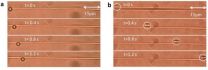
A speech-based system for the early detection of Alzheimer's disease
2015-03-18
This news release is available in Spanish. Alzheimer's disease is the most significant cause of dementia in the elderly: it affects over 35 million people worldwide. It is reckoned that Alzheimer's could reach epidemic proportions in developed countries unless therapies to cure or prevent it are obtained. Studies conducted so far reveal that the therapies are more effective when they are applied before the brain has become severely damaged. What is more, the spotting of early phases of the disease may help to develop new treatments. Right now, to make a clinical diagnosis ...
New molecular tool assesses vaginal microbiome health, diagnoses infections -- fast
2015-03-18
A new microarray-based tool, called VaginArray, offers the potential to provide a fast, reliable and low-cost assessment of vaginal health and diagnoses of infections. The research is published ahead of print March 2, in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
The VaginArray has 17 probe sets, each one specific for one of the most representative bacterial species inhabiting the vaginal ecosystem, including those associated with both healthy and unhealthy conditions. Each probe set is designed to be complementary to the ...
Iron rain fell on early Earth, new Z machine data supports
2015-03-18
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories' Z machine have helped untangle a long-standing mystery of astrophysics: why iron is found spattered throughout Earth's mantle, the roughly 2,000-mile thick region between Earth's core and its crust.
At first blush, it seemed more reasonable that iron arriving from collisions between Earth and planetesimals -- ranging from several meters to hundreds of kilometers in diameter -- during Earth's late formative stages should have powered bullet-like directly to Earth's core, where so much iron already exists.
A ...
An antihypertensive drug improves corticosteroid-based skin treatments
2015-03-18
This news release is available in French. Basic research on blood pressure has led researchers from Inserm (Inserm Unit 1138, "Cordeliers Research Centre") to obtain unexpected results: drugs used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure) reduce side effects from corticosteroid-based creams used to treat certain skin diseases.
This work is published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Corticosteroid-based dermatological creams are indicated for the symptomatic treatment of inflammatory skin conditions, such as atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, for example. ...
17-million-year-old whale fossil provides first exact date for East Africa's puzzling uplift
2015-03-18
Uplift associated with the Great Rift Valley of East Africa and the environmental changes it produced have puzzled scientists for decades because the timing and starting elevation have been poorly constrained.
Now paleontologists have tapped a fossil from the most precisely dated beaked whale in the world -- and the only stranded whale ever found so far inland on the African continent -- to pinpoint for the first time a date when East Africa's mysterious elevation began.
The 17 million-year-old fossil is from the beaked Ziphiidae whale family. It was discovered 740 ...
30 years after C60: Fullerene chemistry with silicon
2015-03-18
This news release is available in German.
FRANKFURT. The discovery of the soccer ball-shaped C60 molecule in 1985 was a milestone for the development of nanotechnology. In parallel with the fast-blooming field of research into carbon fullerenes, researchers have spent a long time trying in vain to create structurally similar silicon cages. Goethe University chemists have now managed to synthesise a compound featuring an Si20 dodecahedron. The Platonic solid, which was published in the "Angewandte Chemie" journal, is not just aesthetically pleasing, it also opens ...
Measuring the effect of urban planning changes
2015-03-18
This news release is available in French. With a population likely to grow 27% by 2031, putting an end to urban sprawl in Greater Montreal appears impossible for the short to medium term. But it is possible to slow the pace of urban sprawl by harnessing the full development potential of central areas, according to forecasts by Guillaume Marois, a recent Ph.D. from INRS who has developed a spatial microsimulation model called Local Demographic Simulations (LDS).
These findings are presented in an article co-authored by Guillaume Marois and Professor Alain Bélanger ...
Understanding proteins involved in fertility could help boost IVF success
2015-03-18
Women who have difficulty getting pregnant often turn to in-vitro fertilization (IVF), but it doesn't always work. Now scientists are taking a new approach to improve the technique by studying the proteins that could help ready a uterus for an embryo to implant in its wall. Their report could help researchers develop a new treatment that could potentially increase the success rate of IVF. The study appears in ACS' Journal of Proteome Research.
Chen Xu, Hu Zhou and colleagues note that nearly 50 million couples worldwide require some kind of medical intervention to conceive. ...
Out-of-wedlock childbearing increasingly common among educated women in Latin America
2015-03-18
New York (18 March 2015)--"Consensual unions," two people living in the same dwelling in a relationship akin to marriage, have been an integral part of family life in Latin America for centuries. In fact, in Latin America, legal marriages and consensual unions are seen as similarly acceptable family arrangements for bearing and raising children. However, consensual unions have historically been more common among disadvantaged populations and in rural areas than among more advantaged populations and in urban areas--indicating that such unions are rooted in limited economic ...
Many plastics labeled 'biodegradable' don't break down as expected
2015-03-18
Plastic products advertised as biodegradable have recently emerged, but they sound almost too good to be true. Scientists have now found out that, at least for now, consumers have good reason to doubt these claims. In a new study appearing in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology, plastics designed to degrade didn't break down any faster than their more conventional counterparts.
Susan Selke, Rafael Auras and colleagues note that to deal with our plastic waste problem, many countries and local governments have adopted laws, such as single-use bag bans, to ...
How green tea could help improve MRIs
2015-03-18
Green tea's popularity has grown quickly in recent years. Its fans can drink it, enjoy its flavor in their ice cream and slather it on their skin with lotions infused with it. Now, the tea could have a new, unexpected role -- to improve the image quality of MRIs. Scientists report in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces that they successfully used compounds from green tea to help image cancer tumors in mice.
Sanjay Mathur and colleagues note that recent research has revealed the potential usefulness of nanoparticles -- iron oxide in particular -- to make biomedical ...
Finding out what's in 'fracking' wastewater
2015-03-18
In early January, almost 3 million gallons of wastewater from a hydraulic fracturing ("fracking") operation in North Dakota spilled into nearby creeks. The accident highlighted ongoing concerns about what's in fracking fluids and wastewater, and whether they pose a threat to human health or the environment. An article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, details what scientists are doing to answer these questions.
Celia Henry Arnaud, a senior editor at C&EN, notes that figuring out what potential harm fracking ...
Light as puppeteer
2015-03-18
This news release is available in Japanese.
Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) have demonstrated a more robust method for controlling single, micron-sized particles with light.
Passing light along optical microfibers or nanofibers to manipulate particles has gained popularity in the past decade and has an array of promising applications in physics and biology. Most research has focused on using this technique with the basic profile of light, known as the fundamental mode. Researchers in the OIST Light-Matter ...
Understanding democracy and development traps using a data-driven approach
2015-03-18
Why do some countries seem to develop quickly while others remain poor? This question is at the heart of the so-called poverty or development trap problem. Using mathematics on open data sets researchers now present new insights into this issue, and also suggest which countries can be expected to develop faster. The paper is published in the journal Big Data.
Why do some countries seem to develop quickly while others remain poor? This question is at the heart of so-called poverty or development trap problem. Development economists have identified several potential causes ...
Submarine groundwater discharge adds as much nutrients as rivers to the Mediterranean Sea
2015-03-18
Submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) consists of a mixture of continental freshwater and seawater, which recirculates through the coastal aquifer. In addition to its importance in the water cycle, as a potentially exploitable water resource and a source of water for brackish coastal environments such as marshes and coastal lagoons, it also can serve as an important source of dissolved chemical compounds such as nutrients and trace and toxic metals.
Now, a study led by researchers from the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology (ICTA) and the Department of ...
Extent of Moon's giant volcanic eruption is revealed
2015-03-18
Scientists have produced a new map of the Moon's most unusual volcano showing that its explosive eruption spread debris over an area much greater than previously thought.
A team of astronomers and geologists, led by experts in the Institute for Computational Cosmology and Department of Earth Sciences at Durham University, UK, studied an area of the lunar surface in the Compton-Belkovich Volcanic Complex.
By mapping the radioactive element thorium which spewed out during the eruption they discovered that, with the help of the Moon's low gravity, debris from the unnamed ...
NCCS pioneers new drug regimen which reduces toxicities for renal cancer patients
2015-03-18
Singapore, 11 March 2015 - A study led by the Genitourinary (GU) oncology team at National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS) has revealed conclusive results in reducing toxicities for Asian patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) or cancer that has spread beyond the kidney.
The seven-year study began in 2007 and the findings revolutionised the standard protocol for patient management in NCCS with an attenuated-dose regimen of sunitinib for patients with mRCC.
The new treatment regimen for sunitinib has been accepted by oncologists in Singapore. For the patients, ...
EU ban on ditching unwanted fish 'will be difficult for industry to comply with'
2015-03-18
The fishing industry will have difficulty complying with new EU Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) rules banning the throwing away of unwanted fish, according to research at the University of Strathclyde.
The aim of the regulations, which come into force in January 2015, is to reduce waste and improve fish stocks - but the Strathclyde study concluded that this outcome was uncertain.
It found that, over time, quantities of fish discarded have declined since the early 1980s - because overall catches have decreased. However, the proportion of catch which is discarded has increased ...
Fatal uncoupling in the epileptic brain
2015-03-18
Epilepsy is a very prevalent neurological disorder. Approximately one-third of patients are resistant to currently available therapies. A team of researchers under the guidance of the Institute of Cellular Neurosciences at the University of Bonn has discovered a new cause to explain the development of temporal lobe epilepsy: At an early stage, astrocytes are uncoupled from each other. This results in the extracellular accumulation of potassium ions and neurotransmitters, which cause hyperexcitability of the neurons. The results are being published in advance online in the ...
Frequency of blood tests in heart surgery patients may lead to anemia, transfusions
2015-03-18
Chicago, March 18, 2015 - Laboratory testing among patients undergoing cardiac surgery can lead to excessive bloodletting, which can increase the risk of developing hospital-acquired anemia and the need for blood transfusion, according to an article in the March 2015 issue of The Annals of Thoracic Surgery.
Key points
Excessive lab tests prior to and following cardiac surgery can lead to excessive bloodletting, which can increase the risk of developing hospital-acquired anemia and the need for transfusion during surgery.
The study found that heart surgery patients ...
The new frontier in plasma medicine
2015-03-18
Applications of plasmas in medicine are a new frontier in therapeutic treatment. For example, they can help in stimulating tissue regeneration in the contexts of wound healing and dermatology. Before these and further applications can be developed, it is essential to understand the processes at work in plasmas - a unique kind of gas-like state of matter containing charged particles. Now a study published in EPJ D by a team led by Zoran Petrovi? from the University of Belgrade, Serbia, provides previously unavailable data on oxygen ion transport and the likelihood of such ...
Superradiant matter: A new paradigm to explore dynamic phase transitions
2015-03-18
If you put water in the freezer to make ice, you trigger a dynamic phase transition.
Physicists gave that fancy name to a process which takes a system across a phase transition in a realistic time, to distinguish it from the hypothetical process which goes across the transition infinitely slow. This latter, hypothetical case is discussed in any college textbook, while its dynamic, and therefore realistic, counterpart continues to pose fundamental questions. It matters how fast you 'quench' the system: If you cool water below its freezing point slowly, you'll ...
Exciting data presented at the 4th Gut Microbiota For Health Summit
2015-03-18
On March 14 and 15, 2015, internationally leading experts in gut microbiota research met in Barcelona, Spain, to present the latest findings and discuss their significance for health and diet. Fact sheets covering the following hot topics from the Summit are now freely available on http://www.gutmicrobiotaforhealth.com/gmfh-2015-media-room.
Breast milk: Protecting infants against diseases
Breast milk can provide the infant's gut with beneficial bacteria that induce protective effects against a number of conditions. Recent findings show that the mother's gut microbiota ...
Moral decisions can be influenced by eye tracking
2015-03-18
Our opinions are affected by what our eyes are focusing on in the same instant we make moral decisions. Researchers at Lund University and other institutions have managed to influence people's responses to questions such as "is murder defensible?" by tracking their eye movements. When the participants had looked at a randomly pre-selected response long enough, they were asked for an immediate answer. Fifty-eight per cent chose that answer as their moral position.
The study shows that our moral decisions can be influenced by what we are looking at when we make the decision. ...
Improving productivity of welding by reducing groove angle
2015-03-18
LUT has been developing materials and technology suitable for Arctic conditions. Principles for safe and ecological design and manufacturing of structures and devices used for energy production in the Arctic have been defined in the Arctic Materials Technologies Development project.
The LUT research focuses on the properties of new high-strength steel grades suitable for Artic construction and the welding methods they require. As a result, the productivity of welding has been significantly improved through reducing the groove angle essential to welding from 45 degrees ...
[1] ... [3080]
[3081]
[3082]
[3083]
[3084]
[3085]
[3086]
[3087]
3088
[3089]
[3090]
[3091]
[3092]
[3093]
[3094]
[3095]
[3096]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.