Vitamin D may help prevent and treat diseases associated with aging, Loyola study finds
2015-03-17
Vitamin D may play a vital role in the prevention and treatment of diseases associated with aging, according to researchers at Loyola University Chicago Marcella Niehoff School of Nursing (MNSON). These findings were published in the latest issue of the Journal of Aging and Gerontology.
Researchers reviewed evidence that suggests an association between vitamin D deficiency and chronic diseases associated with aging such as cognitive decline, depression, osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes and cancer.
"Vitamin D deficiency is a ...
Women retain insulin sensitivity better than men
2015-03-17
Hamilton, ON (March 17, 2015) - It's long been known that obese men are more likely to develop type two diabetes than obese women, but researchers at McMaster University have discovered it may be related to a difference between the sexes in the activity of a protein in the muscle.
As people become overweight, their skeletal muscle develops insulin resistance that can lead to type two diabetes. In a paper published by Scientific Reports today, the research team found the activity of this protein, called PTEN (for Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10), ...
'Distracted driving' at an all-time high; new approaches needed
2015-03-17
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Young, inexperienced drivers have always gotten into more automobile accidents, but if you add in a lot of distractions, it's a recipe for disaster - and a new Pacific Northwest research program is learning more about these risks while identifying approaches that may help reduce them.
Distractions have been an issue since the age of the Model T, whether a driver was eating a sandwich or talking to a passenger. But the advent of cell phones, text messaging and heavy urban traffic has taken those distractions to a historic level, say researchers, who ...
Conifers' helicoptering seeds are result of long evolutionary experiment
2015-03-17
The whirling, winged seeds of today's conifers are an engineering wonder and, as University of California, Berkeley, scientists show, a result of about 270 million years of evolution by trees experimenting with the best way to disperse their seeds.
The first conifer species that produced seeds that whirl when they fall used a variety of single- and double-winged designs. Whirling, or helicoptering, keeps a seed aloft longer, increasing the chance that a gust of wind will carry a seed to a clearing where it can sprout and grow unimpeded by competitors
"Winged seeds may ...
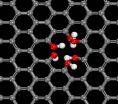
Imperfect graphene opens door to better fuel cells
2015-03-17
The honeycomb structure of pristine graphene is beautiful, but Northwestern University scientists, together with collaborators from five other institutions, have discovered that if the graphene naturally has a few tiny holes in it, you have a proton-selective membrane that could lead to improved fuel cells.
A major challenge in fuel cell technology is efficiently separating protons from hydrogen. In a study of single-layer graphene and water, the Northwestern researchers found that slightly imperfect graphene shuttles protons -- and only protons -- from one side of the ...
Graphene membrane could lead to better fuel cells, water filters
2015-03-17
An atomically thin membrane with microscopically small holes may prove to be the basis for future hydrogen fuel cells, water filtering and desalination membranes, according to a group of 15 theorists and experimentalists, including three theoretical researchers from Penn State.
The team, led by Franz Geiger of Northwestern University, tested the possibility of using graphene, the robust single atomic layer carbon, as a separation membrane in water and found that naturally occurring defects, essentially a few missing carbon atoms, allowed hydrogen protons to cross the ...
Genetic background determines whether aspirin/NSAIDS will reduce colorectal cancer risk
2015-03-17
An analysis of genetic and lifestyle data from 10 large epidemiologic studies confirmed that regular use of aspirin or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) appears to reduce the risk of colorectal cancer in most individuals. The study being published in the March 17 issue of JAMA found that a few individuals with rare genetic variants do not share this benefit. The study authors note, however, that additional questions need to be answered before preventive treatment with these medications can be recommended for anyone.
"Previous studies, including randomized ...
Effect of aspirin, NSAIDs on colorectal cancer risk may differ from genetic variations
2015-03-17
Among approximately 19,000 individuals, the use of aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) was associated with an overall lower risk of colorectal cancer, although this association differed according to certain genetic variations, according to a study in the March 17 issue of JAMA.
Considerable evidence demonstrates that use of aspirin and other NSAIDs is associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer. However, the mechanisms behind this association are not well understood. Routine use of aspirin, NSAIDs, or both for prevention of cancer is not currently ...
Study examines diagnostic accuracy of pathologists interpreting breast biopsies
2015-03-17
In a study in which pathologists provided diagnostic interpretation of breast biopsy slides, overall agreement between the individual pathologists' interpretations and that of an expert consensus panel was 75 percent, with the highest level of concordance for invasive breast cancer and lower levels of concordance for ductal carcinoma in situ and atypical hyperplasia, according to a study in the March 17 issue of JAMA.
Approximately 1.6 million women in the United States have breast biopsies each year. The accuracy of pathologists' diagnoses is an important and inadequately ...
Early imaging for back pain in older adults not associated with better outcomes
2015-03-17
Older adults who had spine imaging within 6 weeks of a new primary care visit for back pain had pain and disability over the following year that was not different from similar patients who did not undergo early imaging, according to a study in the March 17 issue of JAMA.
When to image older adults with back pain remains controversial. Many guidelines recommend that older adults undergo early imaging because of the higher prevalence of serious underlying conditions. However, there is not strong evidence to support this recommendation. Adverse consequences of early imaging ...
Duration of antiplatelet therapy following PCI, risk of adverse events
2015-03-17
An additional 18 months of dual antiplatelet therapy among patients who received a bare metal coronary stent did not result in significant differences in rates of stent thrombosis (formation of a blood clot), major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events, or moderate or severe bleeding, compared to patients who received placebo, according to a study in the March 17 issue of JAMA. The authors note that limitations in sample size may make definitive conclusions regarding these findings difficult.
Current clinical practice guidelines recommend a minimum of only 1 month ...
Study raises concerns about reporting of noninferiority trials
2015-03-17
An examination of the reporting of noninferiority clinical trials raises questions about the adequacy of their registration and results reporting within publicly accessible trial registries, according to a study in the March 17 issue of JAMA.
Noninferiority clinical trials are designed to determine whether an intervention is not inferior to a comparator by more than a prespecified difference (known as the noninferiority margin). Selection of an appropriate margin is fundamental to noninferiority trial validity, yet a point of frequent ambiguity. Given the increasing ...
Winter hack: Textured rubber that grips slick, icy surfaces
2015-03-17
WASHINGTON, D.C., March 17, 2015 - Winter storms dumped records amounts of snow on the East Coast and other regions of the country this February, leaving treacherous, icy sidewalks and roads in their wake. Now researchers from Canada are developing new methods to mass-produce a material that may help pedestrians get a better grip on slippery surfaces after such storms.
The material, which is made up of glass fibers embedded in a compliant rubber, could one day be used in the soles of slip-resistant winter boots. The researchers describe the manufacturing process in a ...
Teens' approach to social media risk is different from adults'
2015-03-17
For every parent who ever wondered what the heck their teens were thinking when they posted risky information or pictures on social media, a team of Penn State researchers suggests that they were not really thinking at all, or at least were not thinking like most adults do.
In a study, the researchers report that the way teens learn how to manage privacy risk online is much different than how adults approach privacy management. While most adults think first and then ask questions, teens tend to take the risk and then seek help, said Haiyan Jia, post-doctoral scholar in ...
West Coast waters shifting to lower-productivity regime, new NOAA report finds
2015-03-17
Large-scale climate patterns that affect the Pacific Ocean indicate that waters off the West Coast have shifted toward warmer, less productive conditions that may affect marine species from seabirds to salmon, according to the 2015 State of the California Current Report delivered to the Pacific Fishery Management Council.
The report by NOAA Fisheries' Northwest Fisheries Science Center and Southwest Fisheries Science Center assesses productivity in the California Current from Washington south to California. The report examines environmental, biological and socio-economic ...
New cystic fibrosis research takes aim at deadly pathogen
2015-03-17
AUSTIN, Texas - A new method of testing the most common cause of life-threatening infection in people with cystic fibrosis could improve efforts to study and combat the illness.
The bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a leading contributor to hospitalizations, serious illness and early death for people with cystic fibrosis (CF). Scientists at The University of Texas at Austin have found a way to re-create conditions specific to the environment in which the bacterium spreads in the lungs of a person with CF, allowing them to identify several genes that appear to be necessary ...
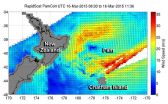
RapidScat eyes Ex-Tropical Cyclone Pam's winds near Chatham Islands
2015-03-17
The New Zealand Meteorological Service issued a Storm Warning for the Chatham Islands today as NASA's RapidScat instrument found that winds in one quadrant of Ex-Tropical Cyclone Pam is still generating tropical-storm-force winds east of its center.
The International Space Station's RapidScat instrument captured data on Ex-Tropical Cyclone Pam's winds on March 16 from 08:30 to 11:36 UTC. RapidScat revealed sustained winds over 30 meters per second (108 kph/67 mph) were still occurring southeast of the center.
The forecast calls for southwesterly winds to 50 knots (57 ...
Genetic markers play role in who benefits from aspirin, NSAIDs to lower colon cancer risk
2015-03-17
INDIANAPOLIS - An Indiana University cancer researcher and her colleagues have identified genetic markers that may help determine who benefits from regular use of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for lowering one's risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Previous studies have shown that regular use of aspirin and NSAIDs lower one's risk of colorectal cancer, but their use is not recommended as a way to prevent the disease because of uncertainty about the risks and benefits. Thus, the researchers set out to examine the interrelationship between genetic ...
The need for a more open attitude towards invasive alien species data
2015-03-17
New research published with the support of the FP7 large-scale bioinformatics project Building the European Biodiversity Observation Network (EU BON) and the Alien Challenge COST action reveals the importance of open data in the study and control of invasive alien species. The study was published online in open access in the journal Management of Biological Invasions.
Invasive alien species cause a wide variety of problems, including issues related to conservation; to human and animal health; to agriculture and to fisheries management. But how can science be useful to ...
Chronic bowel inflammation is diagnosed too late in children and adolescents
2015-03-17
Cramping abdominal pains, diarrhea, bloody stools--these are common symptoms of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Every year, up to 1470 children and adolescents in Germany develop the disease. But chronic inflammatory bowel disease is mostly diagnosed too late in these patients, as Stephan Buderus, Dietmar Scholz, and colleagues show in an original article in the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2015; 112: 121-7). The average delay between initial symptoms and diagnosis is four to six months. In most cases, the inflammation ...
Study: Erectile dysfunction drug relieves nerve damage in diabetic mice
2015-03-17
DETROIT - New animal studies at Henry Ford Hospital found that sildenafil, a drug commonly used to treat erectile dysfunction, may be effective in relieving painful and potentially life-threatening nerve damage in men with long-term diabetes.
The research targeted diabetic peripheral neuropathy, the most common complication of diabetes, affecting as many as 70 percent of patients.
The study was recently published online in PLOS ONE.
Lei Wang, M.D., the Henry Ford neuroscientist who led the research, said that although numerous drugs have been shown to be effective in ...
Hormones with statins may help women's hearts after menopause
2015-03-17
CLEVELAND, Ohio (March 17, 2015)--Hormones may not protect women from heart disease or stroke after menopause, but when combined with cholesterol-lowering statin drugs, they may help protect women from these killers, shows a population study from Sweden to be published in the April issue of Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS). During the study, women who took both hormones and statins had a significantly lower risk of dying of any cause and a moderately lower risk of dying of cardiovascular disease.
Using health information from national ...
Social media training works best for student-athletes, study shows
2015-03-17
CLEMSON, S.C. -- Placing less reliance on monitoring software and modifying new media training to align with student-athletes' habits and input will promote more positive and responsible usage of social networks.
This is the key finding by researchers from Clemson University, Baylor University and the University of Florida and published in the International Journal of Sport Communication.
The study explored college athletes' social media use and their experiences with and attitudes about a rising trend in college athletics: social media education.
Given the media ...
Finding a new test for children with concussions
2015-03-17
This news release is available in French. Researchers at the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital -The Neuro, at McGill University and the MUHC, are working to develop a much needed tool for helping diagnose concussions or mild traumatic brain injuries suffered by thousands of young Canadians ---hockey and football players among them. Post-concussion symptoms can include physical ailments, emotional disturbances and sleep disruption. Objective methods for predicting how severely mild brain trauma can affect a young person's brain are sorely needed. The potential ...
First global review on the status, future of Arctic marine mammals
2015-03-17
For Arctic marine mammals, the future is especially uncertain. Loss of sea ice and warming temperatures are shifting already fragile Northern ecosystems.
The precarious state of those mammals is underscored in a multinational study led by a University of Washington scientist, published this week in Conservation Biology, assessing the status of all circumpolar species and subpopulations of Arctic marine mammals, including seals, whales and polar bears. The authors outline the current state of knowledge and their recommendations for the conservation of these animals over ...
[1] ... [3082]
[3083]
[3084]
[3085]
[3086]
[3087]
[3088]
[3089]
3090
[3091]
[3092]
[3093]
[3094]
[3095]
[3096]
[3097]
[3098]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.