areas.
University of Otago, Wellington ...
Acetic acid, found in vinegar, shown to be effective against bacteria found in burn wounds
2015-09-15
Highly diluted acetic acid, an active ingredient of household vinegar, has been shown to be an effective alternative agent to prevent infection and kill bacteria found in burn wounds.
Researchers from the University of Birmingham and the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Surgical Reconstruction and Microbiology Research Centre (SRMRC) investigated the antibacterial activity of acetic acid against key burn wound colonising organisms growing both planktonically and as biofilms.
Burns are a common traumatic injury and prone to becoming infected due to loss ...
NASA's SDO catches a double photobomb
2015-09-15
On Sept. 13, 2015, as NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, kept up its constant watch on the sun, its view was photobombed not once, but twice. Just as the moon came into SDO's field of view on a path to cross the sun, Earth entered the picture, blocking SDO's view completely. When SDO's view of the sun emerged from Earth's shadow, the moon was just completing its journey across the sun's face.
Though SDO sees dozens of Earth eclipses and several lunar transits each year, this is the first time ever that the two have coincided. This alignment of the sun, moon and ...
A more acidic ocean will bend the mermaid's wineglass
2015-09-15
New research from the University of Washington's Friday Harbor Laboratories shows that a more acidic ocean can weaken the protective shell of a delicate alga. The findings, published Sept. 9 in the journal Biology Letters, come at a time when global climate change may increase ocean acidification.
The creature in question is Acetabularia acetabulum, commonly called the mermaid's wineglass. Reaching a height of just a few inches, this single-celled alga lives on shallow seafloors, where sunlight can still filter down for photosynthesis. Like many marine creatures, the ...
Crunching numbers to combat cancer
2015-09-15
UC San Francisco has received a National Cancer Institute grant of $5 million over the next five years to lead a massive effort to integrate the data from all experimental models across all types of cancer. The web-based repository is an important step in moving the fight against cancer toward precision medicine.
The goal is to accelerate cancer research to improve the way we diagnose, treat and conduct further research on the disease. The resulting database, called the Oncology Models Forum (OMF), will be accessible to researchers through the National Institutes of ...
New drugs could stop the growth of drug-resistant childhood tumors
2015-09-15
Current drugs may stop working against the most common type of brain tumor in children, medulloblastoma, but the tumor could be targeted in a new way, according to Stanford University scientists.
In research to be published in the journal eLife, a team led by Prof. Matthew P. Scott at the University's School of Medicine tested a drug called Roflumilast in mice with a brain tumor that is resistant to Vismodegib, the drug in current use. Roflumilast is normally used to treat inflammatory lung diseases. It dramatically inhibited tumor growth from the first day of treatment. ...
Research breakthrough in fight against muscle wasting diseases
2015-09-15
This news release is available in French.
Montreal, September 15th 2015 - It is estimated that half of all cancer patients suffer from a muscle wasting syndrome called cachexia. Cancer cachexia impairs quality of life and response to therapy, which increases morbidity and mortality of cancer patients. Currently, there is no approved treatment for muscle wasting but a new study from the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) and University of Alberta could be a game changer for patients, improving both quality of life and longevity. The ...
World loses trillions of dollars worth of nature's benefits each year due to land degradation
2015-09-15
To better inform the tradeoffs involved in land use choices around the world, experts have assessed the value of ecosystem services provided by land resources such as food, poverty reduction, clean water, climate and disease regulation and nutrients cycling.
Their report today estimates the value of ecosystem services worldwide forfeited due to land degradation at a staggering US $6.3 trillion to $10.6 trillion annually, or the equivalent of 10-17% of global GDP.
Furthermore, the problem threatens to force the migration of millions of people from affected areas. ...
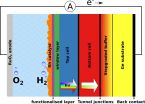
New efficiency record for solar hydrogen production is 14 percent
2015-09-15
Solar energy is abundantly available globally, but unfortunately not constantly and not everywhere. One especially interesting solution for storing this energy is artificial photosynthesis. This is what every leaf can do, namely converting sunlight to chemical energy. That can take place with artificial systems based on semiconductors as well. These use the electrical power that sunlight creates in individual semiconductor components to split water into oxygen and hydrogen. Hydrogen possesses very high energy density, can be employed in many ways and could replace fossil ...
[1] ... [2778]
[2779]
[2780]
[2781]
[2782]
[2783]
[2784]
[2785]
2786
[2787]
[2788]
[2789]
[2790]
[2791]
[2792]
[2793]
[2794]
... [8822]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.