Stress main cause of smoking after childbirth
2015-09-10
Mothers who quit smoking in pregnancy are more likely to light-up again after their baby is born if they feel stressed - according to a new report from the University of East Anglia.
Researchers studied interviews with more than 1,000 new mothers and found that the stress of caring for a newborn, sleepless nights, social pressure, and the idea that they no longer need to protect the baby - all contribute to relapse.
The study also found that women who felt they were being supported by a partner were less likely to start smoking again.
Lead researcher Dr Caitlin Notley, ...
Major European study moves a step closer to treatments for severe asthma
2015-09-10
Major European study moves a step closer to treatments for severe asthma
Initial findings from a major European study have helped identify key characteristics of severe asthma, which will help with the development of new treatments for patients with the condition.
The new paper, published online today (10 September, 2015) in the European Respiratory Journal, is one of the largest assessments of adults with severe asthma to date, looking at several characteristics including symptoms, patients' quality of life and blood and airway measurements.
Over 30 million adults ...
Brief bouts of exercise begin to reverse heart abnormalities in people with type 2 diabetes
2015-09-10
A new study in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) is the first to show that high intensity intermittent exercise training improves heart structure and benefits diabetes control in patients with type 2 diabetes. The study is led by Professor Michael Trenell and Dr Sophie Cassidy from Newcastle University (UK) and was funded by the National Institute for Health Research.
People with type 2 diabetes are twice as likely as those without diabetes to have heart disease, and heart disease is the leading cause of death and complications ...
Higher-earning men would take a pay cut to spend more time with partners
2015-09-10
Most men in Europe want to spend fewer hours at work and more time with their families even though it would cut their income, a major study on employment shows.
The common belief that higher-earning men like to work longer to build their careers is shown to be wrong by the study - men who earn the majority of their household's income were most likely to want to work less.
Sociologists Dr Shireen Kanji and Dr Robin Samuel also found that for men breadwinners the attraction of spending more time with their partner is as strong a pull as children's company.
Dr Kanji, ...
Penn team: Sustained remission of multiple myeloma after personalized cellular therapy
2015-09-10
PHILADELPHIA - A multiple myeloma patient whose cancer had stopped responding after nine different treatment regimens experienced a complete remission after receiving an investigational personalized cellular therapy known as CTL019 developed by a team at the University of Pennsylvania. The investigational treatment was combined with chemotherapy and an autologous stem cell transplant - a new strategy designed to target and kill the cells that give rise to myeloma cells.
The team's findings are published in a case report today in the New England Journal of Medicine. Prior ...
New enzyme-replacement therapy shows promise for genetic lipid disease treatment
2015-09-10
PHILADELPHIA--Of the more than 50 known lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs)-rare inherited metabolic disorders-only seven can be treated with approved enzyme-replacement therapies. Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency (LALD) is an LSD that causes fatty liver disease and cirrhosis. There is no treatment for the disease, which afflicts 1- 40,000 - 1 in 300,000 people across the world. In this week's New England Journal of Medicine, researchers report results of a trial showing the efficacy of a new enzyme-replacement therapy for LALD. In an accompanying editorial, Daniel J. Rader, ...
Study defines clinical trials likely to exclude patients with brain metastases
2015-09-09
Non-small cell lung cancer frequently spreads to the central nervous system (CNS), but patients with CNS metastases may be excluded from clinical trials of new drugs. A University of Colorado Cancer Center study being presented at the 16th World Conference on Lung Cancer reveals the full extent to which the CNS may be under-explored in clinical research.
The study combed the website ClinicalTrials.gov to identify 413 open lung cancer clinical trials. Overall, 41 percent of trials only included patients if their CNS disease was previously treated. Twenty-six percent allowed ...
A new marker for migraine?
2015-09-09
MINNEAPOLIS - Researchers may have discovered a new marker found in the blood for episodic migraine, according to a study published in the September 9, 2015, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Episodic migraine is defined as having less than 15 headaches per month.
"While more research is needed to confirm these initial findings, the possibility of discovering a new biomarker for migraine is exciting," said study author B. Lee Peterlin, DO, with the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore and a member ...
Patients prefer relief from lower back pain over improved mobility
2015-09-09
A new study out today in the journal Neurology examines the question of quality of life for individuals with a common form of lower back pain called lumbar spinal stenosis. The findings show that, when asked to choose between treatments that reduced pain or would help them stand or walk, patients overwhelmingly chose pain relief.
"There has long been a debate in the medical community over striking the right balance between pain relief and physical function," said John Markman, M.D., director of the Translational Pain Research Program in the University of Rochester ...
Last chance for oasis in China's desert
2015-09-09
This news release is available in German.
Ten percent of the world's cotton is produced in the Xinjiang region in northwestern China. Irrigating the cotton fields, however, is causing ecological problems. After many years of research, a team of international researchers headed by Prof. Markus Disse at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has developed a set of recommendations aimed at preserving the local environment.
The Tarim basin in the Xinjiang region of northwestern China is unique. No other natural landscape is located as far from the ocean. It has ...
Discrimination during adolescence has lasting effect on body
2015-09-09
EVANSTON, Ill. --- In both blacks and whites, everyday feelings of discrimination can mess with the body's levels of the primary stress hormone, cortisol, new research suggests.
In African-Americans, however, the negative effects of perceived discrimination on cortisol are stronger than in whites, according to the study, one of the first to look at the biological response to the cumulative impact of prejudicial treatment.
The team of researchers, led by Northwestern University, also found that the teenage years are a particularly sensitive period to be experiencing ...
Can black Republicans win black votes? Not likely, UC study finds
2015-09-09
Are black voters more likely to vote for black candidates, regardless of political party affiliation?
A new study by a University of Cincinnati researcher presents discouraging news for Republican leaders hoping to win over this Democratic stronghold by nominating black Republican candidates for political offices.
"There are some very successful African-American Republicans, but those folks don't attract African-American votes," said the study's author, David Niven, a University of Cincinnati professor of political science. "Party matters so much more than race."
In ...
Michigan 'See You in 7' program helps reduce heart failure readmissions
2015-09-09
Michigan hospitals participating in the American College of Cardiology's "See You in 7" program demonstrated important reductions in 30-day readmission rates for Medicare heart failure patients when compared to non-participating hospitals despite only modest increases in seven-day follow-up appointments, according to a study today in JACC: Heart Failure.
"See You in 7" is part of the ACC's Hospital-to-Home initiative, a national quality improvement program aimed at reducing heart disease-related hospital readmissions and improving the transition from hospital to home. ...
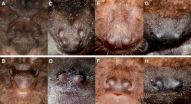
Bats may use bidirectional echolocation to detect prey, orient themselves
2015-09-09
The barbastelle bat may emit two different types of weak echolocation signals alternately, one upward through the nose and one downward through the mouth, to find prey while undetected and to sufficiently keep track of the environment, respectively, according to a study published September 9, 2015 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Anna-Maria Seibert and colleagues from the University of Tübingen, Germany.
Barbastelle bats prey almost exclusively on eared moths, using "stealth echolocation" signals that are 10-100 times weaker than those of other aerial hawking ...
UQ scientists close in on first dengue treatment
2015-09-09
Clinical trials for a dengue fever treatment could start within a year, following a discovery by University of Queensland scientists.
UQ's School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences Head Professor Paul Young said the researchers had identified similarities in how the body reacted to dengue virus and bacterial infections, in a finding that would allow them to re-purpose existing drugs.
"We have discovered that the dengue virus NS1 protein acts as a toxin in the body, in a similar manner to the way bacterial cell wall products lead to septic shock in bacterial infections," ...
NFL fans and ESPN reporters overly optimistic about team prospects
2015-09-09
US fans of the National Football League (NFL) and sports reporters assigned to specific teams have unrealistic expectations about how well their team will perform, finds new research from UCL and Oxford University.
The study, published in PLOS ONE, also reveals which teams are most liked and disliked, as well as which teams have the most optimistic fans.
The main results are from an April 2015 survey of 1,116 US-based NFL fans, who were asked to predict how many games their favourite and least favourite teams would win in the 2015 season. As each team plays 16 games ...
Paying farmers to help the environment works, but 'perverse' subsidies must be balanced
2015-09-09
New research suggests that offering financial incentives for farming industries to mitigate the impact agriculture has on the environment, by reducing fertiliser use and 'sparing' land for conservation, for example, actually has a positive effect on critical areas such as greenhouse gas reduction and increased biodiversity.
It has been a point of contention whether such 'cash for conservation' initiatives succeed. For the latest study, researchers aggregated investment in environmental incentives at a national level for the first time, and, by comparing them to broad ...
A hint of increased brain tumor risk -- 5 years before diagnosis
2015-09-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study suggests that changes in immune function can occur as long as five years before the diagnosis of a brain tumor that typically produces symptoms only three months before it is detected.
Using blood samples collected an average of 15 years before brain tumor diagnosis to analyze interactions between 12 allergy-related proteins, researchers looked at how those relationships differed between people later diagnosed with brain tumors and cancer-free controls.
Among people who were subsequently diagnosed with this brain tumor, called a glioma, ...
New video series 'Beyond the Desktop' explores potential of 3-D printing
2015-09-09
The Wilson Center's Science and Technology Innovation Program (STIP) is releasing a five-episode video series looking at the potential for additive manufacturing to transform how we build things - and what we need to do to fully realize this potential.
Beyond the Desktop explores how additive manufacturing could affect the fields of medicine, aerospace, space technology and more. Beginning Sept. 9, 2015, a new episode will be released each Wednesday through early October. Episodes will be posted on the Wilson Center homepage: https://www.wilsoncenter.org/3dprinting
Many ...
Ocean life triggers ice formation in clouds
2015-09-09
Researchers have shown for the first time that phytoplankton (plant life) in remote ocean regions can contribute to rare airborne particles that trigger ice formation in clouds. Results published this week (Wednesday 9 September) in the journal Nature show that the organic waste from life in the oceans, which is ejected into the atmosphere along with sea spray from breaking waves, stimulates cloud droplets to freeze into ice particles. This affects how clouds behave and influence global climate, which is important for improved projections of future climate change.
Clouds ...
How to spawn an 'exceptional ring'
2015-09-09
CAMBRIDGE, Mass.--The Dirac cone, named after British physicist Paul Dirac, started as a concept in particle and high-energy physics and has recently became important in research in condensed matter physics and material science. It has since been found to describe aspects of graphene, a two dimensional form of carbon, suggesting the possibility of applications across various fields.
Now physicists at MIT have found another unusual phenomenon produced by the Dirac cone: It can spawn a phenomenon described as a "ring of exceptional points." This connects two fields of ...
Cells from human umbilical cord blood improve cognition in Alzheimer's disease model mice
2015-09-09
Putnam Valley, NY. (Sept. 9, 2015) - Alzheimer's disease (AD), which affects an estimated 26 million people worldwide, is the fourth leading cause of death among the elderly and the leading cause of dementia. Predictions are that the number of AD cases will quadruple by 2050.
Although pharmacological methods for treating AD have been discovered, none significantly delay the progression of the disease. However, cell transplantation research using animals modeled with AD has indicated that human umbilical cord blood cells (HUCBCs) can ameliorate some cognitive deficits ...
The Industrial Revolution put an end to 1,800 years of ocean cooling
2015-09-09
The high frequency and magnitude of volcanic eruptions could have been the cause of the progressive cooling of ocean surfaces over a period of 1,800 years. This is made apparent in an international study published recently in the journal Nature Geoscience, involving researcher P. Graham Mortyn of the Institute for Environmental Science and Technology (ICTA-UAB) and the UAB Department of Geography.
The study emphasises that this trend came to an end with the beginning of the Industrial Revolution and the resulting global warming caused by human activity. It further shows ...
Tree planting can harm ecosystems
2015-09-09
The world's grassy biomes are key contributors to biodiversity and ecosystem services, and are under immense pressure from conversion to agriculture and tree planting, report Joseph W. Veldman, of Iowa State University, and his colleagues in an article for the October issue of BioScience. The authors argue that forest- and tree-focused environmental policies and conservation initiatives have potentially dire ecological consequences for undervalued ecosystems, such as grasslands, savannas, and open-canopy woodlands.
To illustrate this forest bias and its consequences, ...
Researchers reawaken sleeping HIV in patient cells to eliminate the virus
2015-09-09
LA JOLLA, Calif., September 9, 2015 - A consortium of investigators led by scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute (SBP) have found that a new class of drugs may be used to purge pockets of dormant HIV from a patient's body, eliminating the virus once and for all. Since these agents are already being explored in clinical trials for treating cancer, the route to approval for treating HIV may be significantly shorter than usual.
Antiretroviral therapies have made it possible for people to live with HIV for decades. However, patients continue to ...
[1] ... [2800]
[2801]
[2802]
[2803]
[2804]
[2805]
[2806]
[2807]
2808
[2809]
[2810]
[2811]
[2812]
[2813]
[2814]
[2815]
[2816]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.