New imaging method reveals if antibiotics reach bacteria hiding in tissues
2021-01-05
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and the University of Western Australia have developed a new imaging method to see where antibiotics have reached bacteria within tissues. The method could be used to help develop more effective antibiotic treatments, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
During bacterial infections like tuberculosis, bacteria enter human cells, which poses a challenge for treatment, as antibiotics must reach and enter all infected cells in order to be effective. If researchers could select for or develop more effective antibiotics based on where they reach, this may reduce the length of treatment ...
DeepTFactor predicts transcription factors
2021-01-05
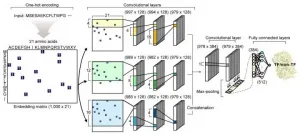
A joint research team from KAIST and UCSD has developed a deep neural network named DeepTFactor that predicts transcription factors from protein sequences. DeepTFactor will serve as a useful tool for understanding the regulatory systems of organisms, accelerating the use of deep learning for solving biological problems.
A transcription factor is a protein that specifically binds to DNA sequences to control the transcription initiation. Analyzing transcriptional regulation enables the understanding of how organisms control gene expression in response to genetic or environmental changes. In this regard, finding the transcription factor of an organism is the first step in the analysis ...
Neither liquid nor solid
2021-01-05
While glass is a truly ubiquitous material that we use on a daily basis, it also represents a major scientific conundrum. Contrary to what one might expect, the true nature of glass remains something of a mystery, with scientific inquiry into its chemical and physical properties still underway. In chemistry and physics, the term glass itself is a mutable concept: It includes the substance we know as window glass, but it may also refer to a range of other materials with properties that can be explained by reference to glass-like behaviour, including, for instance, ...
Impurities boost performance of organic solar cells
2021-01-05
Sunlight offers a potential solution in the search for an energy source that does not harm the planet, but this depends on finding a way to efficiently turn electromagnetic energy into electricity. Researchers from KAUST have shown how a known herbicide can improve this conversion in organic devices.
While solar cells have traditionally been made from inorganic materials such as silicon, organic materials are starting to break through as an alternative because they are light, flexible and relatively inexpensive to make, even offering the possibility for ...
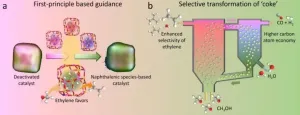
Researchers regenerate deactivated catalyst in methanol-to-olefins process
2021-01-05
MTO process, which was first commercialized in 2010, is a catalytic process converting methanol, which is typically made from coal, natural gas, biomass, and CO2, over SAPO-34 zeolite catalyst. It's becoming one of the main streams for producing light olefins, including ethylene and propylene, from non-oil resources.
One of the major challenges in MTO is the rapid deactivation of zeolite catalyst due to the coke deposition.
In industrial practices, a fluidized bed reactor-regenerator configuration is normally used in order to maintain the continuous operation, in ...
UC-MSC infusion helps repair COVID-19 damage in severe cases
2021-01-05
Dr. Camilo Ricordi, director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, and his team of international collaborators are reporting the results of a groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the most severe COVID-19 patients. Dr. Ricordi's peer-reviewed paper has just been published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine (SCTM) January 2021.
The clinical trial, authorized by the FDA last ...
UC-MSC transfusion helps repair COVID-19 damage in severe cases
2021-01-05
Dr. Camilo Ricordi, director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, and his team of international collaborators are reporting the results of a groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the most severe COVID-19 patients. Dr. Ricordi's peer-reviewed paper has just been published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine (SCTM) January 2021.
The clinical trial, authorized by the FDA last April, was initiated by The Cure Alliance, a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization of research scientists founded ten years ago by Dr. Ricordi for scientists ...
A plant's way to its favorite food
2021-01-05
Like any other plant, Arabidopsis thaliana or mouse-ear cress, needs nitrogen to survive and thrive. But, like maize, beans and sugar beet, it prefers nitrogen in the form of nitrate, growing better on nitrate rich soil. Whereas, pine and rice for example preferentially grow on ammonium nutrition, another form of the key macronutrient nitrogen. If the concentration or the availability of the different forms of nitrogen fluctuate, plants have to adapt quickly. "One of the most important questions is, what is the role of plant hormones in adaptation to the nitrogen availability? How do the machineries within a plant cope with their changing environment?" asks Eva Benková, developmental biologist and Professor at the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria.
Finding the balance
In ...
University of Miami leads groundbreaking trial for COVID-19 treatment
2021-01-05
University of Miami Miller School of Medicine researchers led a unique and groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cell infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the severest COVID-19 patients, according to results published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine in January 2021.
The study's senior author, Camillo Ricordi, M.D., director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, said treating COVID-19 with mesenchymal stem cells makes sense.
Results: treatment group vs. ...
3D-printed smart gel changes shape when exposed to light
2021-01-05
Inspired by the color-changing skin of cuttlefish, octopuses and squids, Rutgers engineers have created a 3D-printed smart gel that changes shape when exposed to light, becomes "artificial muscle" and may lead to new military camouflage, soft robotics and flexible displays.
The engineers also developed a 3D-printed stretchy material that can reveal colors when light changes, according to their study in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Their invention is modeled after the amazing ability of cephalopods such as cuttlefish, octopuses and squids to change the color and texture of their soft skin for camouflage and communication. This is achieved by the ...
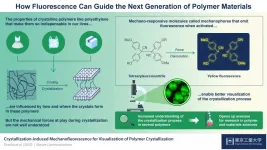
Mechanophores: Making polymer crystallization processes crystal clear
2021-01-05
In modern times, manufacturers produce highly specialized materials for a wide array of uses, called polymers. Polymers have a variety of purposes owing to their versatile properties, ranging from being used in construction due to their high tensile strength and resistance to manufacturing plastic bags that require more lightweight, flexible materials, such as nylon or polyethene.
These differences between the properties of different polymers stems from their internal structure. Polymers are made up of long chains of smaller sub-units, called "monomers." Crystallization occurs when crystalline polymers are melted, then cooled down slowly, which enables the chains to organize themselves into neatly arranged ...
Uncovering how grasslands changed our climate
2021-01-05
Grasslands are managed worldwide to support livestock production, while remaining natural or semi-natural ones provide critical services that contribute to the wellbeing of both people and the planet. Human activities are however causing grasslands to become a source of greenhouse gas emissions rather than a carbon sink. A new study uncovered how grasslands used by humans have changed our climate over the last centuries.
Grasslands are the most extensive terrestrial biome on Earth and are critically important for animal forage, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. They absorb and release carbon dioxide (CO2), and emit methane (CH4) from grazing livestock and nitrous oxide (N2O) from soils, especially when manure or ...
Increase in pleasurable effects of alcohol over time can predict alcohol use disorder
2021-01-05
A new study out of the University of Chicago Medicine following young adult drinkers for 10 years has found that individuals who reported the highest sensitivity to alcohol's pleasurable and rewarding effects at the start of the trial were more likely to develop an alcohol use disorder (AUD) over the course of the study.
Moreover, when retested on their responses 10 years later, those who became alcoholics had the highest levels of alcohol stimulation, liking and wanting - and these were heightened compared to their baseline with no signs of tolerance to these pleasurable effects.
The research, published on Jan. 5 in the American Journal of Psychiatry, followed a ...
Eurasian eagle owl diet reveals new records of threatened giant bush-crickets
2021-01-05
Bird diets provide a real treasure for research into the distribution and conservation of their prey, such as overlooked and rare bush-cricket species, point out scientists after studying the diet of the Eurasian Eagle Owl (Bubo bubo) in southeastern Bulgaria.
In their END ...
The true cost of chemotherapy
2021-01-05
Chemotherapy for breast cancer costs the UK economy more than £248 million annually, including 'out-of-pocket' personal costs of more than £1,000 per patient - according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today is the first to investigate the total non-healthcare cost of chemotherapy to the UK.
It includes the cost of lost productivity, work absence, and personal costs such as paying for transport and parking for treatment, the cost of wigs and new bras, and over the counter medications.
The UEA research team say that better targeting of treatment could help avoid placing unnecessary costs upon patients, their caregivers and wider society.
Prof Richard Fordham, from UEA's ...
State laws promoting flu vaccination for hospital workers may help prevent deaths from flu and pneum
2021-01-05
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. State laws promoting flu vaccination for hospital workers may help prevent deaths from flu and pneumonia
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-0413
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
Research ...
Bacteriophage has important role in agriculture and aquaculture
2021-01-04
New Rochelle, NY, January 4, 2021--Crop plants and animals can be infected by bacterial pathogens that reduce yield, cause food wastage, and carry human pathogens that spread disease on consumption. Bacteriophage can play an important role in microbial control, according to a new Special Issue on Agriculture and Aquaculture published in the peer-reviewed journal PHAGE: Therapy, Applications, and Research. Click here to read the issue.
"Although the number of problems associated with bacterial diseases in agriculture and aquiculture has increased, food producers ...
Reawakened geyser does not foretell Yellowstone volcanic eruptions, study shows
2021-01-04
When Yellowstone National Park's Steamboat Geyser -- which shoots water higher than any active geyser in the world -- reawakened in 2018 after three and a half years of dormancy, some speculated that it was a harbinger of possible explosive volcanic eruptions within the surrounding geyser basin. These so-called hydrothermal explosions can hurl mud, sand and rocks into the air and release hot steam, endangering lives; such an explosion on White Island in New Zealand in December 2019 killed 22 people.
A new study by geoscientists who study geysers throws cold water on that idea, finding few indications of underground magma movement that would be a prerequisite to an eruption. The geysers sit just outside the nation's largest ...
Traditional stereotypes about masculinity may help explain support for Trump
2021-01-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- American politicians have long been expected to uphold a certain veneer: powerful, influential and never vulnerable. New Penn State research has found that these idealized forms of masculinity may also help explain support for Donald Trump in the 2016 presidential election and in the days leading up to the 2020 election.
Across several studies, the researchers found that when men and women endorsed "hegemonic masculinity" -- a culturally idealized form of masculinity that says men should be strong, tough, and dominant -- they were more likely to vote for and have positive feelings about Trump.
The researchers found this was true ...
Scientists develop new approach to understanding massive volcanic eruptions
2021-01-04
A geosciences team led by the University of South Florida (USF) has developed a new way to reconstruct the sizes of volcanic eruptions that occurred thousands of years ago, creating a first-of-its kind tool that can aid scientists in understanding past explosive eruptions that shaped the earth and improve the way of estimating hazards of future eruptions.
The advanced numerical model the USF team developed allows scientists to reconstruct eruption rates through time by estimating the dimensions of the umbrella clouds that contribute to the accumulation ...
One in four doctors attacked, harassed on social media
2021-01-04
CHICAGO --- While many physicians benefit from social media by networking with potential collaborators or interfacing with patients, a new study from Northwestern University and the University of Chicago found many physicians also report being sexually harassed and personally attacked on these platforms on the basis of their religion, race or medical recommendations.
Although the data were collected before the COVID-19 outbreak, the findings highlight the intensity of online harassment before the pandemic, which has only intensified since the spring, the study authors said.
"If anything, our data is likely an underestimate of the true ...
More women embracing 'going flat' after mastectomy
2021-01-04
LOS ANGELES -- A growing number of women forgoing reconstruction after a mastectomy say they're satisfied with their choice, even as some did not feel supported by their physician, according to a study led by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The study, published in the Journal Annals of Surgical Oncology, surveyed 931 women who had a unilateral or bilateral mastectomy without current breast mound reconstruction to assess the motivating factors for forgoing the procedure and to measure whether surgeons provided adequate information and support for "going flat."
Out of the women surveyed, 74% were satisfied with their outcome and 22% experienced "flat denial," where the procedure was not initially offered, the ...
Focusing on diversion yields positive results for kids with behavioral issues
2021-01-04
Of the 5,300 children enrolled in the Ohio Behavioral Health Juvenile Justice Initiative since 2006, 21% reported that someone close them had been murdered in the past year. Nearly half of the boys and more than a quarter of the girls in the program have both a substance abuse and mental health disorder.
But there's good news, too: From 2017 through 2019, 81% of the participants--aged 10 through 17--successfully completed the state's juvenile diversion program, and data indicated that 79% of youth reduced their contact with police while in treatment.
Those findings are from a new detailed evaluation of the Ohio Behavioral Health Juvenile Justice Initiative (BHJJ) by researchers at the Jack, Joseph and ...
Gas pressure depletion and seismicity
2021-01-04
Boulder, Colo., USA: Europe's largest gas field, the Groningen field in the Netherlands, is widely known for induced subsidence and seismicity caused by gas pressure depletion and associated compaction of the sandstone reservoir. Whether compaction is elastic or partly inelastic, as implied by recent experiments, is key to forecasting system behavior and seismic hazard.
Bart Verberne and colleagues sought evidence for a role of inelastic deformation through comparative microstructural analysis of unique drill-core, recovered from the seismogenic center of the field in 2015, 50 years after gas production started, versus core recovered before production (1965). Quartz grain fracturing, crack healing, and stress-induced Dauphiné twinning are ...
Study resolves long-running controversy over critical step in gene silencing
2021-01-04
BOSTON - A long-running debate over how an important gene-silencing protein identifies its targets has been resolved by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). Their findings, reported in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, also explain certain mysteries about the behavior of this protein, known as Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2).
PRC2 helps regulate whether genes are active ("on) or silent ("off"). PRC2's role in gene silencing is critical throughout the lifespan, from embryo formation to old age. For example, PRC2 determines whether genes that suppress the growth of malignant tumors are turned on or off, which has made it the focus of pharmaceutical companies ...
[1] ... [2781]
[2782]
[2783]
[2784]
[2785]
[2786]
[2787]
[2788]
2789
[2790]
[2791]
[2792]
[2793]
[2794]
[2795]
[2796]
[2797]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.