'Jumping genes' unusually active in many gastrointestinal cancers, studies find
2015-08-17
Results of a trio of studies done on human cancer tissue biopsies have added to growing evidence that a so-called jumping gene called LINE-1 is active during the development of many gastrointestinal cancers. The Johns Hopkins scientists who conducted the studies caution there is no proof that the numerous new "insertions" of these rogue genetic elements in the human genome actually cause cancers, but they say their experiments do suggest that these elements, formally known as transposons, might one day serve as a marker for early cancer diagnosis.
Collectively, the studies ...
Smoking cessation drug not boosting number of smokers who quit
2015-08-17
The introduction of a new prescription smoking-cessation aid, varenicline, in 2006 has had no significant impact on the rate at which Americans age 18 and older successfully quit smoking, according to a study led by researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine.
The findings, published online August 17 in Tobacco Control, suggest that the primary effect of varenicline (marketed as Chantix) has been to displace the use of older tobacco addiction therapies, such as nicotine patches and the antidepressant, bupropion (Zyban).
Moreover, in this population ...
Opiate addiction spreading, becoming more complex
2015-08-17
The growing availability of heroin, combined with programs aimed at curbing prescription painkiller abuse, may be changing the face of opiate addiction in the U.S., according to sociologists.
While heroin abuse is still relatively rare, the use of the drug is not only increasing, but it is now being coupled with the abuse of prescription painkillers, said Shannon Monnat, assistant professor of rural sociology, demography, and sociology, Penn State. She added that the heroin-prescription drug combination is also hitting groups that were not traditionally viewed as widespread ...
Energy in chemical bonds and the plant-pollution connection
2015-08-17
Researchers from the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory will be honored and present new work at the 250th American Chemical Society national meeting in Boston, Massachusetts, Aug. 16-20. Highlights include:
Energy Storage: Putting molecular hydrogen together and taking it apart
Storing electrical energy in chemicals and pulling it back out again to use for renewable energy requires inexpensive catalysts, which are molecules that can speed up the chemical reactions in either direction. PNNL researchers have been exploring the nuts and bolts of ...
Overcoming ethnic divides key to fueling stock market growth in emerging economies
2015-08-17
On the heels of President Barack Obama's trip to Kenya this summer, in which the U.S. president called on Kenya to overcome ethnic divisions, a new study provides insights into the economic cost of segregation in developing countries and how to overcome it.
The study, published in Administrative Science Quarterly, looks at how actors from diverse and competing social groups can come to identify as members of a common market.
In "Mobilizing a Market: Ethnic Segmentation and Investor Recruitment into the Nairobi Securities Exchange, University of Chicago Booth School ...
Turkish whistling makes asymmetries in the brain disappear
2015-08-17
Researchers at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum have debunked the theory that the left brain hemisphere is dominant in the processing of all languages. To date, it has been assumed that that dominance is not determined by the physical structure of a given language. However, the biopsychologists have demonstrated that both hemispheres are equally involved in the perception of whistled Turkish. Onur Güntürkün, Monika Güntürkün and Constanze Hahn report in the journal "Current Biology".
Common theory: left hemisphere dominant in language perception
The ...
Protective eyewear reduces field hockey eye injuries without increased concussion risk
2015-08-17
PROVIDENCE, R.I. - A study conducted by researchers at Hasbro Children's Hospital, Boston Children's Hospital, Fairfax (VA) County Public Schools and the University of Colorado School of Medicine has found that nationally mandated protective eyewear results in a greater than three-fold reduced risk of eye and orbital injuries in high school (HS) girls' field hockey players without increasing rates of concussion.
Each academic year, more than 64,000 girls participate in HS-sanctioned field hockey in the United States. Head, facial, and eye injuries are common among field ...
Whistled Turkish challenges notions about language and the brain
2015-08-17
Generally speaking, language processing is a job for the brain's left hemisphere. That's true whether that language is spoken, written, or signed. But researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on August 17 have discovered an exception to this rule in a most remarkable form: whistled Turkish.
"We are unbelievably lucky that such a language indeed exists," says Onur Güntürkün of Ruhr-University Bochum in Germany. "It is a true experiment of nature."
Whistled Turkish is exactly what it sounds like: Turkish that has been adapted into ...
Health care must be key issue in Canada's federal election
2015-08-17
Health care is a major responsibility of Canada's federal government and must be a key issue in the fall election, argues Dr. Matthew Stanbrook in an editorial in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"The federal government seems to be trying to get itself out of the health care business," states Dr. Stanbrook, deputy editor, CMAJ. "It cannot. Many essential aspects of health care are a federal responsibility, and our biggest, most complex problems in the health care system cannot be solved without federal leadership."
He argues that over most of the last 10 ...
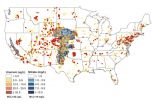
Study: 2 major US aquifers contaminated by natural uranium
2015-08-17
Nearly 2 million people throughout the Great Plains and California above aquifer sites contaminated with natural uranium that is mobilized by human-contributed nitrate, according to a study from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
Data from roughly 275,000 groundwater samples in the High Plains and Central Valley aquifers show that many Americans live less than two-thirds of a mile from wells that often far exceed the uranium guideline set by the Environmental Protection Agency.
The study reports that 78 percent of the uranium-contaminated sites were linked to the ...
Peripherally inserted central catheters can cause blood clots in lower limbs
2015-08-17
Philadelphia, PA, August 17, 2015 -- Peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs), a type of IV typically inserted in a vein in the arm, are frequently used by healthcare professionals to obtain long-term central venous access in hospitalized patients. While there are numerous benefits associated with PICCs, a potential complication is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), or blood clots, in upper limbs. A new study of more than 70,000 patients in 48 Michigan hospitals indicates that PICC use is associated not only with upper-extremity DVT, but also with lower-extremity DVT. The ...
Discovery of a salamander in amber sheds light on evolution of Caribbean islands
2015-08-17
CORVALLIS, Ore. - More than 20 million years ago, a short struggle took place in what is now the Dominican Republic, resulting in one animal getting its leg bitten off by a predator just before it escaped. But in the confusion, it fell into a gooey resin deposit, to be fossilized and entombed forever in amber.
The fossil record of that event has revealed something not known before - that salamanders once lived on an island in the Caribbean Sea. Today, they are nowhere to be found in the entire Caribbean area.
The never-before-seen and now extinct species of salamander, ...
Women's health, education, marital status pre-pregnancy affect birth weight of girls
2015-08-17
Irvine, Calif., August 17, 2015 - A woman's weight at birth, education level and marital status pre-pregnancy can have repercussions for two generations, putting her children and grandchildren at higher risk of low birth weight, according to a new study by Jennifer B. Kane, assistant professor of sociology at the University of California, Irvine. The findings are the first to tie social and biological factors together using population data in determining causes for low birth weight.
"We know that low-birth-weight babies are more susceptible to later physical and cognitive ...
Stanford engineers develop a wireless, implantable device to stimulate nerves in mice
2015-08-17
A miniature device that combines optogenetics - using light to control the activity of the brain - with a newly developed technique for wirelessly powering implanted devices is the first fully internal method of delivering optogenetics.
The device dramatically expands the scope of research that can be carried out through optogenetics to include experiments involving mice in enclosed spaces or interacting freely with other animals. The work is published in the Aug. 17 edition of Nature Methods.
"This is a new way of delivering wireless power for optogenetics," said ...
In first year, 2 Florida laws reduce amount of opioids prescribed, study suggests
2015-08-17
Two Florida laws, enacted to combat prescription drug abuse and misuse in that state, led to a small but significant decrease in the amount of opioids prescribed the first year the laws were in place, a new study by Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health researchers suggests.
One measure created a Prescription Drug Monitoring Program, a database that tracks individual prescriptions, including patient names, dates and amounts prescribed, so physicians can be on the lookout for excesses associated with addiction and illicit use. Another addresses so-called "pill ...
Children of military parents, caregivers at greater risk for adverse outcomes
2015-08-17
Children with parents or caregivers currently serving in the military had a higher prevalence of substance use, violence, harassment and weapon-carrying than their nonmilitary peers in a study of California school children, according to an article published online by JAMA Pediatrics.
While most young people whose families are connected to the military demonstrate resilience, war-related stressors, including separation from parents because of deployment, frequent relocation and the worry about future deployments, can contribute to struggles for some of them, according ...
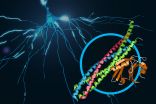
Scientists discover atomic-resolution details of brain signaling
2015-08-17
Menlo Park, Calif. -- Scientists have revealed never-before-seen details of how our brain sends rapid-fire messages between its cells. They mapped the 3-D atomic structure of a two-part protein complex that controls the release of signaling chemicals, called neurotransmitters, from brain cells. Understanding how cells release those signals in less than one-thousandth of a second could help launch a new wave of research on drugs for treating brain disorders.
The experiments, at the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray laser at the Department of Energy's SLAC National ...
Imaging study looks at brain effects of early adversity, mental health disorders
2015-08-17
Adversity during the first six years of life was associated with higher levels of childhood internalizing symptoms, such as depression and anxiety, in a group of boys, as well as altered brain structure in late adolescence between the ages of 18 and 21, according to an article published online by JAMA Pediatrics.
Both altered brain structure and an increased risk of developing internalizing symptoms have been associated with adversity early in life.
Edward D. Barker, Ph.D., of King's College London, and coauthors examined how adverse experiences within the first six ...
Study examines Florida's pill mill law, prescription drug monitoring program
2015-08-17
Legislative efforts by the state of Florida to reduce prescription drug abuse and diversion appear to be associated with modest decreases in opioid prescribing and use, according to an article published online by JAMA Internal Medicine.
Prescription opioids provide necessary pain relief to millions of Americans but rates of opioid diversion, addiction and overdose deaths have soared since the mid-2000s. Florida was at the epicenter of this problem. In 2010, the Florida legislature addressed so-called pill mills or rogue pain management clinics where prescription drugs ...
Effect of presymptomatic BMI, dietary intake, alcohol on ALS
2015-08-17
Presymptomatic patients with the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) consumed more daily calories but had lower body-mass index (BMI) than those individuals without ALS in a study in the Netherlands that also looked at risk for the disease and associations with food and alcohol intake, according to an article published online by JAMA Neurology.
The cause of ALS is poorly understood. Diet is highly modifiable but previous studies have not identified a consistent nutrient that modifies susceptibility to ALS and contradictory results exist for the ...
1,800 years of global ocean cooling halted by global warming
2015-08-17
Prior to the advent of human-caused global warming in the 19th century, the surface layer of Earth's oceans had undergone 1,800 years of a steady cooling trend, according to a new study. During the latter half of this cooling period, the trend was most likely driven by large and frequent volcanic eruptions.
An international team of researchers reported these findings in the August 17, 2015 issue of the journal Nature Geoscience. The study also indicates that the coolest temperatures occurred during the Little Ice Age--a period that spanned the 16th through 18th centuries ...
How traumatic memories hide in the brain, and how to retrieve them
2015-08-17
CHICAGO --- Some stressful experiences - such as chronic childhood abuse - are so overwhelming and traumatic, the memories hide like a shadow in the brain.
At first, hidden memories that can't be consciously accessed may protect the individual from the emotional pain of recalling the event. But eventually those suppressed memories can cause debilitating psychological problems, such as anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder or dissociative disorders.
A process known as state-dependent learning is believed to contribute to the formation of memories that ...
Substantial glacier ice loss in Central Asia's largest mountain range
2015-08-17
17.08.2015: Glaciers in Central Asia experience substantial losses in glacier mass and area. Along the Tien Shan, Central Asia's largest mountain range, glaciers have lost 27% of their mass and 18% of their area during the last 50 years. An international research team led by the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences and including the institute of the French Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) at Rennes University in particular, estimated that almost 3000 square kilometres of glaciers and an average of 5.4 gigatons of ice per year have been lost since ...
New environmental risk assessment of veterinary antibiotics applications
2015-08-17
Lueneburg. Sustainability Scientists at Leuphana University of Lueneburg have devised a simple screening-based predicting procedure for region-specific environmental risks caused by veterinary antibiotics (VA). This procedure, called Usage Pattern-based Exposure Screening (UPES), makes use of utilization patterns of antibiotics in animal husbandry. By improving targeting, it enables the identification of particularly problematic antibiotic substances. It also enables the implementation of more advanced risk prediction tests, for example with the help of soil and water ...
Dancing droplets launch themselves from thin fibers
2015-08-17
DURHAM, N.C. -- We've all seen dewdrops form on spider webs. But what if they flung themselves off of the strands instead?
Researchers at Duke University and the University of British Columbia have now observed this peculiar phenomenon, which could benefit many industrial applications. As long as the strands are moderately hydrophobic and relatively thin, small droplets combining into one are apt to dance themselves right off of the tightrope. The discovery could form the basis of new coalescer technologies for water purification, oil refining and more.
The findings ...
[1] ... [2840]
[2841]
[2842]
[2843]
[2844]
[2845]
[2846]
[2847]
2848
[2849]
[2850]
[2851]
[2852]
[2853]
[2854]
[2855]
[2856]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.