Study is first to quantify global population growth compared to energy use
2015-07-24
Lincoln, Neb., July 24th, 2015 --
If you've lived between the year 1560 and the present day, more power to you. Literally.
That's one of several conclusions reached by University of Nebraska-Lincoln ecologist John DeLong, who has co-authored the first study to quantify the relationship between human population growth and energy use on an international scale.
The study compiled several centuries' worth of data from Great Britain, the United States and Sweden to profile the dynamics between a skyrocketing population and its consumption of energy from fossil fuels and ...
Spines of boys and girls differ at birth
2015-07-24
Looking at measurements of the vertebrae - the series of small bones that make up the spinal column - in newborn children, investigators at Children's Hospital Los Angeles found that differences between the sexes are present at birth. Results of the study, now online in advance of publication in the August issue of the Journal of Pediatrics, suggest that this difference is evolutionary, allowing the female spine to adapt to the fetal load during pregnancy.
Using magnetic resonance imagining (MRI), the researchers found that vertebral cross-sectional dimensions, a key ...
Rice disease-resistance discovery closes the loop for scientific integrity
2015-07-24
When disease-resistant rice is invaded by disease-causing bacteria, a small protein produced by the bacteria betrays the invader. Upon recognizing that protein, the rice plants sense that a microbial attack is underway and are able to mount an immune response to fend off bacterial infection, reports a research team led by the University of California, Davis.
Identification of the tiny protein, called RaxX, holds promise for developing more disease-resistant crop varieties and therapeutic treatments for blocking microbial infections in both plants and animals, said the ...
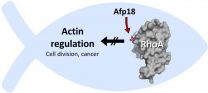
TOPLESS plants provide clues to human molecular interactions
2015-07-24
Grand Rapids, Michigan (July 24, 2015)--Scientists at Van Andel Research Institute (VARI) have revealed an important molecular mechanism in plants that has significant similarities to certain signaling mechanisms in humans, which are closely linked to early embryonic development and to diseases such as cancer.
In plants as in animals and humans, intricate molecular networks regulate key biological functions, such as development and stress responses. The system can be likened to a massive switchboard--when the wrong switches are flipped, genes can be inappropriately turned ...
Seaworld's killer whales live as long as their wild counterparts
2015-07-24
ORLANDO, Fla. (July 21, 2015) - A new peer-reviewed study published in the Journal of Mammalogy by the Oxford University Press adds important insights to the debate over how long killer whales in human care live. The study found no difference in life expectancy between killer whales born at SeaWorld and a well-studied population of wild killer whales.
The study, "Comparisons of life-history parameters between free-ranging and captive killer whale (Orcinus orca) populations for application toward species management," compares current published data for survival and ...
Know it's a placebo? CU-Boulder study shows the 'medicine' could still work
2015-07-24
You don't think you're hungry, then a friend mentions how hungry he is or you smell some freshly baked pizza and whoaaa, you suddenly feel really hungry. Or, you've had surgery and need a bit of morphine for pain. As soon as you hit that button you feel relief even though the medicine hasn't even hit your bloodstream.
These are two examples of the oft-studied placebo effect that demonstrate the amazing and still somewhat confounding powers of the human brain.
Now, CU-Boulder graduate student Scott Schafer, who works in Associate Professor Tor Wager's Cognitive and Affective ...
Inbreeding not to blame for Colorado's bighorn sheep population decline
2015-07-24
The health of Colorado's bighorn sheep population remains as precarious as the steep alpine terrain the animals inhabit, but a new study led by researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder has found that inbreeding--a common hypothesis for a recent decline--likely isn't to blame.
Bighorn herds tend to be small and isolated in their mountain ecosystems, putting the animals at high risk for a genetic "bottleneck," said Catherine Driscoll, a graduate student in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at CU-Boulder and lead author of the study. Previous research ...
Prostate cancer not caused by shift work
2015-07-24
As well as the daily strain of their working lives, shift workers are probably also more likely than other people to develop cancer. While this has been well described for breast cancer, few studies had examined the correlation between shift work and prostate cancer. In a recent original article in Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztbl Int 112: 463-70), Gael P. Hammer et al. show that shift workers do not develop prostate cancer more frequently than their colleagues who work during the day.
Shift work is widespread: between approximately one in five and ...
Object recognition for robots
2015-07-24
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- John Leonard's group in the MIT Department of Mechanical Engineering specializes in SLAM, or simultaneous localization and mapping, the technique whereby mobile autonomous robots map their environments and determine their locations.
Last week, at the Robotics Science and Systems conference, members of Leonard's group presented a new paper demonstrating how SLAM can be used to improve object-recognition systems, which will be a vital component of future robots that have to manipulate the objects around them in arbitrary ways.
The system uses SLAM ...
DNA suggests that the diversity of European butterflies could be seriously underestimated
2015-07-24
This news release is available in Spanish.
Since 2006, the team of researchers has sequenced the mitochondrial DNA of all the known species of butterflies in the Iberian peninsula (228) and its main populations. The result is a report that compiles more than 3500 genetic sequences of all the species, which have been compared to the genetic sequences of other European populations. The paper has 277 pages of supplementary material, including pictures and 80 maps of the geographical distribution of the butterfly genetic lineages identified.
This is the first time ...
Temple-led research analyzes impact of case volume on outcomes for DVT treatment
2015-07-24
(Philadelphia, PA) - Patients who have lower extremity proximal deep vein thrombosis (LE-DVT), or a blood clot in their leg, are increasingly undergoing minimally invasive catheter-based blood clot removal - also referred to as catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT) - rather than solely being treated with traditional blood-thinning medications (anticoagulation alone). This trend is due to recent literature showing reductions in lifestyle-limiting post-thrombotic complications of acute DVT in patients who undergo CDT compared to those that are treated with anticoagulation ...
Toxin from salmonid fish has potential to treat cancer
2015-07-24
This news release is available in German.
Pathogenic bacteria develop killer machines that work very specifically and highly efficiently. Scientists from the University of Freiburg have solved the molecular mechanism of a fish toxin that could be used in the future as a medication to treat cancer. The scientists have now published their research in the journal Nature Communications.
The Yersinia species of pathogens can cause the bubonic plague and serious gastrointestinal infections in humans. The pharmacologist Dr. Thomas Jank and his fellow researchers in the ...
Researchers find new method to halt the advance of liver cancer
2015-07-24
La Jolla, Calif., July 23, 2015 - A new study by researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute (SBP), the National Cancer Institute, and the Chulabhorn Research Institute has found that blocking the activity of a key immune receptor, the lymphotoxin-beta receptor (LTβR), reduces the progression of liver cancer. The results, published today in the online edition of Gut, could provide new treatment strategies for the disease, which is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
"Our findings point to a new way to improve the treatment ...
For prostate cancer patients, risk-specific therapies now more the norm
2015-07-24
After decades of overtreatment for low-risk prostate cancer and inadequate management of its more aggressive forms, patients are now more likely to receive medical care matched to level of risk, according to a study by researchers at UC San Francisco.
In the first study to document updated treatment trends, researchers found that from 2010 to 2013, 40 percent of men with low-risk prostate cancer opted for active surveillance, in which the disease is monitored closely with blood tests, imaging studies and biopsies. Treatment is deferred unless these tests show evidence ...
Astronomers discover Earth's bigger cousin
2015-07-24
Today an international team of astronomers from NASA's Kepler mission have announced the discovery of a near-Earth-sized planet in the habitable zone of a Sun-like star.
Dr Daniel Huber from the University of Sydney's School of Physics is part of the team which made the discovery with NASA's Kepler Space Telescope.
The planet named Kepler-452b is 60 per cent larger than Earth and orbits a Sun-like star with an orbital period of 385 days.
The mere 20 day difference between the planet's orbital period and that of Earth's makes it the closest analogue to Earth ever ...
Wind energy provides 8 percent of Europe's electricity
2015-07-24
EU's grid connected cumulative capacity in 2014 reached 129 GW, meeting 8% of European electricity demand, equivalent to the combined annual consumption of Belgium, the Netherlands, Greece and Ireland. According to a JRC report, the impressive growth of the industry will allow at least 12% electricity share by 2020, a significant contribution to the goal of the European energy and climate package of 20% share of energy from renewable sources.
The 2014 JRC wind status report presents the technology, market and economics of the wind energy sector with a focus on the EU. ...
University of York scientists discover why some tumors are resistant to radiotherapy
2015-07-24
Scientists at the University of York believe they have identified how some tiny regulatory molecules in cells can make prostate cancers resistant to radiotherapy.
It is hoped that this new development could pave the way for more effective treatments - allowing a lower dose of radiotherapy to be used while prolonging the lives of thousands of men.
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed form of male cancer in the UK and kills more than 11,000 men every year.
In the latest studies, published in European Urology and the British Journal of Cancer, scientists in The ...
Patient satisfaction is good indicator of success after spinal surgery
2015-07-24
July 24, 2015 - Patient satisfaction ratings after surgery for spinal degenerative disease--especially in terms of reduced pain and disability--are a good indicator of the procedure's effectiveness, reports a study in the August issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
"Patient satisfaction with outcome may accurately represent the effectiveness of surgical spine care in terms of one-year improvement in pain and disability," according to the new research by Dr. Clinton J. Devin of Vanderbilt ...
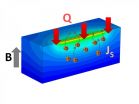
Young scientist discovers magnetic material unnecessary to create spin current
2015-07-24
It doesn't happen often that a young scientist makes a significant and unexpected discovery, but postdoctoral researcher Stephen Wu of the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory just did exactly that. What he found--that you don't need a magnetic material to create spin current from insulators--has important implications for the field of spintronics and the development of high-speed, low-power electronics that use electron spin rather than charge to carry information.
Wu's work upends prevailing ideas of how to generate a current of spins. "This is a ...
'Watch' helps surgeons minimize potential risks of all-inside meniscal repair
2015-07-24
Needham, MA.-JBJS Case Connector, an online case report journal published by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, has issued a "Watch" regarding potential risks with anchor-based all-inside meniscal repairs. While all-inside techniques have many advantages, including shorter surgical time and reduced risk of damage to neurovascular tissues, potential drawbacks include risks of local soft-tissue irritation and implant migration or breakage.
In particular, the "Watch" offers important tips for successfully using FAST-FIX meniscal-repair devices produced by Smith & Nephew. ...
Diagnosis of psychiatric disorders not as important as outcomes
2015-07-24
Nailing the diagnosis of a psychiatric disorder may not be important in prescribing effective treatment, according to Mark Zimmerman, M.D., a clinical researcher at Rhode Island Hospital. His opinion editorial was published online today in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
"During the past 35 years, we have witnessed a revolution in the treatment of psychiatric disorders," said Zimmerman, director of outpatient psychiatry and the partial hospital program at Rhode Island Hospital and director of the Rhode Island Methods to Improve Diagnostic Assessment and Services ...
Stadium lighting affects bat behavior and may threaten biodiversity
2015-07-24
A new Animal Conservation study shows that sports stadium lighting can alter patterns of bat species activity and feeding, which may in turn have cascading effects on other organisms and the ecosystem as a whole.
Using a novel field experiment, Dr. M. Corrie Schoeman demonstrates that urban exploiter bats are more likely to hunt insects attracted to bright light pollution sources such as stadiums than urban avoider bats. (Exploiter organisms can take advantage of food or resources supplied by humans, while avoider organisms have either a history of conflict with humans ...
Study identifies risks related to falling in patients with COPD
2015-07-24
In a recent year-long study, 40% of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) experienced falls, with more than 75% of these falling multiple times.
Factors linked with an increased risk of falling included smoking, having other illnesses, taking multiple medications, having a fear of falling, and falling in the past.
"The findings could be useful for developing preventative strategies," said Dr. Cristino Oliveira, lead author of the Respirology study.
INFORMATION:
...
Attention-control video game curbs combat vets' PTSD symptoms
2015-07-24
A computerized attention-control training program significantly reduced combat veterans' preoccupation with - or avoidance of -- threat and attendant PTSD symptoms. By contrast, another type of computerized training, called attention bias modification - which has proven helpful in treating anxiety disorders - did not reduce PTSD symptoms. NIMH and Israeli researchers conducted parallel trials in which the two treatments were tested in US and Israeli combat veterans.
Daniel Pine, M.D., of the NIMH Emotion and Development Branch, Yair Bar-Haim, Ph.D., School of Psychological ...
Pesticides found in most pollen collected from foraging bees in Massachusetts
2015-07-24
Boston, MA -- More than 70% of pollen and honey samples collected from foraging bees in Massachusetts contain at least one neonicotinoid, a class of pesticide that has been implicated in Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD), in which adult bees abandon their hives during winter, according to a new study from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
The study will be published online July 23, 2015 in the Journal of Environmental Chemistry.
"Data from this study clearly demonstrated the ubiquity of neonicotinoids in pollen and honey samples that bees are exposed to during ...
[1] ... [2859]
[2860]
[2861]
[2862]
[2863]
[2864]
[2865]
[2866]
2867
[2868]
[2869]
[2870]
[2871]
[2872]
[2873]
[2874]
[2875]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.