'Machine teaching' holds the power to illuminate human learning
2015-08-11
MADISON, Wis. -- Human learning is a complex, sometimes mysterious process. Most of us have had experiences where we have struggled to learn something new, but also times when we've picked something up nearly effortlessly.
What if a fusion of computer science and psychology could help us understand more about how people learn, making it possible to design ideal lessons?
That long-range goal is moving toward reality thanks to an effort led by professors in the University of Wisconsin-Madison departments of computer sciences, psychology and educational psychology. Their ...
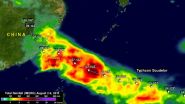
NASA analyzes Typhoon Soudelor's rainfall
2015-08-11
Typhoon Soudelor dropped over two feet of rainfall when it made landfall in China in early August, and soaked Taiwan. NASA estimated that rainfall using data from the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission.
Soudelor formed in the middle of the Pacific Ocean well east of Guam on July 20, 2015. Soudelor became more powerful with peak intensity of about 155 knots (178 mph) reached on August 3, 2015 when the super typhoon was well east of Taiwan over the open waters of the Pacific Ocean.
Soudelor's winds died down a little but rebounded to with over 100 knots (115 ...
How to reduce piglet mortality with sows in loose-housed systems
2015-08-11
Swine housing has been a hot topic in recent years, not only in the United States, but in many countries, such as Denmark. Due to genetic advancements in recent years, the average litter size in Denmark is 16.6 total born piglets. With increased number of piglets, determining the optimal housing system for both the piglet and sow is critical.
In Denmark, gestation crates were banned in new buildings in 1999 and from all existing units in 2013. As of January 1, 2015, sows are required to be loose housed from time of weaning until seven days before expected parturition ...
Dog food processing methods answering questions
2015-08-11
August 6, 2015 - According to the Association for Pet Obesity Prevention in 2014, approximately 53% and 58% of dogs and cats, respectively, in the United States were overweight and obese. These numbers have steadily increased since 2010. However, most pet owners (? 90%) do not realize and cannot identify that their pets are overweight/obese.
What can we do about this growing problem? Pet food companies and nutritionists are searching for ingredients, like prebiotics and probiotics, to combat these conditions. But, could the problem have another solution?
Dr. Aulus Carciofi, ...
Behaviors linked to adult crime differ between abused boys and girls, study finds
2015-08-11
The signs that an abused child might later commit crimes might not be obvious -- that boisterous playground behavior from a third-grade boy, for example, or the 10-year-old girl who seems a little anxious or withdrawn.
But new research from the University of Washington suggests that troubling behaviors exhibited by abused children can be predictors of later criminal activity, and that those indicators differ between boys and girls.
The study, published Aug. 11 in the Journal of Interpersonal Violence, found that elementary-aged boys who show "externalizing" behaviors ...
Skeletal muscle atrophy in congestive heart failure
2015-08-11
It is a paradox: Patients with advanced congestive heart failure lose skeletal muscle mass, but their heart muscles become enlarged to provide the body with an adequate supply of blood and thus with oxygen. It has long been known that the protein angiotensin II plays a villainous role in this process, but the exact mechanism has remained unclear. Now, after seven years of fitting the pieces of this puzzle together, the biologist Dr. Philipp Du Bois and the cardiologist PD Dr. Jens Fielitz of the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), a joint cooperation between ...
UNH scientists provide new tools for predicting arrival, impact of solar storms
2015-08-11
DURHAM, N.H. -- When the sun hurls a billion tons of high-energy particles and magnetic fields into space at speeds of more than a million miles per hour and the "space weather" conditions are right, the resulting geomagnetic storm at Earth can wreak havoc on communication and navigation systems, electrical power grids, and pose radiation hazards to astronauts and airline passengers and crew.
Being able to predict when those conditions are right is a key scientific goal, and researchers from the University of New Hampshire's Space Science Center (SSC) are now adding ...
Research advances potential for test and vaccine for genital and oral herpes
2015-08-11
Findings from a pair of new studies could speed up the development of a universally accurate diagnostic test for human herpes simplex viruses (HSV), according to researchers at Johns Hopkins and Harvard universities and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The work may also lead to the development of a vaccine that protects against the virus.
Depending on the strain and other factors, HSV can cause cold sores -- classically associated with HSV1 -- or genital herpes -- classically HSV2 -- with the latter being the more serious of the two diseases, particularly because ...
Melting glaciers feed Antarctic food chain
2015-08-11
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Nutrient-rich water from melting Antarctic glaciers nourishes the ocean food chain, creating feeding "hot spots" in large gaps in the sea ice, according to a new study.
New research finds that iron stored in the region's glaciers is being shuttled by melting water to open areas of the ocean, called polynyas, where it stimulates growth of phytoplankton, ocean algae that form the base of the marine food chain. Krill and fish thrive on phytoplankton, and these smaller animals support penguins, seals and whales that feed and breed in the polynyas that ...
Single interrupted pregnancy may impact later deliveries, new research finds
2015-08-11
It has been well established that women who have had several abortions or miscarriages are likely to face a slightly higher risk of complications in subsequent pregnancies. They may experience vaginal bleeding during early pregnancy, preterm birth, low fetal birth weight, and placenta-related complications. Women with a medical history of several interrupted pregnancies are usually advised to take extra precautions to ensure healthy full-term pregnancies later in life.
New Tel Aviv University research published in the Journal of Maternal-Fetal and Neonatal Medicine finds ...
Furthering data analysis of next-generation sequencing to facilitate research
2015-08-11
CINCINNATI - Researchers at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center have developed a user-friendly, integrated platform for analyzing the transcriptomic and epigenomic "big data."
Reporting their platform in Genome Biology, scientists say that the new platform--called BioWardrobe--could help biomedical researchers answer questions about both basic biology and disease.
The recent proliferation of next-generation sequencing (NGS)-based methods for analysis of gene expression, chromatin structure and protein-DNA interactions have opened new horizons for molecular ...
Johns Hopkins, Mayo experts suggest upgrades to current heart disease prevention guideline
2015-08-11
Acknowledging key strengths and "lessons learned," preventive cardiologists from Johns Hopkins and Mayo Clinic have developed a short list of suggested upgrades to the controversial heart disease prevention guidelines issued jointly in 2013 by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology.
The recommendations, published in the Aug. 11 issue of Mayo Clinic Proceedings, are designed, the authors say, to improve subsequent guidelines and clarify key points of confusion related to risk prediction and treatment of heart attacks and strokes.
"Given ...
SwRI scientists study nitrogen provision for Pluto's atmosphere
2015-08-11
San Antonio -- August 11, 2015 -- The latest data from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft reveal diverse features on Pluto's surface and an atmosphere dominated by nitrogen gas. However, Pluto's small mass allows hundreds of tons of atmospheric nitrogen to escape into space each hour.
So where does all this nitrogen come from? Dr. Kelsi Singer, a postdoctoral researcher at Southwest Research Institute, and her mentor Dr. Alan Stern, SwRI associate vice president and the science lead for the New Horizons mission, outlined likely sources in a paper titled, "On the Provenance ...
SIV shrugs off antibodies in vaccinated monkeys
2015-08-11
New research on monkeys vaccinated against HIV's relative SIV calls into question an idea that has driven AIDS vaccine work for years. The assumption: a protective vaccine only needs to stimulate moderate levels of antibodies that neutralize the virus.
However, scientists at Yerkes National Primate Research Center and the Emory Vaccine Center have found that when SIV manages to infect vaccinated monkeys that have potent neutralizing antibodies in their blood, the virus appears to shrug the antibodies off. No stealthy escape by mutation was necessary.
The results were ...
C-section could impact baby's ability to focus: York U study
2015-08-11
TORONTO, August 11 2015 -- There can be a difference in how well babies focus attention on an object of interest, depending on whether they were delivered by natural birth or Caesarean section, a recent York University study indicates.
"Our research has revealed that being born by a C-section slows a baby's spatial attention, which plays a role in its ability to focus on a particular area or object of interest," says Professor Scott Adler in the Department of Psychology, Faculty of Health at YorkU.
According to Adler and his co-researcher Audrey Wong Kee-You, very ...
Cutting costs: Sustainability matters even in complex networks
2015-08-11
Every day, we expend energy when we con­trol the net­works in our lives. For example, to drive our car, we utilize a net­work whose com­po­nents include the car's accel­er­ator, steering wheel, and brake. Knowing how much that effort "costs" can help deter­mine which com­po­nents to manipulate--and to what degree--to ensure the smoothest, safest ride as you acclerate from 55 to 90 miles per hour.
On Monday, North­eastern researchers revealed just such a mea­suring strategy in a new paper pub­lished in Nature Physics.
"We ...
New report recommends research priorities for Antarctic and Southern Ocean science
2015-08-11
WASHINGTON -- An initiative to better understand how melting ice sheets will contribute to sea-level rise, efforts to decode the genomes of organisms to understand evolutionary adaptations, and a next-generation cosmic microwave background experiment to address fundamental questions about the origin of the universe are the top research goals for Antarctic and Southern Ocean science recommended in a new report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.
The report, which offers a strategic vision to guide the U.S. Antarctic Program at the National ...
Vortioxetine in depression: No hint of added benefit
2015-08-11
Vortioxetine (trade name: Brintellix) has been approved since December 2013 for the treatment of depression in adults, but did not become actually available before May 2015. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined in a dossier assessment whether this drug offers an added benefit over the appropriate comparator therapy. Such an added benefit cannot be derived from the dossier because it contained no data evaluable for the assessment.
SSRI is drug component of comparator therapy
The Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) distinguished between ...
Insulin degludec plus liraglutide: No hint of added benefit in type 2 diabetes
2015-08-11
The fixed-ratio combination of the two drugs insulin degludec and liraglutide (trade name: Xultophy) has been approved since September 2014 for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is given as an injection in addition to other blood-glucose lowering drugs when these alone or in combination with basal insulin are insufficient to lower blood glucose levels. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined in a dossier assessment whether this fixed-ratio combination offers an added benefit over the appropriate comparator therapy.
Such ...
One technique therapists use that really helps depressed patients
2015-08-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Some depressed patients may be hoping for answers from their therapists, but a new study suggests questions may be the key.
Researchers examined how cognitive therapy for depression achieves its positive effects. Their study is the first to show that depressed patients see substantial improvements in their depressive symptoms when their therapists use a technique called "Socratic questioning."
These are a series of guided questions in which the therapist asks a patient to consider new perspectives on themselves and their place in the world.
"People ...
C-sections could influence babies' ability to focus
2015-08-11
Being delivered through a caesarean section influences at least one form of babies' ability to concentrate. It slows their spatial attention, which plays a role in how well they are able to prioritize and focus on a particular area or object that is of interest. These are the findings of Scott Adler and Audrey Wong-Kee-You of York University in Canada, published in Springer's journal Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics.
Very early birth factors such as birth weight and a mother's age impact the development of a child. However, very little is known about how the actual ...
Chitin of insects and crustaceans found to be active against pathogenic microorganisms
2015-08-11
The study specifically concentrated on chitosan extracted from chitin in the carapaces of insects and crustaceans. The biopolymer was first discovered in 1859 but only recently has it become possible to establish its production within desired parameters, when researchers from the Bioengineering Center of RAS designed narrow-dispersion chitosan. This gave an opportunity to modern scientists to customize the biological properties of certain types of the biopolymer.
"We found that some forms of chitosan are toxic. They can disrupt the membranes of pathogenic microorganisms" ...
Researchers develop fast test for invasive carp
2015-08-11
A Case Western Reserve University graduate student turned a research paper into a field test that quickly determines whether an Asian carp invading Lake Erie is sterile or can reproduce.
If proven successful, the technique could save money and time in the effort to keep the carp out of the Great Lakes, where the fish could grow unchecked and devour food supplies and habitat critical to native species..
Grass carp, the species Ctenopharyngodon idella, have been introduced throughout the Midwest and South to clear ponds choked with weeds. Also called the white amur, fertile ...
NYU study examines top high school students' stress and coping mechanisms
2015-08-11
Over time selective high schools have oriented themselves to address a context of increasingly competitive college admissions
School work, college applications, extracurricular activities, and parental expectations all contribute to teenagers' stress
Youth, schools, and experts identified substance use as a common strategy for coping with stress
"School, homework, extracurricular activities, sleep, repeat--that's what it can be for some of these students," says Noelle Leonard, PhD, a senior research scientist at the New York University College of Nursing (NYUCN). ...
Research pours cold water on ice bath recovery theory
2015-08-11
If the thought of a post workout ice bath is enough to make you shiver, new research from QUT and The University of Queensland (UQ) will warm your heart.
The comprehensive study found cold water immersion after strength training hindered muscle adaptation - pouring cold water on the long-held theory that an ice bath helps speed up recovery.
Dr Llion Roberts, from UQ's School of Human Movement and Nutrition Sciences, and Dr Jonathan Peake, from QUT's School of Biomedical Sciences, led the research, with colleagues from the Queensland Academy of Sport, Norwegian School ...
[1] ... [2835]
[2836]
[2837]
[2838]
[2839]
[2840]
[2841]
[2842]
2843
[2844]
[2845]
[2846]
[2847]
[2848]
[2849]
[2850]
[2851]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.