Researchers develop 'instruction manual' for futuristic metallic glass
2015-09-15
Sydney, Australia -- Creating futuristic, next generation materials called 'metallic glass' that are ultra-strong and ultra-flexible will become easier and cheaper, based on UNSW Australia research that can predict for the first time which combinations of metals will best form these useful materials.
Just like something from science fiction - think of the Liquid-Metal Man robot assassin (T-1000) in the Terminator films - these materials behave more like glass or plastic than metal.
While still being metals, they become as malleable as chewing gum when heated and can ...
Virus in cattle linked to human breast cancer
2015-09-15
BERKELEY -- A new study by University of California, Berkeley, researchers establishes for the first time a link between infection with the bovine leukemia virus and human breast cancer.
In the study, published this month in the journal PLOS ONE and available online, researchers analyzed breast tissue from 239 women, comparing samples from women who had breast cancer with women who had no history of the disease for the presence of bovine leukemia virus (BLV). They found that 59 percent of breast cancer samples had evidence of exposure to BLV, as determined by the presence ...
Social media data could contribute to conservation science
2015-09-15
Planning conservation actions requires up-to-date information on
Biodiversity is diminishing at unprecedented rates, and quick decisions are needed in what and where to protect.
"The decisions should be based on comprehensive information, but scientists do not have enough resources to collect more data and effectively monitor all species and habitats that need protection. As human are the main driving force of global change, conservation also needs information on human presence and behaviour" says Enrico Di Minin, a researcher in conservation science at the Department ...
Study finds growing public support in the USA and Canada for smokefree outdoor laws
2015-09-15
A new study has found increasing support in the United States and Canada for smokefree laws for outdoor areas, especially in playgrounds and school grounds.
The collaborative study between the University of Otago, New Zealand and University of Alberta, Canada, provides new and some unexpected insights for health promotion in North America. A key finding is that most residents welcome smokefree laws. Support was strongest for smokefree playgrounds and school grounds, but there was also majority support for a range of other smokefree areas.
University of Otago, Wellington ...
Acetic acid, found in vinegar, shown to be effective against bacteria found in burn wounds
2015-09-15
Highly diluted acetic acid, an active ingredient of household vinegar, has been shown to be an effective alternative agent to prevent infection and kill bacteria found in burn wounds.
Researchers from the University of Birmingham and the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Surgical Reconstruction and Microbiology Research Centre (SRMRC) investigated the antibacterial activity of acetic acid against key burn wound colonising organisms growing both planktonically and as biofilms.
Burns are a common traumatic injury and prone to becoming infected due to loss ...
NASA's SDO catches a double photobomb
2015-09-15
On Sept. 13, 2015, as NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, kept up its constant watch on the sun, its view was photobombed not once, but twice. Just as the moon came into SDO's field of view on a path to cross the sun, Earth entered the picture, blocking SDO's view completely. When SDO's view of the sun emerged from Earth's shadow, the moon was just completing its journey across the sun's face.
Though SDO sees dozens of Earth eclipses and several lunar transits each year, this is the first time ever that the two have coincided. This alignment of the sun, moon and ...
A more acidic ocean will bend the mermaid's wineglass
2015-09-15
New research from the University of Washington's Friday Harbor Laboratories shows that a more acidic ocean can weaken the protective shell of a delicate alga. The findings, published Sept. 9 in the journal Biology Letters, come at a time when global climate change may increase ocean acidification.
The creature in question is Acetabularia acetabulum, commonly called the mermaid's wineglass. Reaching a height of just a few inches, this single-celled alga lives on shallow seafloors, where sunlight can still filter down for photosynthesis. Like many marine creatures, the ...
Crunching numbers to combat cancer
2015-09-15
UC San Francisco has received a National Cancer Institute grant of $5 million over the next five years to lead a massive effort to integrate the data from all experimental models across all types of cancer. The web-based repository is an important step in moving the fight against cancer toward precision medicine.
The goal is to accelerate cancer research to improve the way we diagnose, treat and conduct further research on the disease. The resulting database, called the Oncology Models Forum (OMF), will be accessible to researchers through the National Institutes of ...
New drugs could stop the growth of drug-resistant childhood tumors
2015-09-15
Current drugs may stop working against the most common type of brain tumor in children, medulloblastoma, but the tumor could be targeted in a new way, according to Stanford University scientists.
In research to be published in the journal eLife, a team led by Prof. Matthew P. Scott at the University's School of Medicine tested a drug called Roflumilast in mice with a brain tumor that is resistant to Vismodegib, the drug in current use. Roflumilast is normally used to treat inflammatory lung diseases. It dramatically inhibited tumor growth from the first day of treatment. ...
Research breakthrough in fight against muscle wasting diseases
2015-09-15
This news release is available in French.
Montreal, September 15th 2015 - It is estimated that half of all cancer patients suffer from a muscle wasting syndrome called cachexia. Cancer cachexia impairs quality of life and response to therapy, which increases morbidity and mortality of cancer patients. Currently, there is no approved treatment for muscle wasting but a new study from the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) and University of Alberta could be a game changer for patients, improving both quality of life and longevity. The ...
World loses trillions of dollars worth of nature's benefits each year due to land degradation
2015-09-15
To better inform the tradeoffs involved in land use choices around the world, experts have assessed the value of ecosystem services provided by land resources such as food, poverty reduction, clean water, climate and disease regulation and nutrients cycling.
Their report today estimates the value of ecosystem services worldwide forfeited due to land degradation at a staggering US $6.3 trillion to $10.6 trillion annually, or the equivalent of 10-17% of global GDP.
Furthermore, the problem threatens to force the migration of millions of people from affected areas. ...
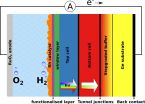
New efficiency record for solar hydrogen production is 14 percent
2015-09-15
Solar energy is abundantly available globally, but unfortunately not constantly and not everywhere. One especially interesting solution for storing this energy is artificial photosynthesis. This is what every leaf can do, namely converting sunlight to chemical energy. That can take place with artificial systems based on semiconductors as well. These use the electrical power that sunlight creates in individual semiconductor components to split water into oxygen and hydrogen. Hydrogen possesses very high energy density, can be employed in many ways and could replace fossil ...
Researchers explore cocoa as novel dietary source for prevention of cognitive deterioration in AD
2015-09-15
Amsterdam, NL, September 9, 2015 - The potential benefits of dietary cocoa extract and/or its final product in the form of chocolate have been extensively investigated in regard to several aspects of human health. Cocoa extracts contain polyphenols, which are micronutrients that have many health benefits, including reducing age-related cognitive dysfunction and promoting healthy brain aging, among others.
Dr. Giulio Maria Pasinetti, MD, PhD, Saunders Family Chair and Professor of Neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Director of Biomedical Training ...
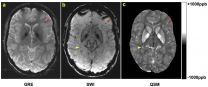
MRI improves diagnosis of microbleeding after brain injury in military personnel
2015-09-15
OAK BROOK, Ill. - Imaging patients soon after traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs can lead to better (more accurate) detection of cerebral microhemorrhages, or microbleeding on the brain, according to a study of military service members, published online in the journal Radiology.
Cerebral microhemorrhages occur as a direct result of TBI and can lead to severe secondary injuries such as brain swelling or stroke. The ability to monitor the evolution of microhemorrhages could provide important information regarding disease progression or recovery.
According to the Centers ...
Effects of prenatal myelomeningocele closure on the need for a CSF shunt
2015-09-15
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (SEPTEMBER 15, 2015). Management of Myelomeningocele Study (MOMS) investigators analyzed updated data on the effects of prenatal myelomeningocele closure on the need for placement of a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunt within the first 12 months of life. These researchers reaffirm the initial MOMS finding that prenatal repair of a myelomeningocele results in less need for a shunt at 12 months and introduce the new finding that prenatal repair reduces the need for shunt revision in those infants who do require shunt placement. The researchers also found ...
Link between air pollution, increased deaths and increased deaths from heart disease affirmed
2015-09-15
In what is believed to be the largest, most detailed study of its kind in the United States, scientists at NYU Langone Medical Center and elsewhere have confirmed that tiny chemical particles in the air we breathe are linked to an overall increase in risk of death.
The researchers say this kind of air pollution involves particles so small they are invisible to the human eye (at less than one ten-thousandth of an inch in diameter, or no more than 2.5 micrometers across).
In a report on the findings, published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives online Sept. ...
'Our chairs are killing us,' say researchers
2015-09-15
Amsterdam, The Netherlands, September 15, 2015 -- Prolonged sitting time as well as reduced physical activity contribute to the prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a study of middle-aged Koreans. These findings support the importance of both reducing time spent sitting and increasing physical activity, say researchers. Their results are published in the Journal of Hepatology.
Physical activity is known to reduce the incidence and mortality of various chronic diseases. However, more than one half of the average person's waking day involves sedentary ...
Combining epigenetic therapies with immunotherapies likely to improve cancer patient outcomes
2015-09-15
PHILADELPHIA -- Recent data suggest that epigenetic therapies are likely to provide additional clinical benefit to cancer patients when rationally combined with immunotherapeutic drugs, according to a review published in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"The term epigenetics refers to the study of cellular changes in gene expression that are heritably transmitted during cell replication," said Michele Maio, MD, PhD, chair of medical oncology and immunotherapy, Ospedale Santa Maria alle Scotte, Istituto Toscano Tumori, ...
Video game warnings fall far short in rating tobacco content
2015-09-15
Video games are not adequately rated for tobacco content, according to a new UC San Francisco study that found video gamers are being widely exposed to tobacco imagery.
The researchers concluded that a national ratings board set up more than 20 years ago is not a reliable source for learning whether video games contain tobacco imagery.
The study will be published online September 14 in Tobacco Control.
"Parents should stop relying on the ratings to screen for tobacco use in buying video games for their kids," said first author Susan Forsyth, a PhD candidate at ...
Heightened injury risk linked to shift length for emergency services clinicians
2015-09-15
Working shifts of 16 to 24 hours in length is linked to a 60% heightened risk of injury and illness among emergency services (EMS) clinicians, compared to shifts of 8-12 hours, finds research published online in Occupational & Environmental Medicine.
This risk rises in tandem with shift length, the findings show.
The nature of the job requires physical strength to lift and move patients, clear mental focus to deliver medical care in uniquely stressful and often chaotic situations, and sufficient alertness to drive safely, say the researchers.
Yet EMS clinicians often ...
Widely used software doesn't note differences in care quality among hospital readmissions
2015-09-15
The 3M software program, increasingly used to make payments to US hospitals based on readmission rates, doesn't clearly distinguish differences in care quality--one of the key factors involved in readmission--between readmissions that are preventable and those that aren't, suggests research published online in BMJ Quality and Safety.
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) posts data on 30 day readmissions for three common causes of hospital admissions: heart attack; heart failure; and pneumonia.
Hospitals with high rates of readmissions are penalised ...
Study suggests improving blood sugar control could help prevent dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes
2015-09-15
A study of 350,000 patients with type 2 diabetes shows that those with poor blood sugar control have 50% higher risk of being admitted to hospital in future for dementia as those with good control. The research, which suggests improving blood sugar control could prevent many cases of dementia, is by Dr Aidin Rawshani, National Diabetes Register and Institute of Medicine, Gothenburg, Sweden, and colleagues, and is presented at this year's annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Stockholm.
Evidence is growing that diabetes increases ...
Diabetic women at 34 percent higher risk of heart attack than diabetic men as they age
2015-09-15
New research presented at this year's annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes in Stockholm shows that diabetic women are more at risk than diabetic men of having a heart attack and other complications as they age. The study is by Dr Giuseppe Seghieri, Regional Health Agency, Florence, Italy, and colleagues.
Previous research has revealed that diabetic women have a higher risk of cardiovascular events than diabetic men, when compared with the respective non-diabetic counterparts. However, it is unclear when this risk begins or how long it ...
Studies covering 11 million patients show diabetic women around 40 percent more likely to suffer severe heart problems than diabetic men
2015-09-15
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 19 studies containing almost 11 million patients shows that diabetic women are around 40% more likely to suffer acute coronary syndromes (heart attack or angina) than diabetic men. The study is by Dr Xue Dong, the Affiliated ZhongDa Hospital of Southeast University, Nanjing, China, and colleagues, and is presented at this year's annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Stockholm.
Diabetes is a strong risk factor for acute coronary syndrome, yet whether diabetes confers the same excess risk ...
The Lancet: Study reveals England's improving health performance compared to other wealthy countries
2015-09-15
In 2013, England performed better than average on a variety of key health outcomes compared with 18 other high-income countries in the European Union [1], and Australia, Canada, Norway, and the USA (EU15+), according to new research published in The Lancet.
However, the findings also reveal the impact of substantial health disparities within English regions, the significant toll of chronic disabling conditions, and the importance of tackling preventable diseases. It is likely that around 40% of NHS workload is due to potentially preventable risk factors.
Using data ...
[1] ... [2788]
[2789]
[2790]
[2791]
[2792]
[2793]
[2794]
[2795]
2796
[2797]
[2798]
[2799]
[2800]
[2801]
[2802]
[2803]
[2804]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.