Breakthrough in 'marriage-broker' protein
2015-08-12
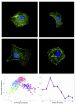
This news release is available in French. Scientists at the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital -The Neuro, at McGill University and the McGill University Health Centre, have made a breakthrough in understanding an important protein that appears to act as a kind of cellular "marriage broker." The protein called Netrin1 brings cells together and maintains their healthy relationships. Netrin1 plays an essential role in the growth of the human organism, directing cell migration and the formation of cell circuits both at the embryo stage and after birth.
The ...
Antidepressant drug trials criteria not generalizable
2015-08-12
PROVIDENCE, R.I. - Mark Zimmerman, M.D., a clinical researcher at Rhode Island Hospital, and his team analyzed the criteria used in antidepressant efficacy studies (AETs) and learned that the inclusion/exclusion criteria for AETs have narrowed over the past five years so that the most patients are excluded. The research was published today in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
"The inclusion/exclusion criteria for AETs have narrowed over the past five years, thereby suggesting that AETs may be even less generalizable than they were previously," said Zimmerman, director of outpatient ...
Rice University bioengineers advance computing technique for health care and more
2015-08-12
Rice University scientists have developed a big data technique that could have a significant impact on health care.
The Rice lab of bioengineer Amina Qutub designed an algorithm called "progeny clustering" that is being used in a hospital study to identify which treatments should be given to children with leukemia.
Details of the work appear today in Nature's online journal Scientific Reports.
Clustering is important for its ability to reveal information in complex sets of data like medical records. The technique is used in bioinformatics -- a topic of interest to ...
This week from AGU: Natural arches, Italian earthquake, Canadian rivers & research papers
2015-08-12
GeoSpace
Natural arches hum their health and scientists are listening
For the first time, scientists have found a way to detect if the breathtaking natural arches of Utah's Canyonlands and Arches national parks are suffering from internal damage that could lead to their collapse, according to a new study in Geophysical Research Letters.
16th century Italian earthquake changed river's course
In 1570, a 5.8-magnitude earthquake struck the northern Italian city of Ferrara, causing dozens of deaths, major damage to the city and thousands to flee. A new study in Journal ...
Pulmonary hypertension: A growing problem in US children
2015-08-12
Fast Facts:
Study reveals pediatric pulmonary hypertension hospitalizations on the rise, resulting in skyrocketing costs.
Findings uncover need to initiate a national registry to track individual patients over time and to provide a foundation for clinical trials to test new and better treatments.
Study finds pulmonary hypertension hospitalizations now higher in children without congenital heart disease.
A review of 15 years' worth of data in a national pediatric medical database has documented a substantial increase in the rate of hospitalizations for children ...
Brain plasticity after vision loss has an 'on-off switch'
2015-08-12
KU Leuven biologists have discovered a molecular on-off switch that controls how a mouse brain responds to vision loss. When the switch is on, the loss of sight in one eye will be compensated by the other eye, but also by tactile input from the whiskers. When the switch is off, only the other eye will take over. These findings may help improve patient susceptibility to sensory prosthetics such as cochlear implants or bionic eyes.
Our brain adjusts to changes of all kind. This brain plasticity is useful for neural development and learning, but also comes into play when ...
Fireflies predict network loyalty
2015-08-12
Online social networking generates vast quantities of data that might be useful to the service providers, advertising agencies, and even the users themselves. Writing in the International Journal of Communication Networks and Distributed Systems this month, researchers in India describe an approach to establishing new connections in a network using what they refer to as a "firefly swarm approach"
Ebin Deni Raj and Dhinesh Babu of the School of Information Technology and Engineering, VIT University, in Tamil Nadu, explain that the emergence of social computing, especially ...
Researchers reveal mystery of how contractions in labour grow stronger
2015-08-12
Scientists, for the first time, have identified a mechanism in the muscle cells of the uterus that could point to how contractions in childbirth grow stronger.
It is understood that the hormone oxytocin plays a significant role in stimulating contractions during labour, which helps to move a baby down the birth canal. It is not known, however, how these contractions increase and sustain their strength during hours of labour.
A team at Liverpool investigated how uterine contractions grow stronger when the human body's 'biological rules' dictates that contractions ...
Statistical model predicts with high accuracy play-calling tendency of NFL teams
2015-08-12
SEATTLE, WA, AUGUST 12, 2015 - If a defensive coordinator of a National Football League (NFL) team could predict with high accuracy whether their team's opponent will call a pass or run play during a game, he would become a rock star in the league and soon be a head coach candidate.
William Burton, an industrial engineering student who is minoring in statistics at North Carolina State University (NCSU), and collaborator Michael Dickey, a statistics major who graduated from NCSU in May, have built a statistical model that predicts the play-calling tendency of NFL teams ...
Statisticians using social media to track foodborne illness and improve disaster response
2015-08-12
SEATTLE, WA, AUGUST 12, 2015 - The growing popularity and use of social media around the world is presenting new opportunities for statisticians to glean insightful information from the infinite stream of posts, tweets and other online communications that will help improve public safety.
Two such examples--one that enhances systems to track foodborne illness outbreaks and another designed to improve disaster-response activities--were presented this week at the 2015 Joint Statistical Meetings (JSM 2015) in Seattle.
Tracking Foodborne Illness Outbreaks:
In a presentation ...
Value-added models focus of JSM 2015 panel discussion
2015-08-12
SEATTLE, WA, AUGUST 12, 2015 - Panelists talked about various aspects of value-added models, commonly referred to as VAMs, while the discussant posed a new question about the use of evaluation models during a panel discussion on the hot-button topic today at the 2015 Joint Statistical Meetings (JSM 2015) in Seattle.
The panel discussion, titled "Value-Added Models: A Primer and Discussion," featured four experts in the areas of statistics, education research and VAMs. They are:
Jennifer E. Broatch, assistant professor of statistics at Arizona State University
Jennifer ...
Target healthy cells to stop brain cancer 'hijack': UBC study
2015-08-12
New UBC research into brain cancer suggests treatments should target the cells around a tumor to stop it from spreading.
UBC research team Christian Naus, Wun Chey Sin and John Bechberger study glioma, the most aggressive form of adult brain cancer. Glioma has a low five-year survival rate of 30 per cent because it is difficult to completely remove cancer cells without compromising brain functions and chemotherapy and radiotherapy do not prevent the regrowth of remaining cancer cells.
With this new research, the team reveals an alternative route to rein in the glioma ...
Molecular discovery paves way for new diabetic heart disease treatments
2015-08-12
Researchers at New Zealand's University of Otago have discovered why heart disease is the number-one killer of people with diabetes, a breakthrough finding opening the way for new treatments to combat the disease in diabetic patients by targeting a key protein called Beclin-1.
Diabetes affects more than 365 million people worldwide with rates expected to double by 2030. Recent studies show that at least 60% of people with the disease die because of cardiovascular complications.
Why diabetes takes such a toll on heart health has long remained a mystery. Now, in a new ...
Powering off TB: New electron transport gene is a potential drug target
2015-08-12
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recently approved the first new drug to fight tuberculosis (TB) in more than 40 years, but treatment still takes six months, 200 pills and leaves 40 percent of patients uncured. Thus, new targets are needed. Today in ACS Central Science, researchers report they have identified one such target -- a gene that allows the disease to camp out in human immune cells, and is thus essential for the organism's proliferation.
TB kills about 1.3 million people around the world every year. The microorganism that causes the disease, Mycobacterium ...
Retrieving eggs earlier during IVF may improve success rates for older women
2015-08-12
IVF success rates for women aged 43 and above could improve by retrieving eggs from their ovaries at an earlier stage of fertility treatment, according to a new study published today in the Journal of Endocrinology.
US-based researchers found that the function of cells which nurse and support the development of eggs declines rapidly after 43, causing the egg to be bombarded by hormones that are normally only released after ovulation. Retrieving eggs from smaller follicles at an earlier stage in the IVF process was found to minimise this risk, resulting in a higher quality ...
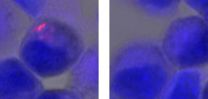
Blood vessel 'doorway' lets breast cancer cells spread through blood stream
2015-08-12
August 12, 2015--(BRONX, NY)--Using real-time, high-resolution imaging, scientists have identified how a "doorway" in the blood vessel wall allows cancer cells to spread from breast tumors to other parts of the body. The findings lend support to emerging tests that better predict whether breast cancer will spread, which could spare women from invasive and unnecessary treatments, and could lead to new anti-cancer therapies. The research, conducted by investigators at the NCI-designated Albert Einstein Cancer Center (AECC) and Montefiore Einstein Center for Cancer Care, utilized ...
Postmenopausal women prefer vaginal estrogen to achieve higher sexual quality of life
2015-08-12
CLEVELAND, Ohio (August 12, 2015)--Local vaginal estrogen (VE) appears to have escaped the shroud of doubt cast upon hormone therapy as a result of the Women's Health Initiative Study (WHI) by providing numerous medical benefits without systemic effects. That's according to a new study reported online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
The study demonstrated that postmenopausal women who suffer from painful intercourse and vaginal dryness are more likely to use VE, regardless of whether they use any other type of hormone therapy. ...
Radiation costs vary among Medicare patients with cancer
2015-08-11
Cost of radiation therapy among Medicare patients varied most widely because of factors unrelated to a patient or that person's cancer, report University of California, San Diego School of Medicine researchers in the Journal of Oncology Practice.
Year of diagnosis, location of treatment, clinic type and individual radiation provider accounted for 44 to 61 percent of the variation in cost for patients with breast, lung and prostate cancer therapies, according to the study published August 11 online. Factors associated with the patient or patient's tumor accounted for less ...
Deceptive woodpecker uses mimicry to avoid competition
2015-08-11
Birds of a feather may flock together, but that doesn't mean they share a genetic background. Though birds were first classified into groups primarily based on appearance, research forthcoming in The Auk: Ornithological Advances by Brett Benz of the American Museum of Natural History, Mark Robbins of the University of Kansas Biodiversity Institute, and Kevin Zimmer of the Los Angeles County Museum of Natural History demonstrates that this method isn't necessarily accurate: in a group of very similar-looking South American woodpecker species, genetic analysis has now shown ...
Penn study details 'rotten egg' gas' role in autoimmune disease
2015-08-11
The immune system not only responds to infections and other potentially problematic abnormalities in the body, it also contains a built-in brake in the form of regulatory T cells, or Tregs. Tregs ensure that inflammatory responses don't get out of hand and do damage. In autoimmune diseases, sometimes these Treg cells don't act as they should.
A new study led by Songtao Shi of the University of Pennsylvania has demonstrated how Tregs can themselves be regulated, by an unexpected source: hydrogen sulfide, a gas produced by the body's muscle cells and one often associated ...
Discovery in growing graphene nanoribbons could enable faster, more efficient electronics
2015-08-11
MADISON, Wis. -- Graphene, an atom-thick material with extraordinary properties, is a promising candidate for the next generation of dramatically faster, more energy-efficient electronics. However, scientists have struggled to fabricate the material into ultra-narrow strips, called nanoribbons, that could enable the use of graphene in high-performance semiconductor electronics.
Now, University of Wisconsin-Madison engineers have discovered a way to grow graphene nanoribbons with desirable semiconducting properties directly on a conventional germanium semiconductor wafer. ...
New combination treatment effective against melanoma skin
2015-08-11
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- In findings never before seen in melanoma, a novel combination therapy was found to be highly effective at treating patients with skin metastases, new research from UC Davis has shown.
Led by Emanual Maverakis of the UC Davis Department of Dermatology, the research found that Interleukin (IL)-2 combined with imiquimod and topical retinoid therapy in patients with so-called "in-transit metastases" is a promising therapeutic option.
The findings have been published online first in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.06.060).
"It's ...
Hepatitis C infection may fuel heart risk
2015-08-11
People infected with the hepatitis C virus are at risk for liver damage, but the results of a new Johns Hopkins study now show the infection may also spell heart trouble.
The findings, described online July 27 in The Journal of Infectious Diseases, emerged from a larger ongoing study of men who have sex with men, many but not all of whom were infected with HIV and followed over time to track risk of infection and disease progression. A subset of the participants had both HIV and hepatitis C, two infections that often occur together.
Even though people infected with ...
Sport TV exposing children to thousands of alcohol-adverts per year
2015-08-11
New research from Monash University shows that children are being exposed to thousands of alcohol adverts when watching sport TV, questioning the effectiveness of advertising regulations designed to protect children.
The study, published in the international journal PLOS ONE, found that 87 per cent of all alcohol adverts during the daytime were in sport TV when hundreds of thousands of children were watching. A clause in Australia's advertising regulations allowing alcohol advertising in live sport programming during the day when children are watching appears to be responsible ...
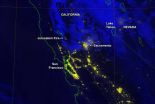
California's Jerusalem fire at night
2015-08-11
From its orbit around the Earth, the NASA-NOAA Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite or Suomi NPP satellite, captured a night-time image of California's Jerusalem Fire.
InciWeb is an interagency all-risk incident information management system that coordinates with federal, state and local agencies to manage wildfires. According to Inciweb, this fire is burning on lands managed by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management within the Berryessa Snow Mountain National Monument. It is being managed by the Sonoma-Lake-Napa Unit of the California Department of Forestry ...
[1] ... [2834]
[2835]
[2836]
[2837]
[2838]
[2839]
[2840]
[2841]
2842
[2843]
[2844]
[2845]
[2846]
[2847]
[2848]
[2849]
[2850]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.