Neurobiology -- tuning of timing in auditory axons
2015-08-26
This news release is available in German. An LMU team has shown that the axons of auditory neurons in the brainstem which respond to low and high-frequency sounds differ in their morphology, and that these variations correlate with differences in the speed of signal conduction.
As a rule, the axons (i.e. signal-transmitting fibers) of the neurons in the central nervous systems of vertebrates are ensheathed in layers of myelin, which serves as a form of insulation that improves their electrical conduction properties. In fact, the fat-rich myelin coating largely consists ...
Rehabilitation improves the prognosis of serious heart disease
2015-08-26
Rehabilitation is recommended for many patients following a hospital stay for acute heart disease. In a recent original article in Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl int 112: 527-34) Axel Schlitt et al. show that this improves prognosis for heart disease and can thus reduce patient mortality.
More than 1900 patients in Saxony-Anhalt were contacted and asked to fill out a questionnaire. They had spent time in the hospital for serious cardiovascular disease an average of 11 years earlier. The authors used the data to analyze how many of the patients who ...
Routine surgery
2015-08-26
Cholecystectomy and treatment for inguinal, femoral, umbilical, or abdominal hernia are common surgeries and are considered routine in Germany. In an original article in the current edition of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 112: 535-43), Ulrike Nimptsch and Thomas Mansky show that fewer than 0.5% of patients die as a result of such surgeries. However, in those who do die risks are frequently apparent even before surgery.
Between 2009 and 2013, 731 000 cholecystectomies and 1 023 000 herniotomies took place in Germany. Over 2400 of the patients ...
The fear of trying new foods may have negative dietary implications
2015-08-26
This news release is available in Spanish. The behaviour involving rejection of new foodstuffs is a typical phase in infant development, above all in 2- to 3-year-olds and which subsides around the age of 5. The children who go through dietary neophobia also display signs of anguish and anxiety and this behaviour may even turn into a habit in adulthood.
In her PhD thesis the researcher of the UPV/EHU's Faculty of Psychology Edurne Maiz conducted a study on 831 schoolchildren between the ages of 8 and 16. In the study she used questionnaires on infant neophobia -adapted ...
The missing link
2015-08-26
University of Alberta paleontologists have discovered a new species of lizard, named Gueragama sulamericana, in the municipality of Cruzeiro do Oeste in Southern Brazil in the rock outcrops of a Late Cretaceous desert, dated approximately 80 million years ago.
"The roughly 1700 species of iguanas are almost without exception restricted to the New World, primarily the Southern United States down to the tip of South America," says Michael Caldwell, biological sciences professor from the University of Alberta and one of the study's authors. Oddly however, iguanas closest ...
Home sweet microbe: Dust in your house can predict geographic region, gender of occupants
2015-08-26
The humble dust collecting in the average American household harbors a teeming menagerie of bacteria and fungi, and as researchers from the University of Colorado Boulder and North Carolina State University have discovered, it may be able to predict not only the geographic region of a given home, but the gender ratio of the occupants and the presence of a pet as well.
The new findings, which were published today in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, highlight the impressive amount of microbial diversity in the average household and the degree to which these ...
Police professionals are better observers than ordinary civilians
2015-08-26
Dutch research shows that trained detectives of specialized observation teams are much better at registering details of a drug deal than ordinary civilians. Previous legal-psychological research revealed no relevant differences in observation skills between police professionals and civilians. The findings have been published in Legal and Criminological Psychology.
Judges and juries often assume that police officers' statements are more reliable than those of regular eyewitnesses. Because of this assumption, police officers' statements typically carry more weight in legal ...
Few gay teenage boys get tested for HIV
2015-08-26
Only one in five gay and bisexual teen boys have been tested for HIV
HIV infections are on the rise for young men who have sex with men
Text messages, online program can identify nearby confidential testing sites
Testing in schools would 'normalize' the process.
CHICAGO --- Young men who have sex with men have the highest risk for HIV infection, but only one in five has ever been tested for HIV, a much lower rate than testing for non-adolescents, reports a new national Northwestern Medicine study conducted in partnership with the Center for Innovative Public ...
Foes can become friends on the coral reef
2015-08-26
On the coral reef, knowing who's your friend and who's your enemy can sometimes be a little complicated.
Take seaweed, for instance. Normally it's the enemy of coral, secreting toxic chemicals, blocking the sunlight, and damaging coral with its rough surfaces. But when hordes of hungry crown-of-thorns sea stars invade the reef, everything changes, reports a study to be published August 25 in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Seaweeds appear to protect coral from the marauding sea stars, giving new meaning to the proverb: "The enemy of my enemy is my friend." ...
Chocolate physics: How modeling could improve 'mouthfeel'
2015-08-26
Lecithin is an ingredient that you've probably never heard of, but one that plays a vital role in the production of chocolate and many other foods. It's never been clear how this ingredient works on a molecular level, and confectioners have relied on observational methods - essentially trial and error - to perfect their recipes.
Now, scientists have shown how the field of molecular dynamics (simulation on a molecular level) could be a valuable tool in understanding chocolate conching - the part of the chocolate-making process where aromatic sensation, texture and 'mouthfeel' ...
New cardiovascular disease death rates show stark inequalities between European countries
2015-08-26
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels are the most common cause of death in Europe, resulting in over four million deaths a year (45% of all deaths) according to the latest available figures published today (Wednesday) in the European Heart Journal [1].
Although deaths from cardiovascular disease (CVD) are declining in most of Europe, there are large inequalities between European countries, with higher death rates seen in Eastern Europe. These high death rates correspond to the lower life expectancy also found in these countries, indicating the impact of CVD on inequalities ...
Project in West Africa sees dramatic drop in TB death rates
2015-08-26
Doctors in Togo, West Africa have seen a 10% drop in tuberculosis death rates after redesigning diagnosis and treatment services in one of the country's health districts.
The full results are published in BMJ Quality Improvement Reports today - an open access forum to help clinicians share improvement ideas.
Tuberculosis (TB) is the second leading cause of death among infectious diseases worldwide, killing nearly 2 million people each year, mostly in less developed countries.
Even though there have been improvements in tuberculosis control over the past two decades, ...
The Lancet Infectious Diseases: Experimental post-exposure antiviral treatment may protect humans from Ebola virus
2015-08-26
For the first time, UK physicians have demonstrated that antiviral-based therapies have the potential to protect humans from the deadly Ebola virus. The report, published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases journal, describes a case-series of eight British health-care workers who were evacuated to the Royal Free Hospital in London, UK after possible accidental exposure to Ebola virus in Sierra Leone between January and March 2015.
Four of the health-care workers were considered to have been at significant risk of exposure to Ebola from needlestick injuries and were given ...
Study validates monkey model of visual perception
2015-08-26
A new study from The Journal of Neuroscience shows that humans and rhesus monkeys have very similar abilities in recognizing objects "at a glance," validating the use of this animal model in the study of human visual perception. In the study, published August 26, humans and monkeys not only demonstrated similar ease in recognizing objects in varied positions and landscapes, but both species also tended to make the same errors.
For the study, researchers from MIT compared the performance of two rhesus macaque monkeys and 638 adult human subjects on a large set of object ...
Study finds major lack of resources for rehab patients in Malawi
2015-08-26
Baltimore, Md., August 25, 2015 - Malawi has a population of 16 million, yet, only one inpatient rehabilitation center for individuals with stroke, spinal cord injury, and similar conditions. With just 40 beds, the Kachere Rehabilitation Center in Blantyre, Malawi's second largest city, provides services to the entire country. Because there is little funding for rehabilitation in the country, there is essentially no rehabilitation and follow-up services for patients after they return to their families, homes, and communities.
Leslie B. Glickman, PT, PhD, an assistant ...
Quitting smoking after heart attack reduces chest pain, improves quality of life
2015-08-25
DALLAS, Aug. 25, 2015 -- Smokers who quit after having a heart attack have similar levels of chest pain and mental health as non-smokers, according to research in the American Heart Association journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Researchers assessed 4,003 adults in two U.S. multi-center heart attack patient registries for smoking, chest pain and health-related quality of life measures, such as physical and mental components at admission, at one, six and 12 months after their heart attacks.
At admission, patients were identified as those who never ...
Quitting smoking after heart attack gives quick boost to mental health, quality of life
2015-08-25
A new study shows that quitting smoking after a heart attack has immediate benefits, including less chest pain, better quality of daily life and improved mental health. Many of these improvements became apparent as little as one month after quitting and are more pronounced after one year, according to the research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
"Even in people who smoked and had a heart attack, we see fairly rapid improvements in important measures of health and quality of life when they quit smoking after their heart attacks, compared with ...
Algorithm helps identify elusive genes that express like clockwork
2015-08-25
Genes that express in precisely timed patterns, known as oscillatory genes, play an essential role in development functions like cell division, circadian rhythms and limb formation. But without a time-lapse view of genetic expression, these genes have gone largely undiscovered.
An algorithm developed by scientists at the Morgridge Institute for Research and the University of Wisconsin-Madison is giving scientists a new way to identify the dynamics of oscillatory genes, and perhaps defining the roles of these early-development forces for the first time.
A paper published ...
Many parents unaware of e-cigarette dangers to children?
2015-08-25
As the use of e-cigarettes has risen dramatically in the United States in recent years, so have calls to poison centers about them. Yet many parents who use e-cigarettes - or "vape" - aren't aware of the dangers to children, according to a new study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
The devices are used like typical cigarettes but instead of tobacco, they vaporize a liquid mixture of nicotine, glycerin and glycol ethers. The liquid form is flavored, which appeals to children. If ingested, a teaspoon of this "e-liquid" can be lethal to a child, ...
Study finds paramedic care delivered on-scene for 10-35 minutes leads to better outcomes
2015-08-25
Less than 10 per cent of paediatric patients who suffer a cardiac arrest outside of the hospital survive. There are many factors which can influence survival rates; paramedic care is one of them.
Thanks to the advanced training of paramedics, today, they can spend more time on the scene doing CPR or providing medical care including administering intravenous fluids and medications. However until now, it has not been known if the length of time spent on the scene and onsite medical interventions by paramedics are associated with improved survival for paediatric patients.
In ...
Comprehensive study of genetic risks for inflammatory bowel disease in African-Americans
2015-08-25
Fast Facts:
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has been historically underdiagnosed in African-Americans and is increasing in frequency.
Several gene variants for IBD in whites are key risk factors in African-Americans.
Also important are unique African ancestral variants that cause protection against IBD.
In African-Americans, as in whites and Asians, the dominant region for ulcerative colitis genetic risk in is the human leukocyte antigen region, a major determinant of immune regulation.
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, along ...
Developing a new tool to detect a frequently missed sex chromosome disorder in boys
2015-08-25
NEW YORK, NY (August 25, 2015)-- Klinefelter syndrome is the most common disorder of the male sex chromosomes, yet is rarely diagnosed in children. A new assessment tool is being developed by researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) to help pediatricians detect the physical traits of the syndrome. The tool could pave the way for early interventions that prevent and treat a range of physical, psychological, social, and cognitive impairments. The study was published in The Journal of Pediatrics.
According to lead author Sharron Close, PhD, boys with Klinefelter ...
Batting practice in the genome
2015-08-25
In the biochemical game of genetics, it was thought that the proteins controlling gene regulation in animals were either spectators or players.
But in research appearing in the current issue of eLife, Michigan State University researchers found that spectator proteins are actually practicing up for the big game. They discovered that the proteins are biochemically interacting with thousands of regions of the genome to change the structure of chromosomal material, although only few of them actually are able to change gene expression.
"The previous thinking was that these ...
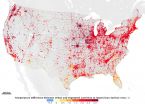
NASA finds vegetation essential for limiting city warming effects
2015-08-25
Cities are well known hot spots - literally. The urban heat island effect has long been observed to raise the temperature of big cities by 1 to 3°C (1.8 to 5.4°F), a rise that is due to the presence of asphalt, concrete, buildings, and other so-called impervious surfaces disrupting the natural cooling effect provided by vegetation. According to a new NASA study that makes the first assessment of urbanization impacts for the entire continental United States, the presence of vegetation is an essential factor in limiting urban heating.
Impervious surfaces' biggest ...
The greater a country's gender equality in employment, the higher its homicide rate
2015-08-25
The greater a country's gender equality when it comes to employment, the higher the overall homicide rate, according to a Baylor University study of 146 countries.
"The finding does not mean that gender equality in employment increases homicide rates, but there is a correspondence," said sociologist Katie Corcoran, Ph.D. "What remains uncertain is the 'why' behind this relationship, although prior research suggests it may be due to threatening male status.
"The research findings are significant because they show that gender inequality does not only affect women," she ...
[1] ... [2825]
[2826]
[2827]
[2828]
[2829]
[2830]
[2831]
[2832]
2833
[2834]
[2835]
[2836]
[2837]
[2838]
[2839]
[2840]
[2841]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.