World's turtles face plastic deluge danger
2015-09-14
An international study led by a University of Queensland researcher has revealed more than half the world's sea turtles have ingested plastic or other human rubbish.
The study, led by Dr Qamar Schuyler from UQ's School of Biological Sciences, found the east coasts of Australia and North America, Southeast Asia, southern Africa, and Hawaii were particularly dangerous for turtles due to a combination of debris loads and high species diversity.
"The results indicate that approximately 52 per cent of turtles world-wide have eaten debris," Dr Schuyler said.
The study ...
Elite tennis players feel the heat at Australian Open as summers intensify
2015-09-14
Melbourne summer temperatures have been steadily climbing over the past 25 years, but even more so during the two weeks of the Australian Open in late January, new data analysis reveals.
The average afternoon temperature in January has risen by 0.8 degrees Celsius per decade since 1987. But in the two weeks of the Australian Open - usually held in mid-late January - temperatures have increased by 1.25 degrees per decade.
Ben Hague, a third-year Atmosphere and Ocean Sciences student at the University of Melbourne, said extreme summer temperatures have also become more ...
Does social capital explain community-level differences in organ donor designation?
2015-09-14
MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, Mass. (Sept. 14, 2015)--A new study finds that the characteristics of one's community may be as important as individual factors on the decision to become an organ donor. The study, published in The Milbank Quarterly, shows an association between sociodemographic/social capital measures and organ donor registrations across 4,466 Massachusetts neighborhoods. In order to increase organ donation registrations, the research suggests that future health policies adopt a community-level focus.
The shortage of organs for transplantation has reached unprecedented ...
World has lost 3 percent of its forests since 1990
2015-09-14
The globe's forests have shrunk by three per cent since 1990 - an area equivalent to the size of South Africa - despite significant improvements in conservation over the past decade.
The UN's Global Forest Resources Assessment (GFRA) 2015 was released this week, revealing that while the pace of forest loss has slowed, the damage over the past 25 years has been considerable.
Total forest area has declined by three per cent between 1990 and 2015 from 4,128 million hectares to 3,999 million hectares - a loss of 129 million hectares.
Significantly, loss of natural forested ...
Alzheimer's-disease-related proteases control axonal guidance by regulating growth cone dynamics
2015-09-14
Alzheimer's-disease-related proteases, BACE1 and APH1B-y-secretase, control axonal guidance by regulating growth cone dynamics
BACE1 is the major drug target for Alzheimer's disease, but we know surprisingly little about its normal function in the CNS. Soraia Barão and Bart De Strooper (VIB/KU Leuven) now show that this protease is critically involved in axonal guidance processes in thalamic and hippocampal neurons. An active membrane bound proteolytic CHL1 fragment is generated by BACE1 upon Sema3A binding. This fragment relays the Sema3A signal to the neuronal ...
Long sleep and high blood copper levels go hand in hand
2015-09-14
Persons sleeping less than 6 hours or more than 10 hours suffer from low-grade inflammation more often than persons sleeping 7-8 hours per night. This was observed in a University of Eastern Finland study focusing on the health and lifestyle habits among middle-aged men.
"Earlier studies have found a relation between reduced sleep and low-grade inflammation," says Maria Luojus, MHSc, one of the study researchers.
Furthermore, low-grade inflammation occurs in overweight, depression and diabetes.
The study is the first to analyse the association between sleep duration ...
20-year follow-up of academic EORTC boost no-boost trial earns Best Abstract at ECC 2015
2015-09-14
Results of a 20-year follow-up of the academic EORTC 22881-10882 boost no-boost trial presented as a "Best Abstract" at the European Cancer Congress 2015 in Vienna show that young age, high-grade invasive tumor, and the presence of associated ductal carcinoma in situ were all factors increasing the local recurrence rate. An earlier analysis had already shown that young age and high-grade invasive carcinoma were the most important risk factors for local relapse in this trial conducted from 1989 to 1996.
Dr. Conny Vrieling of the Clinique des Grangettes in Geneva, Switzerland, ...
Smokers at higher risk of losing their teeth, research shows
2015-09-14
A new study has confirmed that regular smokers have a significantly increased risk of tooth loss.
Male smokers are up to 3.6 times more likely to lose their teeth than non-smokers, whereas female smokers were found to be 2.5 times more likely.
The research, published in the Journal of Dental Research, is the output of a long-term longitudinal study of the EPIC Potsdam cohort in Germany carried out by researchers at the University of Birmingham and the German Institute of Human Nutrition.
Tooth loss remains a major public health problem worldwide. In the UK, 15% of ...
Nutritional deficiencies common before weight loss surgery
2015-09-14
Malnutrition is a known complication of weight loss surgery, but findings from a small study by researchers at Johns Hopkins show many obese people may be malnourished before they undergo the procedure.
"Our results highlight the often-overlooked paradox that abundance of food and good nutrition are not one and the same," says senior investigator Kimberley Steele, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor of surgery at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. "Overweight and obese people can suffer from nutritional deficiencies, and those who care for them should be aware ...
An even more versatile optical chip
2015-09-14
Telecommunication networks will soon reach the physical limits of current technology and in order to overcome the current bottleneck, they will have to exploit the quantum properties of light. Roberto Morandotti and his INRS team are paving the way to this technological revolution by removing the technical barriers of quantum photonics through the use of their optical chips. Recently they directly generated cross-polarized (orthogonal) photon pairs on a chip, a first in quantum optics. Polarization will now be among the controllable parameters for harnessing light in a ...
Swinging on 'monkey bars': Motor proteins caught in the act
2015-09-14
The first images of motor proteins in action are published in the journal Nature Communications today.
These proteins are vital to complex life, forming the transport infrastructure that allows different parts of cells to specialise in particular functions. Until now, the way they move has never been directly observed.
Researchers at the University of Leeds and in Japan used electron microscopes to capture images of the largest type of motor protein, called dynein, during the act of stepping along its molecular track.
Dr Stan Burgess, at the University of Leeds' ...
Elephants born when mothers are stressed age faster and produce fewer offspring
2015-09-14
Elephants born into stressful situations have fewer offspring and age faster, researchers at the University of Sheffield have found.
Scientists discovered that Asian elephants born during times when their mothers experience highest stress levels produce significantly fewer offspring in their lifetime despite having higher rates of reproduction at an early age.
The research team, from the University's Department of Animal and Plant Sciences, also found that those animals born under stress declined much more rapidly in older age, decades later.
Lead author Dr Hannah ...
Mediterranean diet plus olive oil associated with reduced breast cancer risk
2015-09-14
Eating a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra virgin olive oil was associated with a relatively lower risk of breast cancer in a study of women in Spain, according to an article published online by JAMA Internal Medicine.
Breast cancer is a frequently diagnosed cancer and a leading cause of death in women. Diet has been extensively studied as a modifiable risk factor in the development of breast cancer but epidemiologic evidence on the effect of specific dietary factors is inconsistent.
The Mediterranean diet is known for its abundance of plant foods, fish and ...
Social factors may impact young leukemia patients' survival
2015-09-14
A new study reveals that insurance status, marital status, and county-level income may affect the chances of survival in young patients with acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the findings indicate that efforts are needed to address the social factors that impact critical aspects of health in these patients.
AML will affect approximately 20,830 and kill 10,460 Americans in 2015. Tremendous progress has been made in identifying disease characteristics that cause a patient to have ...
Treatment protocol improves outcomes for infants with neonatal abstinence syndrome
2015-09-14
A new protocol to treat babies born in withdrawal from drugs can be used widely to improve outcomes for these babies.
The protocol reduces length of stay and the duration of treatment with opioids that are used therapeutically to wean babies off of drugs.
"The incidence of neonatal abstinence syndrome after an infant's in utero exposure to opioids has risen dramatically in recent years," says Eric Hall, PhD, a researcher in the Perinatal Institute at Cincinnati Children's and lead author of the study. "After adoption of the protocol, opioid treatment went from 34 to ...
Pedaling like a Tour de France winner is a losing strategy for most of us
2015-09-14
Pedalling like Chris Froome or Alberto Contador might seem appealing, but Oxford University researchers have found that for most of us it's likely to reduce rather than improve our performance.
A team from Oxford's Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences looked at a common measure of aerobic fitness called VO2 max. While it can be measured accurately in a laboratory, it is often more practical to use techniques that estimate VO2 max for individuals by getting them to exercise to their maximal level. These include the 'bleep test' of shuttle runs used by police forces ...
Astronomers peer into the 'amniotic sac' of a planet-hosting star
2015-09-14
Astronomers have successfully peered through the 'amniotic sac' of a star that is still forming to observe the innermost region of a burgeoning solar system for the first time.
In a research paper published today in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, an international team of astronomers describe surprising findings in their observations of the parent star, which is called HD 100546.
Lead author Dr Ignacio Mendigutía, from the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Leeds, said: "Nobody has ever been able to probe this close ...
Study links marijuana use to poor blood sugar control in middle age
2015-09-14
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) shows that current and former users of marijuana are more likely to have prediabetes--the state of poor blood sugar control that can progress to type 2 diabetes--than never users of marijuana. However the researchers, led by Mike Bancks (University of Minnesota School of Public Health, Minneapolis, MN, USA) failed to establish a direct link between marijuana use and type 2 diabetes.
Marijuana is the most frequently used illicit drug in America (and is estimated to ...
Climate research: Where is the world's permafrost thawing?
2015-09-13
Bremerhaven (Germany), 14th September 2015. This Saturday at a conference in Quebec, Canada an international research team will present the first online data portal on global permafrost. In the Global Terrestrial Network for Permafrost researchers first collect all the existing permafrost temperature and active thickness layer data from Arctic, Antarctic and mountain permafrost regions and then make it freely available for download. This new portal can serve as an early warning system for researchers and decision-makers around the globe. A detailed description of the data ...
Study: No sex differences in research funding at Johns Hopkins Department of Medicine
2015-09-12
Though national data suggest that women researchers are less likely to obtain independent research funding than men, a study published in the Journal of Women's Health found that male and female researchers at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine are funded at nearly the same rate.
Rita Rastogi Kalyani, M.D., M.H.S.; Hsin-Chieh Yeh, Ph.D.; Jeanne Clarke, M.D., M.P.H.; Myron Weisfeldt, M.D.; Terry Choi; and Susan McDonald, M.D., all of Johns Hopkins, authored the study.
Kalyani points out that, in recent years, Johns Hopkins has demonstrated a commitment to ...
Resveratrol impacts Alzheimer's disease biomarker
2015-09-11
WASHINGTON (Sept. 11, 2015) -- The largest nationwide clinical trial to study high-dose resveratrol long-term in people with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease found that a biomarker that declines when the disease progresses was stabilized in people who took the purified form of resveratrol.
Resveratrol is a naturally occurring compound found in foods such as red grapes, raspberries, dark chocolate and some red wines.
The results, published online today in Neurology, "are very interesting," says the study's principal investigator, R. Scott Turner, MD, PhD, director ...
Achieving effective health care with a new approach to caring for chronic illnesses
2015-09-11
CORAL GABLES, Fla. (September 11, 2015) -- Researchers from the University of Miami and Harvard University address the challenges of effective universal health coverage in low- and middle-income countries, focusing on solving one of the most pressing issues: the care of chronic illnesses. Their suggestions, aimed at strengthening health care systems, include recommendations based on a "diagonal approach" for managing health care. Their report is published in the September issue of the journal Health Affairs.
The authors shared their findings on Wednesday, September 9, ...
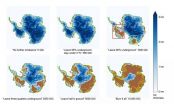
Burning remaining fossil fuel could cause 60-meter sea level rise
2015-09-11
Washington, DC--New work from an international team including Carnegie's Ken Caldeira demonstrates that the planet's remaining fossil fuel resources would be sufficient to melt nearly all of Antarctica if burned, leading to a 50- or 60-meter (160 to 200 foot) rise in sea level. Because so many major cities are at or near sea level, this would put many highly populated areas where more than a billion people live under water, including New York City and Washington, DC. It is published in Science Advances.
"Our findings show that if we do not want to melt Antarctica, we ...
Burning all fossil energy would eliminate all ice of Antarctica
2015-09-11
Burning all of the world's available fossil-fuel resources would result in the complete melting of the Antarctic ice sheet, a new study to be published in Science Advances shows. The Antarctic ice masses store water equivalent to more than 50 meters of sea-level rise. The new calculations show that Antarctica's long-term contribution to sea-level rise could likely be restricted to a few meters that could still be manageable, if global warming did not exceed 2 degrees. Crossing this threshold, however, would in the long run destabilize both West and East Antarctica - causing ...
Study shows Africanized bees continue to spread in California
2015-09-11
A study conducted by biologists at UC San Diego has found that the Africanized honey bee--an aggressive hybrid of the European honey bee--is continuing to expand its range northward since its introduction into Southern California in 1994.
The study, published in this week's edition of the journal PLOS ONE, found that more than 60 percent of the foraging honey bees in San Diego County are Africanized and that Africanized bees can now be found as far north as California's delta region.
"Our study shows that the large majority of bees one encounters in San Diego County are ...
[1] ... [2795]
[2796]
[2797]
[2798]
[2799]
[2800]
[2801]
[2802]
2803
[2804]
[2805]
[2806]
[2807]
[2808]
[2809]
[2810]
[2811]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.