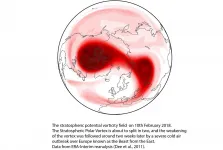
Imminent sudden stratospheric warming to occur, bringing increased risk of snow over coming weeks
2021-01-05
A new study led by researchers at the Universities of Bristol, Exeter, and Bath helps to shed light on the winter weather we may soon have in store following a dramatic meteorological event currently unfolding high above the North Pole.
Weather forecasting models are predicting with increasing confidence that a sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) event will take place today, 5 January 2021.
The stratosphere is the layer of the atmosphere from around 10-50km above the earth's surface. SSW events are some of the most extreme of atmospheric phenomena and can see polar stratospheric temperature increase by up to 50°C over the course of a few days. Such events ...
Novel method identifies areas most suitable for conservation of black lion tamarin
2021-01-05
By André Julião | Agência FAPESP - The black lion tamarin (Leontopithecus chrysopygus) once inhabited most forest areas in the state of São Paulo, Southeast Brazil, but currently occupies only some Atlantic Rainforest remnants there. In recent years, after various studies of the endangered species, environmental NGO Instituto de Pesquisas Ecológicas (IPÊ) moved groups of these animals to areas from which the species had disappeared.
Similar initiatives have now been reinforced by a group of researchers at IPÊ, São Paulo State University (UNESP) and the Federal University of Mato Grosso (UFMT), who cross-tabulated climate data and data on landscape (forest cover) to determine the sites best suited for future ...
Leaf fossils show severe end-Cretaceous plant extinction in southern Argentina
2021-01-05
The asteroid impact 66 million years ago that ushered in a mass extinction and ended the dinosaurs also killed off many of the plants that they relied on for food. Fossil leaf assemblages from Patagonia, Argentina, suggest that vegetation in South America suffered great losses but rebounded quickly, according to an international team of researchers.
"Every mass extinction event is like a reset button, and what happens after that reset depends on which organisms survive and how they shape the biosphere," said Elena Stiles, a doctoral student at the University of Washington who completed the research as part of her master's thesis at Penn State. "All the biodiversity ...
Remote sensing data sheds light on when and how asteroid Ryugu lost its water
2021-01-05
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Last month, Japan's Hayabusa2 mission brought home a cache of rocks collected from a near-Earth asteroid called Ryugu. While analysis of those returned samples is just getting underway, researchers are using data from the spacecraft's other instruments to reveal new details about the asteroid's past.
In a study published in Nature Astronomy, researchers offer an explanation for why Ryugu isn't quite as rich in water-bearing minerals as some other asteroids. The study suggests that the ancient parent body from which Ryugu was formed had likely dried out in some kind of heating event before Ryugu came into being, which left Ryugu itself drier than expected.
"One of the ...
Repeated ketamine infusions reduce PTSD symptom severity
2021-01-05
Repeated intravenous (IV) ketamine infusions significantly reduce symptom severity in individuals with chronic post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and the improvement is rapid and maintained for several weeks afterwards, according to a study conducted by researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The study, published September XX in the American Journal of Psychiatry, is the first randomized, controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic PTSD and suggests this may be a promising treatment for PTSD patients.
"Our findings provide insight into the treatment efficacy of repeated ketamine ...
Protecting the global food supply chain
2021-01-05
As the world grows increasingly globalized, one of the ways that countries have come to rely on one another is through a more intricate and interconnected food supply chain. Food produced in one country is often consumed in another country -- with technological advances allowing food to be shipped between countries that are increasingly distant from one another.
This interconnectedness has its benefits. For instance, if the United States imports food from multiple countries and one of those countries abruptly stops exporting food to the United States, there are still other countries that can be relied on ...
Journal article reviews century of data showing COVID-19 likely to impact the brain
2021-01-05
SAN ANTONIO and CHICAGO - An article published Jan. 5 in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association cites decades of published scientific evidence to make a compelling case for SARS-CoV-2's expected long-term effects on the brain and nervous system.
Dementia researchers from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) are the first and senior authors of the report and are joined by coauthors from the Alzheimer's Association and Nottingham and Leicester universities in England.
"Since the flu pandemic of 1917 and 1918, many of the flulike diseases have been associated with brain disorders," said lead author ...
Self-controlled children tend to be healthier middle-aged adults
2021-01-05
DURHAM, N.C. -- Self-control, the ability to contain one's own thoughts, feelings and behaviors, and to work toward goals with a plan, is one of the personality traits that makes a child ready for school. And, it turns out, ready for life as well.
In a large study that has tracked a thousand people from birth through age 45 in New Zealand, researchers have determined that people who had higher levels of self-control as children were aging more slowly than their peers at age 45. Their bodies and brains were healthier and biologically younger.
In interviews, the higher self-control group also showed they may be better equipped to handle the health, financial and social challenges of later life as well. The researchers used structured interviews and credit checks ...
ADDF presents vision of a consortium to accelerate research into speech and language biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease
2021-01-05
NEW YORK, NY (1/5/2021) - Subtle changes in speech and language can be an early warning sign of Alzheimer's -- sometimes appearing long before other more serious symptoms. The challenge is recognizing these changes and determining what may signal Alzheimer's or other neurodegenerative disorders. In a commentary in END ...
Sweat, bleach and gym air quality
2021-01-05
One sweaty, huffing, exercising person emits as many chemicals from their body as up to five sedentary people, according to a new University of Colorado Boulder study. And notably, those human emissions, including amino acids from sweat or acetone from breath, chemically combine with bleach cleaners to form new airborne chemicals with unknown impacts to indoor air quality.
"Humans are a large source of indoor emissions," said Zachary Finewax, CIRES research scientist and lead author of the new study out in the current edition of Indoor Air. "And chemicals in indoor air, whether from our bodies or cleaning products, don't just disappear, they linger and travel around spaces like gyms, reacting with other chemicals."
In 2018, the CU Boulder ...
Heat treatment may make chemotherapy more effective
2021-01-05
Heating up cancer cells while targeting them with chemotherapy is a highly effective way of killing them, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry B, found that "loading" a chemotherapy drug on to tiny magnetic particles that can heat up the cancer cells at the same time as delivering the drug to them was up to 34% more effective at destroying the cancer cells than the chemotherapy drug without added heat.
The magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles that carry the chemotherapy drug shed heat when exposed to an alternating magnetic field. This means that, once the nanoparticles have accumulated in the tumour area, an alternating magnetic field can be applied from outside the ...
Magnets dim natural glow of human cells, may shed light on how animals migrate
2021-01-05
Researchers in Japan have made the first observations of biological magnetoreception - live, unaltered cells responding to a magnetic field in real time. This discovery is a crucial step in understanding how animals from birds to butterflies navigate using Earth's magnetic field and addressing the question of whether weak electromagnetic fields in our environment might affect human health.
"The joyous thing about this research is to see that the relationship between the spins of two individual electrons can have a major effect on biology," said Professor Jonathan Woodward from the University of Tokyo, who conducted the research with doctoral ...
Danish and Chinese tongues taste broccoli and chocolate differently
2021-01-05
Two studies from the University of Copenhagen show that Danes aren't quite as good as Chinese at discerning bitter tastes. The research suggests that this is related to anatomical differences upon the tongues of Danish and Chinese people.
For several years, researchers have known that women are generally better than men at tasting bitter flavours. Now, research from the University of Copenhagen suggests that ethnicity may also play a role in how sensitive a person is to the bitter taste found in for example broccoli, Brussels sprouts and dark chocolate. By letting test subjects taste the bitter substance PROP, two studies demonstrate that Danish and Chinese people experience this basic taste differently. The reason seems to be related to an anatomical difference upon ...
In-utero exposures associated with increased risk of thyroid cancer
2021-01-05
A recent study by prof. Tone Bjørge, University of Bergen, and her team shows that thyroid cancer is related to in-utero exposures.
Thyroid cancer is diagnosed at a younger age than most other malignancies and the incidence is higher in women than men.
"The only established modifiable risk factors for thyroid cancer are childhood exposure to ionizing radiation and obesity. Few in-utero and early life risk factors have so far been identified" says Bjørge, professor at Department of Global Public Health and Primary Care, University of Bergen.
Maternal hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, goiter, and benign thyroid neoplasms ...
Reopening Florida schools followed by uptick in COVID-19 infections, Ben-Gurion U. study
2021-01-05
BEER-SHEVA, Israel...January 5, 2021 - Reopening Florida elementary and high schools in September was followed by increased COVID-19 infections, according to data analyzed by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Harvard Medical School and Tel Aviv University researchers.
The findings were just published in END ...
Breaking through the resolution barrier with quantum-limited precision
2021-01-05
Researchers at Paderborn University have developed a new method of distance measurement for systems such as GPS, which achieves more precise results than ever before. Using quantum physics, the team led by Leibniz Prize winner Professor Christine Silberhorn has successfully overcome the so-called resolution limit, which causes the "noise" we may see in photos, for example. Their findings have just been published in the academic journal "Physical Review X Quantum" (PRX Quantum). In "Physics", the publisher's online magazine, the paper has also been highlighted with an expert Viewpoint - an honour which is given to only certain selected publications.
Physicist Dr Benjamin Brecht explains the problem of the resolution limit: "In laser distance measurements ...
Bedside EEG test can aid prognosis in unresponsive brain injury patients
2021-01-05
Assessing the ability of unresponsive patients with severe brain injury to understand what is being said to them could yield important insights into how they might recover, according to new research.
A team at the University of Birmingham has shown that responses to speech can be measured using electroencephalography, a non-invasive technique used to record electrical signals in the brain. The strength of these responses can be used to provide an accurate prognosis that can help clinicians make the most effective treatment decisions.
Significantly the assessments can be made while the patient is still in intensive care and does not require any conscious response from the patient - they do not have to ...
Anticoagulants reduce the number of brain metastases in mice
2021-01-05
Brain metastases can only develop if cancer cells first exit the fine blood vessels and enter into the brain tissue. To facilitate this step, cancer cells influence blood clotting, as Heidelberg scientists from the German Cancer Research Center and from Heidelberg University Hospital have now been able to show in mice. The cancer cells actively promote the formation of clots, which helps them to arrest in the brain capillaries and then penetrate through the vessel wall. Drugs that inhibit the clotting factor thrombin were able to reduce the number of brain metastases in this experimental model.
Brain metastases are a feared complication of advanced cancers. Different cancers differ in their tendency to colonize the brain. Advanced-stage melanoma ...
Non-immigrant kids respond differently when immigrant children are bullied
2021-01-05
A recent study finds that, while youth think all bullying is bad, non-immigrant adolescents object less to bullying when the victim is an immigrant. However, the study found that the more contact immigrant and non-immigrant children had with each other, the more strongly they objected to bullying.
"We know that bystanders can play a key role in stopping bullying, and wanted to better understand bystander responses to bias-based bullying," says Seçil Gönülta?, first author of the study and a Ph.D. student at North Carolina State University. "What role does a victim's background play? What role does the bystander's background play? Are children more or less likely to intervene if they come from different backgrounds?"
To explore these questions, the researchers ...
Diet and lifestyle guidelines can greatly reduce gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms
2021-01-05
BOSTON - Findings from the Nurses' Health Study, one of the longest running studies of women's health, show that five diet and lifestyle factors, including regular exercise, can make a significant impact on gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) or heartburn symptoms. GERD is a common condition, affecting about a third of the U.S. population; the main symptom is heartburn and it is often managed with medications. This new study suggests, however, that following diet and lifestyle guidelines may reduce symptoms substantially and could make medication unnecessary for some patients. It was published as a letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The five factors include normal weight, never smoking, moderate-to-vigorous physical activity for at least 30 minutes daily, restricting coffee, tea ...
Story tips: Nanoscale commuting, easy driver and defect detection
2021-01-05
Microscopy -- Nanoscale commuting
Oak Ridge National Laboratory's Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, or CNMS, contributed to a groundbreaking experiment published in Science that tracks the real-time transport of individual molecules.
A team led by the University of Graz, Austria, used unique four-probe scanning tunneling microscopy, or STM, to move a single molecule between two independent probes and observe it disappear from one point and instantaneously reappear at the other.
The STM, made available via the CNMS user program, operates under an applied voltage, scanning material ...
On the road to invisible solar panels: How tomorrow's windows will generate electricity
2021-01-05
Five years after the Paris climate agreement, all eyes are on the world's progress on the road to a carbon-free future. A crucial part of this goal involves the energy transition from fossil fuels to renewable sources, such as sun, water, wind and wave energy. Among those, solar energy has always held the highest hope in the scientific community, as the most reliable and abundant energy source on Earth. In recent decades, solar cells have become cheaper, more efficient, and environment friendly. However, current solar cells tend to be opaque, which prevents their wider use and integration into everyday materials, constrained to being lined up on roofs and in remote solar farms.
But ...
Machine learning improves particle accelerator diagnostics
2021-01-05
Operators of the primary particle accelerator at the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility are getting a new tool to help them quickly address issues that can prevent it from running smoothly. A new machine learning system has passed its first two-week test, correctly identifying glitchy accelerator components and the type of glitches they're experiencing in near-real-time.
An analysis of the results of the first field test of the custom-built machine learning system was recently published in Physical Review Accelerators and Beams.
The Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility, ...
New bacterial culture methods could result in the discovery of new species
2021-01-05
Microorganisms are the most abundant and diverse form of life on Earth. However, the vast majority of them remain unknown. Indeed, only a small fraction of the microorganisms of our planet can be cultured under traditional conditions, leaving a world of unculturable organisms out of our scope. This is especially true for bacteria thriving under extreme conditions as the harsh conditions are hardly reproducible in a lab. While some microbial studies have been performed in the Sahara, the Atacama, and the Gibson desert, European arid lands remain poorly studied.
To finally explore the microbial community of some European deserts, researchers ...
How to motivate people to follow restrictions: 13 principles for COVID-19 communication
2021-01-05
An effective response to a pandemic like the COVID-19 will only be successful if people voluntarily follow the rules and guidelines of decision-makers and experts. Many of the required measures, such as avoiding social contact and significantly changing our daily habits require a strong commitment. Other necessary actions, such as regular hand washing, are often impossible to monitor and enforce. Adherence to the guidelines thus depends on people's personal commitment.
The ability of policy makers and experts to communicate convincingly to citizens has a strong influence on whether ...
[1] ... [2767]
[2768]
[2769]
[2770]
[2771]
[2772]
[2773]
[2774]
2775
[2776]
[2777]
[2778]
[2779]
[2780]
[2781]
[2782]
[2783]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.