New study identifies organic compounds of potential concern in fracking fluids
2015-06-30
A new University of Colorado Boulder framework used to screen hundreds of organic chemical compounds used in hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, shows that 15 may be of concern as groundwater contaminants based on their toxicity, mobility, persistence and frequency of use.
Using a fast groundwater transport scenario, the team predicted that 41 of the 659 organic compounds screened would have 10 percent or more of their initial concentrations remaining at a transport distance of roughly 300 feet. That is the average state "setback" distance in the United States between ...
Protein's impact on colorectal cancer is dappled
2015-06-30
Researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have discovered a cell signaling pathway that appears to exert some control over initiation and progression of colorectal cancer, the third leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States. A key protein in the pathway also appears to be predictive of cancer survival rates.
The study is reported in the June 30 issue of eLife.
The protein, known as Dishevelled-associating protein with a high frequency of leucine residues or Daple, is produced by nearly all healthy cells in the body and is ...
Hospital-wide program for delirium, alcohol withdrawal and suicide/harm impacts readmission rates
2015-06-30
Brigham and Women's Hospital finds that developing and implementing an interdisciplinary care improvement initiative improves outcomes.
Approximately 20 percent of all patients admitted to a hospital have a mental health condition, either as a primary or a secondary diagnosis, and a recent report by the Institute of Medicine warned that there is a critical shortage of health care professionals who are equipped to provide mental health and geriatric care to these patients in the hospital setting. Often, these patients experience delirium, alcohol withdrawal and suicide ...
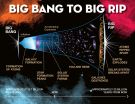
New model of cosmic stickiness favors 'Big Rip' demise of universe
2015-06-30
The universe can be a very sticky place, but just how sticky is a matter of debate.
That is because for decades cosmologists have had trouble reconciling the classic notion of viscosity based on the laws of thermodynamics with Einstein's general theory of relativity. However, a team from Vanderbilt University has come up with a fundamentally new mathematical formulation of the problem that appears to bridge this long-standing gap.
The new math has some significant implications for the ultimate fate of the universe. It tends to favor one of the more radical scenarios ...
Does radiation from X-rays and CT scans really cause cancer?
2015-06-30
MAYWOOD, IL - In recent years, there has been widespread media coverage of studies purporting to show that radiation from X-rays, CT scans and other medical imaging causes cancer.
But such studies have serious flaws, including their reliance on an unproven statistical model, according to a recent article in the journal Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment. Corresponding author is Loyola University Medical Center radiation oncologist James Welsh, MS, MD.
"Although radiation is known to cause cancer at high doses and high-dose rates, no data have ever unequivocally ...
For women with bipolar disorder, sleep quality affects mood
2015-06-30
Poor sleep is associated with negative mood in women with bipolar disorder, according to researchers at Penn State College of Medicine and University of Michigan Medical School.
Bipolar disorder is a brain disorder that causes unusual shifts in mood, energy, activity levels and the ability to carry out day-to-day tasks. The condition is marked by extreme mood episodes characterized as manic (highs) depressive (lows) or mixed.
Sleep problems are common in people with bipolar disorder, and poor sleep quality and bipolar disorder appear to exacerbate each other. Previous ...
Carnegie Mellon chemists characterize 3-D macroporous hydrogels
2015-06-30
Carnegie Mellon University chemists have developed two novel methods to characterize 3-dimensional macroporous hydrogels -- materials that hold great promise for developing "smart" responsive materials that can be used for catalysts, chemical detectors, tissue engineering scaffolds and absorbents for carbon capture.
Researchers working in the lab of Carnegie Mellon Professor Krzysztof Matyjaszewski published their results in the May issue of Advanced Science, with the article featured on the journal's back cover. Their findings are the latest in Matyjaszewski lab's long ...
Bisexual men and women report poorer health than gays, lesbians and heterosexuals
2015-06-30
Bisexual males and females report poorer health than gays, lesbians and heterosexuals, according to a new study from sociologists at Rice University.
"A New Piece of the Puzzle: Sexual Orientation, Gender and Physical Health Status" will appear in an upcoming edition of Demography. The study examined the self-rated health of 10,128 sexual minorities (gay, lesbian and bisexual adults) and 405,145 heterosexual adults to see how it differed across sexual orientation.
"According to the Institute of Medicine, existing health research on the sexual minority population is ...
UW team programs solitary yeast cells to say 'hello' to one another
2015-06-30
For centuries, humans have been playing with yeast. But these simple fungal cells usually do their jobs -- making bread rise or converting sugar into alcohol -- without having to communicate or work together.
Now, a team of University of Washington researchers has engineered yeast cells (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) that can "talk" to one another, using a versatile plant hormone called auxin.
In a paper published June 23 in the American Chemical Society's journal ACS Synthetic Biology, the researchers describe a novel cell-to-cell communication system that enables one ...
To shed weight, go vegan
2015-06-30
People on a vegetarian diet, and especially those following a vegan one that includes no animal products, see better results than dieters on other weight-reducing plans. In fact, they can lose around two kilograms more on the short term, says Ru-Yi Huang of E-Da Hospital in Taiwan after reviewing the results of twelve diet trials. The findings¹ appear in the Journal of General Internal Medicine², published by Springer.
Huang's review includes twelve randomized controlled trials, involving 1,151 dieters who followed a specific eating regime for between nine ...
Osteopathic manipulative therapy significantly improves low back pain in postpartum women
2015-06-30
German researchers found osteopathic manipulative therapy (OMTh) decreased postpartum low back pain by over 70 percent in women who had given birth at least three months before beginning treatment, according to a new study published in July issue of the Journal of the American Osteopathic Association.
The eight week study, devised as a pragmatic randomized controlled trial, surveyed 80 women experiencing low back pain three to 15 months postpartum. Women in the study group received four OMTh treatments at two week intervals. Participants in the control group did not ...
A high-fat diet may alleviate mitochondrial disease
2015-06-30
LA JOLLA-- Mice that have a genetic version of mitochondrial disease can easily be mistaken for much older animals by the time they are nine months old: they have thinning grey hair, osteoporosis, poor hearing, infertility, heart problems and have lost weight. Despite having this disease at birth, these mice have a "secret weapon" in their youth that staves off signs of aging for a time.
New research from the Salk Institute reveals how a longevity hormone helps these mice--born with thousands of mutations in their energy-generating mitochondria--maintain metabolic homeostasis ...
Yosemite forest fire example of possible things to come
2015-06-30
Forest composition, ground cover and topography are the best predictors of forest fire severity in the Western U.S., according to Penn State physical geographers who also see that the long history of fire exclusion on federal lands leads to uncharacteristically severe burns and potentially changes the dynamics of forests and their recovery.
A hunter's illegal campfire in Stanislaus National Forest adjacent to Yosemite National Park started what would become the Rim fire, the third largest fire in California history, that burned from August through October 2013. The fire ...
Atomic force microscope advance leads to new breast cancer research
2015-06-30
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers who developed a high-speed form of atomic force microscopy have shown how to image the physical properties of live breast cancer cells, for the first time revealing details about how deactivation of a key protein may lead to metastasis.
The new findings also are providing evidence for the mechanisms involved in a cell's response to anti-cancer drugs, said Arvind Raman, Purdue University's Robert V. Adams Professor of Mechanical Engineering.
In atomic force microscopy (AFM), a tiny vibrating probe called a cantilever passes over a material, ...
Water: The province of provinces
2015-06-30
This news release is available in French. Montreal, June 30, 2015 -- Unsafe drinking water is a topic usually connected to the developing world. But the regular recurrence of boil-water advisories, and widely publicised outbreaks in towns like Walkerton and Kashechewan have shown that, even in Canada, clean water cannot be taken for granted.
The increased scrutiny that arose from such issues has resulted in widespread criticism of the uneven drinking water regulation among Canada's provinces and territories.. However, centralizing water regulation is not necessarily ...
NASA sees new depression forms near Solomon Islands
2015-06-30
The Southern Pacific Ocean Tropical Cyclone Season just got an extension with the birth of a new tropical depression near the Solomon Islands. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the new depression and saw that it was already affecting some of the islands.
The Solomon Islands make up a nation that consists of hundreds of islands in the South Pacific.
The MODIS or Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Depression 25P as it was forming in the Southern Pacific, just north of the Solomon ...
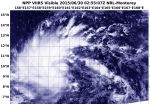
Suomi-NPP satellite sees formation of Tropical Depression Chan-Hom
2015-06-30
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP Satellite passed over the newborn ninth tropical depression of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean typhoon season on June 30.
At 02:55 UTC (10:55 p.m. EDT, June 29), the VIIRS or Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi satellite captured a visible image of the newly developed depression. The VIIRS image revealed bands of thunderstorms wrapping into the low-level center from the north and western quadrants.
VIIRS collects visible and infrared imagery and global observations of land, atmosphere, cryosphere ...
How small genetic change in Yersinia pestis changed human history
2015-06-30
CHICAGO -- While studying Yersinia pestis, the bacteria responsible for epidemics of plague such as the Black Death, Wyndham Lathem, Ph.D., assistant professor in microbiology-immunology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, found a single small genetic change that fundamentally influenced the evolution of the deadly pathogen, and thus the course of human history.
In a paper published in Nature Communications, Lathem and first author Daniel Zimbler, Ph.D., a Feinberg post-doctoral fellow, demonstrated how the acquisition of a single gene caused the ...
Repeated courses of antibiotics may profoundly alter children's development
2015-06-30
June 30, 2015, NEW YORK -- A new animal study by NYU Langone Medical Center researchers adds to growing evidence that multiple courses of commonly used antibiotics may have a significant impact on children's development.
In the study, to be published online June 30 by the journal Nature Communications, female mice treated with two classes of widely used childhood antibiotics gained more weight and developed larger bones than untreated mice. Both of the antibiotics also disrupted the gut microbiome, the trillions of microbes that inhabit the intestinal tract.
Overall, ...
New cardiac arrest recommendations: Increased CPR/AED training will improve survival rates
2015-06-30
Washington, DC - June 30, 2015 - A new report released today from the Institute of Medicine calls for a campaign to promote public education and training opportunities to reduce barriers to the provision of bystander CPR and defibrillation.
Annual rates of CPR and AED use by bystanders remain less than three percent in the United States even though evidence indicates that its use significantly improves cardiac arrest survival. The American Red Cross strongly supports the IOM's recommendation to encourage training through employers, local public health departments, schools ...
Spouses & relatives of celiac disease patients at risk for autoimmune diseases
2015-06-30
Bethesda, MD (June 30, 2015) -- Both spouses and first-degree relatives of patients with celiac disease are at increased risk of nonceliac autoimmune disease, according to a study in the July issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. This risk represents a mixture of genetic, environmental and ascertainment bias mechanisms.
"The prevalence of celiac disease in first-degree relatives of individuals with celiac is approximately 10 percent. Despite these findings, little is ...
Pinaverium shows promising results for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome
2015-06-30
Bethesda, MD (June 30, 2015) -- Pinaverium offers quick and effective relief of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms, according to clinical trial results published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
Pinaverium bromide (pinaverium), an antispasmodic, is used widely in many countries around the world, including European countries, Canada and Mexico. However, original clinical studies on pinaverium are scarce and there has been no convincing evidence for its effectiveness ...
Vitamin A supplementation may cause the immune system to 'forget' past infections
2015-06-30
Although vitamin A supplementation can have profound health benefits when someone is deficient, new evidence is emerging to show that vitamin A supplementation above and beyond normal levels may have negative health consequences. A new research report published in the July 2015 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology may help to explain why too much vitamin A can be harmful. Too much vitamin A shuts down the body's trained immunity, opening the door to infections to which we would otherwise be immune. This study adds to the arguments that vitamin A supplementation should ...
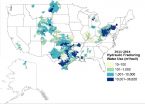
Water used for hydraulic fracturing varies widely across United States
2015-06-30
WASHINGTON, D.C. - The amount of water required to hydraulically fracture oil and gas wells varies widely across the country, according to the first national-scale analysis and map of hydraulic fracturing water usage detailed in a new study accepted for publication in Water Resources Research, a journal of the American Geophysical Union. The research found that water volumes for hydraulic fracturing averaged within watersheds across the United States range from as little as roughly 9,800 liters (2,600 gallons) to as much as 37 million liters (9.7 million gallons) per well.
In ...
Sialic acid: A key to unlocking brain disorders
2015-06-30
A new report published in the July 2015 issue of The FASEB Journal suggests that a common molecule found in higher animals, including humans, affects brain structure. This molecule may play a significant role in how brain cells communicate, possibly shedding light on the underlying causes of certain brain disorders. The study, involving mice, shows that small changes in how sialic acid attaches to cell surfaces result in damaging effects on brain structure, poor motor skills, hyperactivity, and difficulty in learning.
"Sialic acid is part of the molecular language that ...
[1] ... [2864]
[2865]
[2866]
[2867]
[2868]
[2869]
[2870]
[2871]
2872
[2873]
[2874]
[2875]
[2876]
[2877]
[2878]
[2879]
[2880]
... [8789]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.