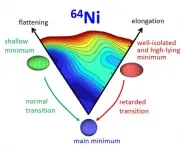
The map of nuclear deformation takes the form of a mountain landscape
2021-01-02
Kraków, 30 December 2020
The map of nuclear deformation takes the form of a mountain landscape
Until recently, scientists believed that only very massive nuclei could have excited zero-spin states of increased stability with a significantly deformed shape. Meanwhile, an international team of researchers from Romania, France, Italy, the USA and Poland showed in their latest article that such states also exist in much lighter nickel nuclei. Positive verification of the theoretical model used in these experiments allows describing the properties of nuclei unavailable in Earth laboratories.
More than ...
LSU Health New Orleans discovers potential new RX strategy for stroke
2021-01-02
New Orleans, LA - Research conducted at LSU Health New Orleans Neuroscience Center of Excellence reports that a combination of an LSU Health-patented drug and selected DHA derivatives is more effective in protecting brain cells and increasing recovery after stroke than a single drug. The findings are published in Brain Circulation, available here.
Nicolas Bazan, MD, PhD, Boyd Professor, Professor of Neurology and Director of the Neuroscience Center of Excellence at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, and Ludmila ...
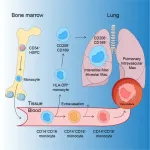
New research may explain severe virus attacks on the lungs
2021-01-02
In some cases, immune cells in the lungs can contribute to worsening a virus attack. In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden describe how different kinds of immune cells, called macrophages, develop in the lungs and which of them may be behind severe lung diseases. The study, which was published in Immunity, may contribute to future treatments for COVID-19, among other diseases.
The structure of the lungs exposes them to viruses and bacteria from both the air and the blood. Macrophages are immune cells that, among other things, protect the lungs from such attacks. ...
Scientists explore deficits in processing speed in individuals with spinal cord injury
2021-01-02
East Hanover, NJ. December 30, 2020. A team of rehabilitation researchers has studied processing speed deficits in individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI), comparing their brain activation patterns with those of healthy age-matched controls, and older healthy individuals. They found that the SCI group and older controls had similar activation patterns, but the SCI group differed significantly from their age-matched controls.
The article, "The neural mechanisms underlying processing speed deficits in individuals who have sustained a spinal cord injury: A pilot study" (doi: 10.1007/s10548-020-00798-x) was ...
Published data from Moderna COVID-19 vaccine trial show 94.1 percent efficacy
2021-01-02
BOSTON -- A peer-reviewed paper published in The New England Journal of Medicine provides data from the much-anticipated COVE study, which evaluated mRNA-1273, a vaccine candidate against COVID-19 manufactured by Moderna, Inc. Results from the primary analysis of the study, which will continue for two years, provide evidence that the vaccine can prevent symptomatic infection. Among the more than 30,000 participants randomized to receive the vaccine or a placebo, 11 of those in the vaccine group developed symptomatic COVID-19 compared to 185 participants who received the placebo, demonstrating 94.1 percent efficacy in preventing symptomatic COVID-19. Cases ...
How did trauma centers respond to COVID-19? New processes provide care to trauma patients while keeping providers safe
2021-01-02
December 30, 2020 - As the COVID-19 pandemic emerged, trauma centers faced unprecedented obstacles to providing care for injured patients. A look at steps taken by trauma centers in response to COVID-19 is provided by a survey in the January/February Journal for Healthcare Quality (JHQ), the peer-reviewed journal of the National Association for Healthcare Quality (NAHQ). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Trauma centers introduced new processes to optimize use of personal protective equipment (PPE), ICU beds, ventilators, and other limited resources, according to the report by David Bar-Or, MD, of ION Research, Englewood, Colo., ...
Peer-reviewed report on Moderna COVID-19 vaccine publishes
2021-01-02
WHAT:
The investigational vaccine known as mRNA-1273 was 94.1% efficacious in preventing symptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), according to preliminary results from a Phase 3 clinical trial reported in the New England Journal of Medicine. The vaccine also demonstrated efficacy in preventing severe COVID-19. Investigators identified no safety concerns and no evidence of vaccine-associated enhanced respiratory disease (VAERD).
The vaccine was co-developed by Moderna, Inc., a biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes ...
DUAL takes AI to the next level
2021-01-02
"Today's computer applications generate a large amount of data that needs to be processed by machine learning algorithms," says Yeseong Kim of Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST), who led the effort.
Powerful 'unsupervised' machine learning involves training an algorithm to recognize patterns in large datasets without providing labelled examples for comparison. One popular approach is a clustering algorithm, which groups similar data into different classes. These algorithms are used for a wide variety of data analyses, such as identifying fake news on social media, filtering spam in our e-mails, and detecting ...
Blood vessel cells implicated in chronic inflammation of obesity
2021-01-02
DALLAS - Dec. 30, 2020 - When fat cells in the body are stuffed with excess fat, the surrounding tissue becomes inflamed. That chronic, low-level inflammation is one of the driving factors behind many of the diseases associated with obesity. Now, UT Southwestern scientists have discovered a type of cell responsible, at least in mice, for triggering this inflammation in fat tissue. Their findings, published in Nature Metabolism, could eventually lead to new ways to treat obesity.
"The inflammation of fat cells in obese individuals is linked to many of the ...
Bionic idea boosts lithium-ion extraction
2021-01-02
Lithium is an energy-critical element that is considered to be a geopolitically significant resource. However, the supply of lithium may not be enough to meet continuously increasing demand. As a result, scientists are looking for new ways to extract lithium ions.
Ion selective membranes have already been used extensively for water treatment and ion sieving in electrodialysis technology. However, conventional membranes exhibit low and useless Li+ selectivity, making them insufficient for meeting industry requirements.
Chinese scientists have recently made progress in the preparation and application of a bioinspired ...
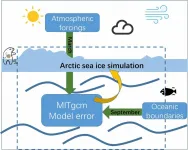
Scientists find the error source of a sea-ice model varies with the season
2021-01-02
Arctic sea ice has been rapidly declining in recent decades, and changes in arctic sea ice can have a significant impact on global weather and climate through interactions with the atmosphere and oceans. In addition, the Arctic shipping routes are a shortcut to connect the major countries in the Northern Hemisphere. The Arctic region is also rich in natural resources and biological resources. Simulation of the Arctic sea ice could provide valuable information for Arctic shipping as well as climate studies, and it is therefore urgent to evaluate the ability to simulate Arctic sea ice and diagnose the sources of simulation errors.
To address the issue of error source identification, ...
See live cells with 7 times greater sensitivity using new microscopy technique
2021-01-02
Experts in optical physics have developed a new way to see inside living cells in greater detail using existing microscopy technology and without needing to add stains or fluorescent dyes.
Since individual cells are almost translucent, microscope cameras must detect extremely subtle differences in the light passing through parts of the cell. Those differences are known as the phase of the light. Camera image sensors are limited by what amount of light phase difference they can detect, referred to as dynamic range.
"To see greater detail using the same image sensor, we must expand the dynamic range so that we can ...
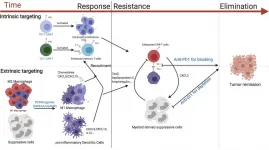
Combined approach could boost breast cancer immunotherapy, study suggests
2021-01-02
Activating an immune signaling pathway best known for fighting viral and bacterial infections can boost the ability of genetically engineered T cells to eradicate breast cancer in mice, according to a new study by researchers at the University of North Carolina. The study, to be published December 31 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), suggests that CAR T cells, which are already used to treat certain blood cancers in humans, may also be successful against solid tumors if combined with other immunotherapeutic approaches.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells are a type of white blood cell that have been genetically engineered to recognize ...
Asian tiger mosquito poses low risk for Zika virus outbreaks
2021-01-02
The Asian tiger mosquito does not pose a major risk for Zika virus epidemics, according to a study published December 31 in the open-access journal PLOS Pathogens by Albin Fontaine of the Institut de Recherche Biomédicale des Armées, and colleagues.
Zika virus has triggered large outbreaks in human populations, in some cases causing congenital deformities, fetal loss, or neurological problems in adults. While the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti is considered the primary vector of Zika ...
New virtual screening strategy identifies existing drug that inhibits Covid-19 virus
2021-01-02
A novel computational drug screening strategy combined with lab experiments suggest that pralatrexate, a chemotherapy medication originally developed to treat lymphoma, could potentially be repurposed to treat Covid-19. Haiping Zhang of the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology in Shenzhen, China, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology.
With the Covid-19 pandemic causing illness and death worldwide, better treatments are urgently needed. One shortcut could be to repurpose existing drugs that were originally developed to ...
Multiple mosquito blood meals accelerate malaria transmission
2021-01-02
Multiple bouts of blood feeding by mosquitoes shorten the incubation period for malaria parasites and increase malaria transmission potential, according to a study published December 31 in the open-access journal PLOS Pathogens by Lauren Childs of Virginia Tech, Flaminia Catteruccia of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, and colleagues. Given that mosquitoes feed on blood multiple times in natural settings, the results suggest that malaria elimination may be substantially more challenging than suggested by previous experiments, which typically involve a single blood meal.
Malaria ...
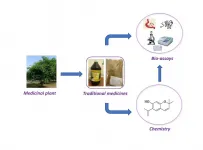
Traditional Ghanaian medicines show promise against tropical diseases
2021-01-02
The discovery of new drugs is vital to achieving the eradication of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) in Africa and around the world. Now, researchers reporting in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases have identified traditional Ghanaian medicines which work in the lab against schistosomiasis, onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis, three diseases endemic to Ghana.
The major intervention for NTDs in Ghana is currently mass drug administration of a few repeatedly recycled drugs, which can lead to reduced efficacy and the emergence of drug resistance. Chronic infections of schistosomiasis, onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis ...
New mutations in malaria parasite encourage resistance against key preventive drug
2021-01-02
In the ongoing arms race between humans and the parasite that causes malaria, Taane Clark and colleagues at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) report that new mutations that enhance resistance to a drug used to prevent malaria in pregnant women and children are already common in countries fighting the disease. The new results are published December 31 in PLOS Genetics.
Malaria causes about 435,000 deaths each year, primarily in young children in sub-Saharan Africa. Despite a long-term global response, efforts to control the disease are hampered by the rise of drug-resistant strains of the parasite species that cause malaria. Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP), ...
Controlling the nanoscale structure of membranes is key for clean water, researchers find
2021-01-02
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A desalination membrane acts as a filter for salty water: push the water through the membrane, get clean water suitable for agriculture, energy production and even drinking. The process seems simple enough, but it contains complex intricacies that have baffled scientists for decades -- until now.
Researchers from Penn State, The University of Texas at Austin, Iowa State University, Dow Chemical Company and DuPont Water Solutions published a key finding in understanding how membranes actually filter minerals from water, online today (Dec. 31) in Science. The article will be featured on the print edition's cover, to be issued tomorrow (Jan. ...
Spontaneous robot dances highlight a new kind of order in active matter
2021-01-02
Predicting when and how collections of particles, robots, or animals become orderly remains a challenge across science and engineering.
In the 19th century, scientists and engineers developed the discipline of statistical mechanics, which predicts how groups of simple particles transition between order and disorder, as when a collection of randomly colliding atoms freezes to form a uniform crystal lattice.
More challenging to predict are the collective behaviors that can be achieved when the particles ...
New proposal for how aerosols drive increased atmospheric convection in thunderstorm clouds
2021-01-02
High in the clouds, atmospheric aerosols, including anthropogenic air pollutants, increase updraft speeds in storm clouds by making the surrounding air more humid, a new study finds. The results offer a new mechanism explaining the widely observed - but poorly understood - atmospheric phenomenon and provide a physical basis for predicting increasing thunderstorm intensity, particularly in the high-aerosol regions of the tropics. Observations worldwide have highlighted aerosols' impact on weather, including their ability to strengthen convection in deep convective clouds, like those ...
Model predicts global threat of sinking land will affect 635 million people worldwide
2021-01-02
A new analysis suggests that, by 2040, 19% of the world's population - accounting for 21% of the global Gross Domestic Product - will be impacted by subsidence, the sinking of the ground's surface, a phenomenon often caused by human activities such as groundwater removal, and by natural causes as well. The results, reported in a Policy Forum, represent "a key first step toward formulating effective land-subsidence policies that are lacking in most countries worldwide," the authors say. Gerardo Herrera Garcia et al. performed a large-scale ...
COVID-19's impact on cancer prevention and control in Africa
2021-01-02
When the COVID-19 pandemic reached Africa, the continent was already struggling to deal with another public health crisis - a growing cancer epidemic characterized by more than one million new cancer cases and nearly 700,000 deaths per year. In a Perspective, Beatrice Wiafe Addai and Wilfred Ngwa discuss the significant challenges COVID-19 imposed on cancer prevention and control in Africa and how the efforts to address these challenges highlight key opportunities where greater investment could improve cancer care globally. At the start of the pandemic, many African ...
Microfabricated elastic diamonds improve material's electronic properties
2021-01-02
Overcoming a key obstacle in achieving diamond-based electronic and optoelectronic devices, researchers have presented a new way to fabricate micrometer-sized diamonds that can elastically stretch. Elastic diamonds could pave the way for advanced electronics, including semiconductors and quantum information technologies. In addition to being the hardest materials in nature, diamonds have exceptional electronic and photonic properties, featuring both ultrahigh thermal and electric conductivity. Not only would diamond-based electronics dissipate heat more quickly, reducing the need for ...
Study points the way to boost immunotherapy against breast cancer, other solid tumors
2021-01-02
CHAPEL HILL, NC--Boosting immune system T cells to effectively attack solid tumors, such as breast cancers, can be done by adding a small molecule to a treatment procedure called chimeric antigen receptor-T (CAR-T) cell therapy, according to a study by researchers at the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center. The boost helps recruit more immune cells into battle at the tumor site. The findings are published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
CAR-T immunotherapy, in which T cells are modified in the laboratory to express chimeric antigen receptors, CARs, that in turn target surface proteins ...
[1] ... [2787]
[2788]
[2789]
[2790]
[2791]
[2792]
[2793]
[2794]
2795
[2796]
[2797]
[2798]
[2799]
[2800]
[2801]
[2802]
[2803]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.