The catch of the day: Fishing for research data at the Museum of Science
2015-08-25
People of all ages recently lined up to do some fishing at the Museum of Science in Boston. And oddly, the fish they hoped to hook were not good ones.
Museum goers were invited to play "Fish Police!!" is a video game that challenged players to rid a river of its bad fish, while sparing its good ones. The catch? All the fish looked exactly alike, and could be told apart only by the way a fish puffed in size: a bad fish puffed just a little faster. After all, it was nervous that it would be caught.
The game's premise may sound a little fishy, but it has helped a team ...
Mental visual imaging training improves multiple sclerosis patients' well-being
2015-08-25
Amsterdam, NL, August 25, 2015 - Patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RR-MS), the most common form of the disease, often have deficits in two neuropsychological functions, autobiographical memory (AM) and episodic future thinking (EFT), which impact quality of life. In a new study published in Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, researchers report that training RR-MS patients in mental visual imagery (MVI) can improve AM/EFT functioning.
AM facilitates the ability to remember personal detailed events within a specific location and timeframe. EFT enables ...
Predicting who will murder his wife or his family
2015-08-25
Murderers who kill intimate partners and family members have a similar profile
One-third of all women murdered in U.S. are killed by male partners
Wives and family members wrongly think 'my husband or son would never hurt me'
CHICAGO --- Murderers who kill intimate partners and family members have a significantly different psychological and forensic profile from murderers who kill people they don't know, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study that examined the demographics, psychiatric history and neuropsychology of these individuals.
The new knowledge about ...
Promising target for new drugs found in pancreatic cancer cells
2015-08-25
HOUSTON, August 25, 2015 - Pancreatic cancer is extremely deadly and often has a poor prognosis. Ranked as the fourth deadliest cancer in the U.S. and poised to move up within the next few years, pancreatic cancer is very difficult to detect in its early stages. Seldom diagnosed early and typically spreading rapidly, the disease has no effective treatment once it advances.
University of Houston researchers are on a mission to develop drugs that will allow physicians to prolong patient survival and, possibly, even eradicate this deadliest of cancers.
"Our research ...
Effect of physical activity, nutrient supplementation interventions on cognition
2015-08-25
Two studies in the August 25 issue of JAMA examine the effect of physical activity and nutrient supplementation on cognitive function.
In one study, Kaycee M. Sink, M.D., M.A.S., of the Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C., and colleagues evaluated whether a 24-month physical activity program would result in better cognitive function, lower risk of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia, or both, compared with a health education program.
Epidemiological evidence suggests that physical activity is associated with lower rates of cognitive decline. ...
Misconduct-related separation from the military linked with risk of being homeless
2015-08-25
Among U.S. veterans who returned from Afghanistan and Iraq, being separated from the military for misconduct was associated with an increased risk of homelessness, according to a study in the August 25 issue of JAMA.
Adi V. Gundlapalli, M.D., Ph.D., M.S., of the VA Salt Lake City Health Care System, Salt Lake City, and colleagues analyzed Veterans Health Administration (VHA) data from U.S. active-duty military service members who were separated (end date of last deployment) from the military between October 2001 and December 2011, deployed in Afghanistan or Iraq, and ...
Delay in administration of adrenaline and survival for children with cardiac arrest
2015-08-25
Among children with in-hospital cardiac arrest with an initial nonshockable heart rhythm who received epinephrine (adrenaline), delay in administration of epinephrine was associated with a decreased chance of 24-hour survival and survival to hospital discharge, according to a study in the August 25 issue of JAMA.
Approximately 16,000 children in the United States have a cardiac arrest each year, predominantly in a hospital setting. Epinephrine is recommended by both the American Heart Association and the European Resuscitation Council in pediatric cardiac arrest. Delay ...
Genetic mutations may help predict risk of relapse, survival for leukemia patients
2015-08-25
In preliminary research, the detection of persistent leukemia-associated genetic mutations in at least 5 percent of bone marrow cells in day 30 remission samples among adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia was associated with an increased risk of relapse and reduced overall survival, according to a study in the August 25 issue of JAMA.
Approximately 20 percent of adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) fail to achieve remission with initial induction chemotherapy, and approximately 50 percent ultimately experience relapse after achieving complete remission. ...
Relapse, poor survival in leukemia linked to genetic mutations that persist in remission
2015-08-25
For patients with an often-deadly form of leukemia, new research suggests that lingering cancer-related mutations - detected after initial treatment with chemotherapy - are associated with an increased risk of relapse and poor survival.
Using genetic profiling to study bone marrow samples from patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), researchers found that those whose cells still carried mutations 30 days after the initiation of chemotherapy were about three times more likely to relapse and die than patients whose bone marrow was cleared of these mutations.
The study, ...
415-million-year-old malformed fossil plankton reveal that heavy metal pollution might have contributed to some of the world's largest extinction events
2015-08-25
Several Palaeozoic mass extinction events during the Ordovician and Silurian periods (ca. 485 to 420 to million years ago) shaped the evolution of life on our planet. Although some of these short-lived, periodic events were responsible for eradication of up to 85% of marine species, the exact kill-mechanism responsible for these crises remains poorly understood.
An international team led by Thijs Vandenbroucke (researcher at the French CNRS and invited professor at UGent) and Poul Emsbo (US Geological Survey) initiated a study to investigate a little known association ...
Pitt, Drexel, and NIH team up to study persistence of Ebola virus in wastewater
2015-08-25
PITTSBURGH--The historic outbreak of Ebola virus disease in West Africa that began in March 2014 and has killed more than 11,000 people since, has raised new questions about the resilience of the virus and tested scientists' understanding of how to contain it. The latest discovery by a group of microbial risk-assessment and virology researchers suggests that the procedures for disposal of Ebola-contaminated liquid waste might underestimate the virus' ability to survive in wastewater.
Current epidemic response procedures from both the World Health Organization and the ...
NASA sees Hurricane Loke moving north
2015-08-25
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Loke as it continued moving north in the Central Pacific early on August 25.
At 01:10 UTC on August 25, 2015 (9:10 p.m. EDT/Aug. 24) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Hurricane Loke. The image showed the thunderstorms wrapping around the northern quadrant of the storm from east to west of the storm's center. Despite attaining hurricane status, however, there was no visible eye although microwave data taken earlier indicated an eye. ...
Mimic woodpecker fools competing birds, but genetics expose its true identity
2015-08-25
LAWRENCE -- To look tougher, a weakling might shave their head and don a black leather jacket, combat boots and a scowl that tells the world, "don't mess with me."
But this kind of masquerade isn't limited to people. Researchers recently have revealed a timid South American woodpecker that evolved to assume the appearance of larger, tougher birds.
Visual mimicry lets the Helmeted Woodpecker (Dryocopus galeatus) live on the threatened Atlantic forest turf of two bigger birds -- the Lineated Dryocopus lineatus and Robust (Campephilus robustus) woodpeckers -- reducing ...
Researchers study tall larkspur toxicity in cattle
2015-08-25
August 24, 2015 - In the western foothills and mountain rangelands of the U.S., wild larkspurs (Delphinium spp.) are a major cause of cattle losses.
For the most part, grazing cattle can self-regulate consumption of larkspurs and avoid toxicity problems. However, when cattle eat too much, too quickly, or they eat low amounts continuously, toxicity can occur. Symptoms of toxicity include muscle weakness. Cattle also can become non-ambulatory and die.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Animal Science, researchers with the USDA-ARS Poisonous Plant Research ...
Female guppies become better swimmers to escape male sexual harassment
2015-08-25
In the animal world, sexual reproduction can involve males attempting to entice or force females to mate with them, even if they are not initially interested.
This male behaviour is driven by conflicts of interest over reproduction and exerts selective pressures on both sexes.
A new study on guppies led by the universities of Glasgow and Exeter has given scientists insight into how this behaviour can lead to physiological changes, much like those in athletes who train to perform better.
Dr Shaun Killen, of the University of Glasgow, said: "Sexual coercion of females ...
Catastrophic landslides post-earthquake
2015-08-25
Boulder, Colo., USA - In the last few months, it has once more become clear that large earthquakes can solicit catastrophic landsliding. In the wake of the Nepal earthquake, the landslide community has been warning of persistent and damaging mass wasting due to monsoon rainfall in the epicentral area. However, very little is actually known about the legacy of earthquakes on steep, unstable hillslopes.
Using a dense time series of satellite images and air photos, Odin Marc and colleague reconstructed the history of landsliding in four mountain areas hit by large, shallow ...
Hepatitis A-like virus identified in seals
2015-08-25
Washington, DC - August 25, 2015 - Scientists in the Center for Infection and Immunity at the Mailman School of Public Health have discovered a new virus in seals that is the closest known relative of the human hepatitis A virus. The finding provides new clues on the emergence of hepatitis A. The research appears in the July/August issue of mBio, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Until now, we didn't know that hepatitis A had any close relatives and we thought that only humans and other primates could be infected by such viruses," ...
New Moffitt study finds black women have higher frequency of BRCA mutations than previously reported
2015-08-25
TAMPA, Fla. - Women who have inherited mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes are more likely to develop breast cancer or ovarian cancer, especially at a younger age. Approximately 5 percent of women with breast cancer in the United States have mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 based on estimates in non-Hispanic white women. Moffitt Cancer Center researchers recently conducted the largest U.S. based study of BRCA mutation frequency in young black women diagnosed with breast cancer at or below age 50 and discovered they have a much higher BRCA mutation frequency than that previously ...
Is incense bad for your health?
2015-08-25
The burning of incense might need to come with a health warning. This follows the first study evaluating the health risks associated with its indoor use. The effects of incense and cigarette smoke were also compared, and made for some surprising results. The research was led by Rong Zhou of the South China University of Technology and the China Tobacco Guangdong Industrial Company in China, and is published in Springer's journal Environmental Chemistry Letters.
Incense burning is a traditional and common practice in many families and in most temples in Asia. It is not ...
Smart phone not a smart choice when facing depression
2015-08-25
Depressed people who turn to their smart phones for relief may only be making things worse.
A team of researchers, that included the dean of Michigan State University's College of Communication Arts and Sciences, found that people who substitute electronic interaction for the real-life human kind find little if any satisfaction.
In a paper published in the journal Computers in Human Behavior, the researchers argue that relying on a mobile phone to ease one's woes just doesn't work.
Using a mobile phone for temporary relief from negative emotions could worsen psychological ...
'Lazy eye' may bully the brain into altering its wiring
2015-08-25
MADISON -- Colorful and expressive, the eyes are central to the way people interact with each other, as well as take in their surroundings.
That makes amblyopia -- more commonly known as "lazy eye" -- all the more obvious, but the physical manifestation of the most common cause of vision problems among children the world over is actually a brain disorder.
"Most often in amblyopia patients, one eye is better at focusing," says Bas Rokers, a University of Wisconsin-Madison psychology professor. "The brain prefers the information from that eye, and pushes down the signal ...
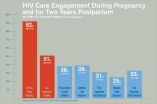
Pregnancy is a missed opportunity for HIV-infected women to gain control over condition
2015-08-25
Pregnancy could be a turning point for HIV-infected women, when they have the opportunity to manage their infection, prevent transmission to their new baby and enter a long-term pattern of maintenance of HIV care after giving birth--but most HIV-infected women aren't getting that chance. That is the major message from a pair of new studies in Philadelphia, one published early online this month in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases, and the other published in July in PLOS ONE.
The studies, led by a team of researchers from Drexel University and the Philadelphia Department ...
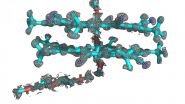
Researchers combine disciplines, computational programs to determine atomic structure
2015-08-25
A team from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Indiana University combined two techniques to determine the structure of cyanostar, a new abiological molecule that captures unwanted negative ions in solutions.
When Semin Lee, a chemist and Beckman Institute postdoctoral fellow at Illinois, first created cyanostar at Indiana University, he knew the chemical properties, but couldn't determine the precise atomical structure. Lee synthesized cyanostar for its unique ability to bind with large, negatively charged ions, which could have applications such as ...
Making a mistake can be rewarding, study finds
2015-08-25
Many political leaders, scientists, educators and parents believe that failure is the best teacher.
Scientists have long understood that the brain has two ways of learning. One is avoidance learning, which is a punishing, negative experience that trains the brain to avoid repeating mistakes. The other is reward-based learning, a positive, reinforcing experience in which the brain feels rewarded for reaching the right answer.
A new MRI study by USC and a group of international researchers has found that having the opportunity to learn from failure can turn it into ...
Women undergoing fertility treatment can succeed with fewer hormones
2015-08-25
Since the early days of fertility treatment, women undergoing IVF treatment have had to place a hormonal gel in their vagina on a daily basis for at least 14 days after embryo transfer. The hormone is necessary to increase the chances of pregnancy, but it may also cause some side effects in the form of irritation and leaky discharge.
However, the results of a new scientific study suggest that women will be able to avoid this kind of discomfort in the future.
"Fertility treatment is a physical and mental challenge for childless couples. The daily treatment with hormonal ...
[1] ... [2814]
[2815]
[2816]
[2817]
[2818]
[2819]
[2820]
[2821]
2822
[2823]
[2824]
[2825]
[2826]
[2827]
[2828]
[2829]
[2830]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.