Depression and extremes of blood pressure predict highest rates of harmful vascular events
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: Depressive symptoms and extremes of blood pressure predict the highest rates of harmful vascular events in patients with existing heart disease, diabetes or stroke, according to research presented at ESC Congress today by Dr Bhautesh Jani, clinical academic fellow in the Institute of Health and Wellbeing, University of Glasgow, UK.1
The study in more than 35 000 patients found that the risk of further stroke or heart attack, heart failure or dying due to heart disease at four years was 83% higher in depressed patients with high blood pressure ...
Prolonged television watchers have higher risk of fatal pulmonary embolism
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: Prolonged television watchers have a higher risk of fatal pulmonary embolism, a condition associated with long haul flights, reveals research presented at ESC Congress today by Mr Toru Shirakawa, public health research fellow in the Department of Social Medicine at Osaka University in Japan.1 The 18 year study in more than 86 000 people found that watching an average of five or more hours of television per day was associated with twice the risk of fatal pulmonary embolism as watching less than two and a half hours daily.
"The association between ...
Midday naps associated with reduced blood pressure and fewer medications
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: Midday naps are associated with reduced blood pressure levels and prescription of fewer antihypertensive medications, according to research presented at ESC Congress today by Dr Manolis Kallistratos, a cardiologist at Asklepieion Voula General Hospital in Athens, Greece.1
"Although William Blake affirms that it is better to think in the morning, act at noon, eat in the evening and sleep at night, noon sleep seems to have beneficial effects," said Dr Kallistratos. "Two influential UK Prime Ministers were supporters of the midday nap. Winston Churchill ...
Coffee linked with increased cardiovascular risk in young adults with mild hypertension
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: Coffee drinking is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular events (mainly heart attacks) in young adults (18-45) with mild hypertension, according to research presented at ESC Congress today by Dr Lucio Mos, a cardiologist at Hospital of San Daniele del Friuli in Udine, Italy.1 The 12 year study in more than 1 200 patients found that heavy coffee drinkers had a four-fold increased risk while moderate drinkers tripled their risk. Future prediabetes attenuated the associations suggesting that the effect of coffee on cardiovascular events ...
Pollution and weather influence outcomes after heart attack
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: Pollution and weather influence outcomes after a heart attack, according to research presented at ESC Congress today by Ms Aneta Cislak, research fellow in the Silesian Centre for Heart Diseases, Medical University of Silesia in Zabrze, Poland.1
"Weather changes like rain or heat affect our daily activity and even our productivity at work," said Ms Cislak. "Since this influence is so noticeable we were interested to see if weather has any connection with cardiovascular diseases including acute coronary syndromes. Moreover, air pollution affects ...
Refractory cardiac arrest patients brought to hospital with ongoing CPR can recover
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: Refractory cardiac arrest patients brought to hospital with ongoing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) can survive with good brain function, according to research in nearly 4 000 patients presented at ESC Congress today by Dr Helle Søholm, a cardiologist at Copenhagen University Hospital Righospitalet in Denmark.1
"The faster a patient with cardiac arrest is resuscitated and brought back to life the better," said Dr Søholm. "The prognosis for patients with refractory cardiac arrest with long resuscitation attempts has previously been ...
ESC guidelines recommend radial approach for percutaneous coronary interventions in ACS
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: For the first time, ESC Guidelines published today give the highest degree of recommendation for the radial approach over the femoral one for coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS). The ACS without persistent ST-segment elevation (NSTE-ACS) guidelines, drafted by an international multidisciplinary Task Force, are published online in European Heart Journal1 and on the ESC Website.2
"New data shows that the radial approach is superior to the femoral not only in terms of ...
ESC infective endocarditis guidelines boost role of imaging in diagnosis
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: ESC Guidelines published today on infective endocarditis boost the role of imaging in diagnosis of this deadly disease.
"We emphasise the need for a multimodality imaging approach to diagnosing endocarditis," said Professor Gilbert Habib, Chairperson of the guidelines Task Force. "While the 2009 guidelines1 focused on echocardiography, the 2015 guidelines show the important role of other imaging techniques such as PET-CT. These new imaging techniques are increasingly useful for the diagnosis and management of infective endocarditis and we recommend ...
New ESC guidelines on pericardial diseases published today
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: New ESC Guidelines on pericardial diseases are published today. Until now there was insufficient evidence for strong recommendations in this group of conditions which can severely restrict quality of life.
"Pericardial diseases include different clinical presentations and various aetiologies that require appropriate management," said Professor Yehuda Adler, Co-Chairperson of the guidelines Task Force. "We hope these new recommendations will help clinicians to manage these diseases with resulting improvements in outcomes and quality of life."
The ...
Novel treatment algorithm launched in ESC/ERS pulmonary hypertension guidelines
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: A novel treatment algorithm for pulmonary arterial hypertension is launched today in new pulmonary hypertension guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Respiratory Society (ERS). The protocol aims to give patients the best chance of a good clinical outcome in a condition with dismal prognosis which puts severe limitations on patient choices including avoiding pregnancy, excessive physical activity and certain types of travel.
The 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension are ...
ESC recommends DNA analysis in post mortems of young sudden death victims
2015-08-29
London, UK - 29 Aug 2015: ESC Guidelines published today recommend DNA analysis as a fundamental component of post mortem assessment in young sudden death victims. Identification of a genetic cause helps to quickly diagnose and protect relatives.
The Guidelines are published online in European Heart Journal1 and on the ESC Website2 and are the European update to the 2006 European/American guidelines.3 They focus on preventing sudden cardiac death in patients with ventricular arrhythmias.
"For the first time these guidelines have incorporated the concept proposed by ...
Can you avoid hangovers after heavy drinking?
2015-08-29
Are some people immune to hangovers, and can eating or drinking water after heavy drinking prevent a hangover? The answers appear to be 'no' and 'no' according to new research presented the ECNP conference in Amsterdam.
Excessive alcohol consumption has familiar consequences, many of them quite damaging. If a person does not experience a hangover - and 25% to 30% of drinkers regularly claim this - they may be more likely to continue drinking, so good research into the outcomes of drinking to excess is needed.
A group of international researchers from the Netherlands ...
NASA, NOAA satellites show Erika affecting Hispaniola
2015-08-28
Tropical Storm Erika was centered in the Eastern Caribbean Sea and affecting Puerto Rico and Hispaniola when NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead mid-day on Friday, August 28, 2015. Two hours after Terra passed, NOAA's GOES-East satellite saw Erika's western side over the Dominican Republic.
At 15:05 UTC (11:05 a.m. EDT) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible light image Tropical Storm Erika approaching Hispaniola. Erika's center was in the eastern Caribbean Sea, and the northern quadrant of the ...
Confidence in parenting could help break cycle of abuse
2015-08-28
To understand how confidence in parenting may predict parenting behaviors in women who were abused as children, psychologists at the University of Rochester have found that mothers who experienced more types of maltreatment as children are more critical of their ability to parent successfully. Intervention programs for moms at-risk, therefore, should focus on bolstering mothers' self-confidence--not just teach parenting skills, the researchers said.
"We know that maltreated children can have really low self-esteem," said Louisa Michl, a doctoral student in the department ...
Study: Better signs could help reduce friction between motorists, bicyclists
2015-08-28
A simple change in the wording of a traffic sign - from "Share the Road" to "Bicycles May Use Full Lane" - could help clarify the rules of the road for bicyclists and motorists, according to a North Carolina State University study.
"'Share the Road' signs are common but what that means in terms of how drivers and bicycle riders should interact can be ambiguous," says George Hess, natural resources professor and co-author of the study in PLOS One. Some bicyclists complain that motorists consider them to be in the way, while some motorists accuse bicyclists of hogging ...
Seeing quantum motion
2015-08-28
Consider the pendulum of a grandfather clock. If you forget to wind it, you will eventually find the pendulum at rest, unmoving. However, this simple observation is only valid at the level of classical physics--the laws and principles that appear to explain the physics of relatively large objects at human scale. However, quantum mechanics, the underlying physical rules that govern the fundamental behavior of matter and light at the atomic scale, state that nothing can quite be completely at rest.
For the first time, a team of Caltech researchers and collaborators has ...
Oysters harbor, transmit human norovirus: Avoid raw ones
2015-08-28
Washington DC - August 28, 2015 - Oysters not only transmit human norovirus; they also serve as a major reservoir for these pathogens, according to research published August 28 in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology. "More than 80 percent of human norovirus genotypes were detected in oyster samples or oyster-related outbreaks," said corresponding author Yongjie Wang, PhD.
"The results highlight oysters' important role in the persistence of norovirus in the environment, and its transmission to humans, and they demonstrate ...
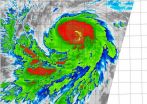
Suomi NPP satellite sees rapidly intensifying Hurricane Jimena
2015-08-28
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite flew over Hurricane Jimena in the Eastern Pacific and saw the strongest thunderstorms building up quickly, especially in the northern quadrant of the storm. Jimena intensified rapidly overnight on August 27 and early August 28 and the National Hurricane Center expects it to become a major hurricane.
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite or VIIRS instrument aboard the satellite provided infrared data of the storm that showed the coldest cloud top temperatures, which indicate the strongest thunderstorms were in Jimena's northern ...
Artificial leaf harnesses sunlight for efficient fuel production
2015-08-28
Generating and storing renewable energy, such as solar or wind power, is a key barrier to a clean-energy economy. When the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis (JCAP) was established at Caltech and its partnering institutions in 2010, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Energy Innovation Hub had one main goal: a cost-effective method of producing fuels using only sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide, mimicking the natural process of photosynthesis in plants and storing energy in the form of chemical fuels for use on demand. Over the past five years, researchers at ...
CPR: It's not always a lifesaver, but it plays one on TV
2015-08-28
If you think that performing CPR on a person whose heart has stopped is a surefire way to save their life, you may be watching too much TV.
The truth is more depressing than fiction, according to a new study by University of Southern California Davis School of Gerontology researchers. While medical dramas Grey's Anatomy and House show cardiopulmonary resuscitation saving a patient's life nearly 70 percent of the time, the real immediate survival rate is nearly half that - around 37 percent.
Researchers also found another discrepancy between reality and TV: Half of ...
Moffitt makes important steps toward developing a blood test to catch pancreatic cancer early
2015-08-28
TAMPA, Fla. - Pancreatic cancer is the fourth most common cause of cancer-related death in the United States and has a 5-year survival rate of only 6 percent, which is the lowest rate of all types of cancer according to the American Cancer Society. This low survival rate is partially attributed to the difficulty in detecting pancreatic cancer at an early stage. According to a new 'proof of principle' study published in Aug. 27 issue of Cancer Prevention Research, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers hope to improve pancreatic cancer survival rates by identifying markers in ...
Staying safe in sandy beaches
2015-08-28
Beach sand contains all kinds of microorganisms, including those that can harm human health. Yet current guidelines are focused exclusively on monitoring the levels of microbes in the water.
Now, an international panel of scientists is recommending monitoring the sand at recreational beaches, to minimize health risks for beachgoers. Their advice is based on the general consensus reached during the international conference "Trends in Environmental Microbiology and Public Health," held in Lisbon Portugal in September 2014.
"Beach sands accumulate contaminants and people ...
New embryo image processing technology could assist in IVF implantation success rates
2015-08-28
A collaboration between biologists and engineers at Monash University has led to the development of a new non-invasive image processing technique to visualise embryo formation. Researchers were able to see, for the first time, the movement of all of the cells in living mammalian embryos as they develop under the microscope. This breakthrough has important implications for IVF (in vitro fertilisation) treatments and pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). In the future, this approach could help with embryo selection before the embryo is implanted back into the uterus to ...
Neurobiology: Light-activated learning
2015-08-28
A German-French team has developed a light-sensitive switch that regulates a protein implicated in the neurobiology of synaptic plasticity. The agent promises to shed new light on the phenomenology of learning, memory and neurodegeneration.
Learning is made possible by the fact that the functional connections between nerve cells in the brain are subject to constant remodeling. As a result of activation-dependent modification of these links ('synaptic plasticity'), circuits that are repeatedly stimulated "learn" to transmit signals ever more efficiently. This process is ...
Lack of folic acid enrichment in Europe causes mortality among fetuses
2015-08-28
This news release is available in German.
A new international study shows that 5,000 foetuses in Europe annually are affected by spina bifida and other severe defects on the central nervous system. Seventy per cent of these pregnancies are terminated, while increased mortality and serious diseases affect the children who are born. At least half of the cases can be avoided by adding folic acid to staple foods as is already being done in seventy non-European countries.
A lack of folic acid enrichment in Europe is the cause of several thousand cases of foaetal abnormalities ...
[1] ... [2806]
[2807]
[2808]
[2809]
[2810]
[2811]
[2812]
[2813]
2814
[2815]
[2816]
[2817]
[2818]
[2819]
[2820]
[2821]
[2822]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.