Electrospray solves longstanding problem in Langmuir-Blodgett assembly
2015-08-20
In the 1930s, Irving Langmuir and his colleague Katharine Blodgett were working long days in the General Electric Company's research laboratory. Together, they discovered that by spreading molecules with volatile organic solvents on the surface of water, they could create a one-molecule-thick film and use it as an anti-reflective coating for glass. Later named Langmuir-Blodgett assembly, this thin-film fabrication technique became popular for creating molecule or nanoparticle monolayers and is commonly used until this day.
Since Langmuir-Blodgett assembly was first reported ...
PET imaging detects fast-growing prostate cancer
2015-08-20
Reston, Va. (August 20, 2015) - A molecular imaging biomarker is able to detect fast-growing primary prostate cancer and distinguish it from benign prostate lesions, addressing an unmet clinical need. The new research, published in the July 2015 issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, is significant for patients with suspected prostate cancer that has not been confirmed by standard biopsy.
"We were able to demonstrate in our research that PSMA PET imaging was more specific than MR imaging for detection of clinically significant high-grade prostate cancer lesions, and ...
Study finds causal connection between genotypes and years of education achieved
2015-08-20
WASHINGTON, D.C., August 20 -- A first-of-its-kind, nationally representative study of siblings supports previously published research on unrelated individuals that links specific genotypes to educational attainment among adults in their mid-20s to early 30s. The research, published today in AERA Open, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association, found that, within families, an adolescent with a higher "polygenic score"--which summarizes previously identified genome-wide associations for educational attainment--than her or his sibling tended ...
Extracorporeal life support is 'bridge-to-life' for patients with sudden onset cardiogenic shock
2015-08-20
Summary: The ideal management strategy for primary cardiogenic shock is a matter of debate. After some early discouraging experiences, the use of extracorporeal life support for patients with cardiogenic shock is having a resurgence. A report from researchers in Padua, Italy finds that patients who have an acute onset of cardiogenic shock, for example following a heart attack, and are placed on extracorporeal life support, fare better than those who have a chronic cardiac pathology. In an accompanying editorial, Dr. Vivek Rao of the University of Toronto puts the findings ...
Virginia Tech researchers discover potential biomarker for pre-diabetes
2015-08-20
Virginia Tech researchers have identified a biomarker in pre-diabetic individuals that could help prevent them from developing Type II diabetes.
Publishing in Clinical Epigenetics, the researchers discovered that pre-diabetic people who were considered to be insulin resistant -- unable to respond to the hormone insulin effectively -- also had altered mitochondrial DNA.
Researchers made the connection by analyzing blood samples taken from 40 participants enrolled in the diaBEAT-it program, a long-term study run by multiple researchers in the Fralin Translational Obesity ...
Harvard's Wyss Institute improves its sepsis therapeutic device
2015-08-20
(BOSTON) - Last year, a Wyss Institute team of scientists described the development of a new device to treat sepsis that works by mimicking our spleen. It cleanses pathogens and toxins from blood circulating through a dialysis-like circuit. Now, the Wyss Institute team has developed an improved device that synergizes with conventional antibiotic therapies and that has been streamlined to better position it for near-term translation to the clinic. The improved design is described in the October volume 67 of Biomaterials.
Sepsis is a common and frequently fatal medical ...
Home births save money, are safe, UBC study finds
2015-08-20
Having a baby at home can save thousands of dollars over a hospital birth and is just as safe for low-risk births, according to a new UBC study.
Researchers with UBC's School of Population and Public Health and the Child and Family Research Institute looked at all planned home births attended by registered midwives in B.C. between 2001 and 2004. They compared them to planned hospital births attended by registered midwives or physicians in which the mothers met the criteria for home birth.
For the first 28 days postpartum, they found planned home births saved an average ...
Middle-aged drivers admit to using cellphones while driving, even with children in the car
2015-08-20
Amsterdam, August 20, 2015 - A new study published in Journal of Transport & Health reveals that middle-aged drivers are at higher risk of crashes because they use their cellphone regularly while driving. The research reveals that most drivers admit to using their cellphones regularly while driving, even with children in the car; drivers also feel pressured to answer work calls while driving.
The authors of the study, from the University of California San Diego, are now working with companies to teach employees about the risks associated with distracted driving, and show ...
Study finds association between people who have had a traumatic brain injury and ADHD
2015-08-20
TORONTO, Aug. 20, 2015--A new study has found a "significant association" between adults who have suffered a traumatic brain injury at some point in their lives and who also have attention deficit hyperactive disorder.
The study, published today in the Journal of Psychiatric Research, supports research that found a similar association in children, said Dr. Gabriela Ilie, lead author of the study and a post-doctoral fellow at St. Michael's Hospital.
The data used in the adult study was collected by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health's Monitor, a continuous, cross-sectional ...
Lighting up cancer cells to identify low concentrations of diseased cells
2015-08-20
Oxford, August 20, 2015 - Researchers in China have developed tiny nanocrystals that could be used in the next generation of medical imaging technologies to light up cancer cells. In a study published in the inaugural issue of the journal Applied Materials Today, a new rapid, online only publication, the team of researchers describe how they make these films which are based on the heavy metals lanthanum and europium.
Dr. Yaping Du of Xi'an Jiaotong University, China, and colleagues have developed a way to make high-quality nanocrystals of lanthanide oxybromides, where ...
New method of closing the incision during scoliosis surgery nearly eliminates infections
2015-08-20
NEW YORK, NY - Patients with scoliosis who undergo surgery may be less likely to develop an infection or other complications after the procedure when a novel wound closure technique pioneered at NYU Langone Medical Center is utilized, according to new research. The study was published online this past July in the Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics.
In this new technique, surgeons use a multilayered flap closure that enables doctors to close several layers of muscle and fascia while maintaining blood supply from the donor site to the recipient site. The researchers believe ...
Home-based treatment is cost-effective alternative for heart patients
2015-08-20
Post-discharge disease management provided in their own homes could be a cost-effective alternative for recently-hospitalised elderly patients with chronic heart failure (CHF).
Just published in the International Journal of Cardiology, this is the finding of a recent economic evaluation conducted by Griffith University using data from a randomised controlled trial (The WHICH Study).
In collaboration with the Australian Catholic University, 280 patients with CHF recruited from three public hospitals, received multidisciplinary disease management.
With the aim of reducing ...
Grape waste could make competitive biofuel
2015-08-20
The solid waste left over from wine-making could make a competitive biofuel, University of Adelaide researchers have found.
Published in the journal Bioresource Technology, the researchers showed that up to 400 litres of bioethanol could be produced by fermentation of a tonne of grape marc (the leftover skins, stalks and seeds from wine-making).
Global wine production leaves an estimated 13 million tonnes of grape marc waste each year. Nationally it is estimated that several hundred thousand tonnes are generated annually and it is generally disposed of at a cost to ...
Manchester team reveal new, stable 2-D materials
2015-08-20
The problem has been that the vast majority of these atomically thin 2D crystals are unstable in air, so react and decompose before their properties can be determined and their potential applications investigated.
Writing in Nano Letters, the University of Manchester team demonstrate how tailored fabrication methods can make these previously inaccessible materials useful.
By protecting the new reactive crystals with more stable 2D materials, such as graphene, via computer control in a specially designed inert gas chamber environments, these materials can be successfully ...
More grasslands in Tibet could bring climate improvements
2015-08-20
In the Arctic, warming increases like a spiral. Global warming means that the periods of growth are becoming longer and vegetation growth is increasing. At the same time, heat transfer to the Arctic from lower latitudes is rising, reducing sea ice there, and this in turn is contributing towards a faster local rise in temperature.
A new research study published in the highly respected research journal PNAS shows that the situation is the reverse on the Tibetan Plateau.
Vegetation on the Tibetan Plateau has also increased as a result of global warming. However, in contrast ...
Small, inexpensive, and incredibly resilient: A new femtosecond laser for industry
2015-08-20
A team at the University of Warsaw, Faculty of Physics has created a laser capable of generating ultrashort pulses of light even under extremely difficult external conditions. This unique combination of precision and resilience is due to the fact that the whole process of generating femtosecond laser pulses takes place within a specially-selected optical fiber.
Its appearance seems quite inconspicuous: just a flat, rectangular box, tens of centimeters across and about the same height, with a thin, shiny-tipped "thread" leading out of it, so long that it is rolled up ...
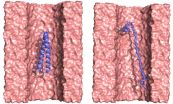
Penn researchers use nanoscopic pores to investigate protein structure
2015-08-20
University of Pennsylvania researchers have made strides toward a new method of gene sequencing a strand of DNA's bases are read as they are threaded through a nanoscopic hole.
In a new study, they have shown that this technique can also be applied to proteins as way to learn more about their structure.
Existing methods for this kind of analysis are labor intensive, typically entailing the collection of large quantities of the protein. They also often require modifying the protein, limiting these methods' usefulness for understanding the protein's behavior in its natural ...
Aquatic hunger games: Archerfish spit the distance for food
2015-08-20
Move over, Katniss Everdeen. For archerfish, the odds are ever in their favor, according to new research from Wake Forest University.
The sharp-shooting fish's ability to spit water to hit food targets has been well documented, but a new study published online in the journal Zoology showed for the first time that there is little difference in the amount of force of their water jets based on target distance. And, when given the choice, the fish preferred closer targets.
The study was co-authored by Wake Forest researchers Morgan Burnette, a biology graduate student, ...
Warming climate is deepening California drought
2015-08-20
A new study says that global warming has measurably worsened the ongoing California drought. While scientists largely agree that natural weather variations have caused a lack of rain, an emerging consensus says that rising temperatures may be making things worse by driving moisture from plants and soil into the air. The new study is the first to estimate how much worse: as much as a quarter. The findings suggest that within a few decades, continually increasing temperatures and resulting moisture losses will push California into even more persistent aridity. The study appears ...
Study shows what business leaders can learn from Formula One racing
2015-08-20
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Formula One racing teams may have a lesson to teach business leaders: Innovation can be overrated.
That's the conclusion from academic researchers who pored over data from 49 teams over the course of 30 years of Formula One racing. They found that the teams that innovated the most - especially those that made the most radical changes in their cars - weren't usually the most successful on the race course.
Moreover, radical innovations were the least successful at exactly the times when many business leaders would be most likely to try them: when there ...
How newts can help osteoarthritis patients
2015-08-20
A research team at York has adapted the astonishing capacity of animals such as newts to regenerate lost tissues and organs caused when they have a limb severed.
The research, which is funded by a £190,158 award from the medical research charity Arthritis Research UK, is published in Nature Scientific Reports.
The scientists, led by Dr Paul Genever in the Arthritis Research UK Tissue Engineering Centre in the University's Department of Biology, have developed a technique to rejuvenate cells from older people with osteoarthritis to repair worn or damaged cartilage ...
New theory: If we want to detect dark matter we might need a different approach
2015-08-20
Physicists suggest a new way to look for dark matter: They beleive that dark matter particles annihilate into so-called dark radiation when they collide. If true, then we should be able to detect the signals from this radiation.
­The majority of the mass in the Universe remains unknown. Despite knowing very little about this dark matter, its overall abundance is precisely measured. In other words: Physicists know it is out there, but they have not yet detected it.
It is definitely worth looking for, argues Ian Shoemaker, former postdoctoral researcher at Centre ...
Stem cells derived from amniotic membrane can benefit retinal diseases when transplanted
2015-08-19
Putnam Valley, NY. (Aug. 19, 2015) - A team of researchers in South Korea has successfully transplanted mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) derived from human amniotic membranes of the placenta (AMSCs) into laboratory mice modeled with oxygen-induced retinopathy (a murine model used to mimic eye disease). The treatment aimed at suppressing abnormal angiogenesis (blood vessel growth) which is recognized as the cause of many eye diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration. The researchers reported that the AMSCs successfully migrated to the retinas ...
NIH scientists and colleagues successfully test MERS vaccine in monkeys and camels
2015-08-19
National Institutes of Health (NIH) scientists and colleagues report that an experimental vaccine given six weeks before exposure to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) fully protects rhesus macaques from disease. The vaccine also generated potentially protective MERS-CoV antibodies in blood drawn from vaccinated camels. A study detailing the synthetic DNA vaccine appears in the Aug. 19 Science Translational Medicine. MERS-CoV, which causes pneumonia deep in the lungs, emerged in 2012 and has sickened more than 1,400 people and killed 500, mostly in ...
Seizures in neonates undergoing cardiac surgery underappreciated and dangerous
2015-08-19
Summary: In 2011, the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society issued a guideline recommending that neonates undergoing cardiac surgery for repair of congenital heart disease be placed on continuous encephalographic (EEG) monitoring after surgery to detect seizures. These recommendations followed reports that seizures are common in this population, may not be detected clinically, and are associated with adverse neurocognitive outcomes. Yet, in a discussion at the 2014 Annual Meeting of The American Association for Thoracic Surgery, 80% to 90% of the audience was not following ...
[1] ... [2826]
[2827]
[2828]
[2829]
[2830]
[2831]
[2832]
[2833]
2834
[2835]
[2836]
[2837]
[2838]
[2839]
[2840]
[2841]
[2842]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.