Research finds copyright confusion has 'chilling effects' in online creative publishing
2014-12-15
Online content creation has become easier than ever and is quickly reaching parity with content consumption. From writing a blog or social media post to letting an app turn your photos into a video montage, anyone with an Internet connection can publish these creations with the click of a button.
But in the age of Web publishing, it has become increasingly confusing for content creators to figure out how to protect their original works or to use other content legally -- such as for remixes or parodies -- on major websites for user-generated content, including YouTube ...
Adolescent childbearing in Iraq rose due to earlier marriages among less-educated women
2014-12-15
New York (15 December 2014)--A study published today is the first detailed assessment of whether the 8-year Iraq War had an effect on childbearing. The study found that before the war, from 1997 to 2003, adolescent fertility in Iraq was stable at just below 70 births per 1,000 girls aged 15-19. However, soon after the beginning of the war, adolescent fertility rose by more than 30 percent, reaching over 95 births per 1,000 girls in 2010. The study is included in the December 2014 issue of Population and Development Review, a peer-reviewed journal published by the Population ...
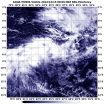
NASA catches Tropical Cyclone Bakung's remnants
2014-12-15
Tropical Cyclone Bakung ran into adverse conditions in the Southern Indian Ocean that weakened it to a remnant low pressure system when NASA's Aqua satellite spotted it on Dec. 15.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard Aqua captured a visible picture of Bakung's elongated remnants on Dec. 5 at 08:05 UTC (3:05 a.m. EST). The storm appeared to be stretched out from west to east in the visible image.
The last advisory on the tropical cyclone came on Dec. 13 when the storm was still a tropical storm with maximum sustained ...
Patients don't understand risks of unnecessary antibiotics, GW study shows
2014-12-15
WASHINGTON (Dec. 15, 2014)--Over prescription of antibiotics is a major factor driving one of the biggest public health concerns today: antibiotic resistance. In a first-of-its-kind study, research led by the George Washington University suggests that public health educational materials may not address the misconceptions that shape why patients expect antibiotics, driving doctors to prescribe them more. The research appeared in October in the journal Medical Decision Making.
Researchers from George Washington, Cornell and Johns Hopkins universities surveyed 113 patients ...
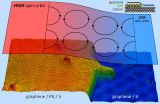
Lead islands in a sea of graphene magnetize the material of the future
2014-12-15
Researchers in Spain have discovered that if lead atoms are intercalated on a graphene sheet, a powerful magnetic field is generated by the interaction of the electrons' spin with their orbital movement. This property could have implications in spintronics, an emerging technology promoted by the European Union to create advanced computational systems.
Graphene is considered the material of the future due to its extraordinary optical and electronic mechanical properties, especially because it conducts electrons very quickly. However, it does not have magnetic properties, ...
Far from powerless: Ant larvae cannibalize eggs, are influenced by relatedness and sex
2014-12-15
To the casual observer, the colonies of social insects like bees and ants appear to be harmonious societies where individuals work together for the common good. But appearances can be deceiving.
In fact, individuals within nests compete over crucial determinants of fitness such as reproductive dominance and production of male eggs. The intensity of competition often depends on the level of kinship between colony members. This is because selfish individuals lose indirect fitness when their behavior harms close relatives. A new study by Eva Schultner and colleagues from ...
New algorithm a Christmas gift to 3-D printing -- and the environment
2014-12-15
Just in time for Christmas, Simon Fraser University computing science professor Richard Zhang reveals how to print a 3D Christmas tree efficiently and with zero material waste, using the world's first algorithm for automatically decomposing a 3D object into what are called pyramidal parts.
A pyramidal part has a flat base with the remainder of the shape forming upwards over the base with no overhangs, much like a pyramid. A pyramidal shape is optimal for 3D printing because it incurs no material waste and saves print time.
The algorithm promises to become a big deal in ...
UTSW researchers identify a therapeutic strategy that may treat a childhood neurological disorder
2014-12-15
DALLAS - Dec. 15, 2014 - UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers have identified a possible therapy to treat neurofibromatosis type 1 or NF1, a childhood neurological disease characterized by learning deficits and autism that is caused by inherited mutations in the gene encoding a protein called neurofibromin.
Researchers initially determined that loss of neurofibromin in mice affects the development of the part of the brain called the cerebellum, which is responsible for balance, speech, memory, and learning.
The research team, led by Dr. Luis F. Parada, Chairman ...
Hazy road to Mecca
2014-12-15
Irvine, Calif., Dec. 15, 2014 - Dangerously high levels of air pollutants are being released in Mecca during the hajj, the annual holy pilgrimage in which millions of Muslims on foot and in vehicles converge on the Saudi Arabian city, according to findings reported today at the American Geophysical Union meeting in San Francisco.
"Hajj is like nothing else on the planet. You have 3 to 4 million people - a whole good-sized city - coming into an already existing city," said Isobel Simpson, a UC Irvine research chemist in the Nobel Prize-winning Rowland-Blake atmospheric ...
NASA's MAVEN mission identifies links in chain leading to atmospheric loss
2014-12-15
Early discoveries by NASA's newest Mars orbiter are starting to reveal key features about the loss of the planet's atmosphere to space over time.
The findings are among the first returns from NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission, which entered its science phase on Nov. 16. The observations reveal a new process by which the solar wind can penetrate deep into a planetary atmosphere. They include the first comprehensive measurements of the composition of Mars' upper atmosphere and electrically charged ionosphere. The results also offer an unprecedented ...
Research: Two drugs before surgery help women with triple-negative breast cancer
2014-12-15
A breast cancer specialist and clinical researcher at Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island presented research yesterday at the 2014 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium showing that adding either the chemotherapy drug carboplatin or the blood vessel-targeting drug bevacizumab to the standard treatment of chemotherapy before surgery helped women who have the basal-like subtype of triple-negative breast cancer.
"We found that adding either carboplatin or bevacizumab to standard preoperative chemotherapy increased pathologic complete response rates for women with basal-like ...
PNNL talks climate, carbon, drinking water and the nexus of health and environment at AGU
2014-12-15
Scientists from the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory will present a variety of research at the 2014 American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting, which runs Monday, Dec. 15 through Friday, Dec. 19 at the Moscone Convention Center in San Francisco. Noteworthy PNNL research presentations include the following topics:
Even with global warming cold air outbreaks will remain
Just because the climate is warming doesn't mean Cold Air Outbreaks are going away, especially in Southwestern Canada and Northwestern United States. Overall, global climate models ...
Nuclear should be in the energy mix for biodiversity
2014-12-15
Leading conservation scientists from around the world have called for a substantial role for nuclear power in future energy-generating scenarios in order to mitigate climate change and protect biodiversity.
In an open letter to environmentalists with more than 60 signatories, the scientists ask the environmental community to "weigh up the pros and cons of different energy sources using objective evidence and pragmatic trade-offs, rather than simply relying on idealistic perceptions of what is 'green' ".
Organized by ecologists Professor Barry Brook and Professor Corey ...
Past global warming similar to today's
2014-12-15
SALT LAKE CITY, Dec. 15, 2014 - The rate at which carbon emissions warmed Earth's climate almost 56 million years ago resembles modern, human-caused global warming much more than previously believed, but involved two pulses of carbon to the atmosphere, University of Utah researchers and their colleagues found.
The findings mean the so-called Paleocene-Eocene thermal maximum, or PETM, can provide clues to the future of modern climate change. The good news: Earth and most species survived. The bad news: It took millennia to recover from the episode, when temperatures rose ...
Algorithm identifies networks of genetic changes across cancers
2014-12-15
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Using a computer algorithm that can sift through mounds of genetic data, researchers from Brown University have identified several networks of genes that, when hit by a mutation, could play a role in the development of multiple types of cancer.
The algorithm, called Hotnet2, was used to analyze genetic data from 12 different types of cancer assembled as part of the pan-cancer project of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). The research looked at somatic mutations -- those that occur in cells during one's lifetime -- and not genetic variants ...
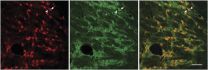
Neuronal circuits filter out distractions in the brain
2014-12-15
Cold Spring Harbor, NY - The next time you are in a crowded room, or a meeting, or even at the park with your kids, take a look around. How many people are on their phone? Distractions invade every aspect of our lives. Status updates, text messages, email notifications all threaten to steal our attention away from the moment. While we fight the urge to check the phone, our brains are making constant judgment calls about where to focus attention. The brain must continually filter important information from irrelevant interference.
Scientists have hypothesized for decades ...
Promising new method for rapidly screening cancer drugs
2014-12-15
AMHERST, Mass. - Traditional genomic, proteomic and other screening methods currently used to characterize drug mechanisms are time-consuming and require special equipment, but now researchers led by chemist Vincent Rotello at the University of Massachusetts Amherst offer a multi-channel sensor method using gold nanoparticles that can accurately profile various anti-cancer drugs and their mechanisms in minutes.
As Rotello and his doctoral graduate student Le Ngoc, one of the lead authors, explain, to discover a new drug for any disease, researchers must screen billions ...
Climate policy pledges are an important step forward but fall short of 2°C
2014-12-15
Researchers have released one of the most comprehensive assessments of the timing and amount of greenhouse gas emissions that each of the world's major economies could produce under different scenarios, i.e. without new climate policies, for the currently discussed pledges, and under a scenario that limits future temperature rise to 2°C. "The pledges made so far lead to earlier emission peaking in many countries, with 1-1.5 °C less total warming than without these policies, but not sufficient to meet the 2oC target. Under the proposed commitments, cumulative CO2 ...
Ancient wisdom boosts sustainability of biotech cotton
2014-12-15
Advocates of biotech crops and those who favor traditional farming practices such as crop diversity often seem worlds apart, but a new study shows that these two approaches can be compatible. An international team led by Chinese scientists and Bruce Tabashnik at the University of Arizona's College of Agriculture and Life Sciences discovered that the diverse patchwork of crops in northern China slowed adaptation to genetically engineered cotton by a wide-ranging insect pest. The results are published in the advance online edition of Nature Biotechnology.
Genetically engineered ...
Migrating 'supraglacial' lakes could trigger future Greenland ice loss
2014-12-15
Predictions of Greenland ice loss and its impact on rising sea levels may have been greatly underestimated, according to scientists at the University of Leeds.
The finding follows a new study, which is published today in Nature Climate Change, in which the future distribution of lakes that form on the ice sheet surface from melted snow and ice - called supraglacial lakes - have been simulated for the first time.
Previously, the impact of supraglacial lakes on Greenland ice loss had been assumed to be small, but the new research has shown that they will migrate farther ...
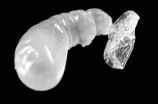
Stunning zinc fireworks when egg meets sperm
2014-12-15
Sparks literally fly when a sperm and an egg hit it off. The fertilized mammalian egg releases from its surface billions of zinc atoms in "zinc sparks," one wave after another, a Northwestern University-led interdisciplinary research team has found.
Using cutting-edge technology they developed, the researchers are the first to capture images of these molecular fireworks and pinpoint the origin of the zinc sparks: tiny zinc-rich packages just below the egg's surface.
Zinc fluctuations play a central role in regulating the biochemical processes that ensure a healthy ...
Molecular 'hats' allow in vivo activation of disguised signaling peptides
2014-12-15
When someone you know is wearing an unfamiliar hat, you might not recognize them. Georgia Institute of Technology researchers are using just such a disguise to sneak biomaterials containing peptide signaling molecules into living animals.
When the disguised peptides are needed to launch biological processes, the researchers shine ultraviolet light onto the molecules through the skin, causing the "hat" structures to come off. That allows cells and other molecules to recognize and interact with the peptides on the surface of the material.
This light-activated triggering ...
Joslin discovery may hold clues to treatments that slow aging
2014-12-15
BOSTON - December 15, 2014 - In a study published today by Nature, researchers at Joslin Diabetes Center used a microscopic worm (C. elegans) to identify a new path that could lead to drugs to slow aging and the chronic diseases that often accompany it--and might even lead to better cosmetics.
The Joslin team looked at how treatments known to boost longevity in the one-millimeter long C. elegans (including calorie restriction and treatment with the drug rapamycin) affected the expression of genes that produce collagen and other proteins that make up the extra-cellular ...
Scientists observe the Earth grow a new layer under an Icelandic volcano
2014-12-15
New research into an Icelandic eruption has shed light on how the Earth's crust forms, according to a paper published today in Nature.
When the Bárðarbunga volcano, which is buried beneath Iceland's Vatnajökull ice cap, reawakened in August 2014, scientists had a rare opportunity to monitor how the magma flowed through cracks in the rock away from the volcano. The molten rock forms vertical sheet-like features known as dykes, which force the surrounding rock apart.
Study co-author Professor Andy Hooper from the Centre for Observation and Modelling ...
The Deep Carbon Observatory: Quantities, movements, forms & origins of Earth's carbon
2014-12-15
The carbon in the atmosphere, ocean, surface life, and other shallow, near surface reservoirs accounts for only about 10% of Earth's carbon. Where is the other 90%? What is it doing? Does it matter?
The Deep Carbon Observatory (DCO), an ambitious 10-year (2009-2019) program of exploration and experimentation, pursues the mysterious 90% while building a new scientific field with a network of scientists from more than 40 countries. Recent results from DCO researchers are filling in the global carbon puzzle with findings that extend our understanding of the origins and limits ...
[1] ... [3121]
[3122]
[3123]
[3124]
[3125]
[3126]
[3127]
[3128]
3129
[3130]
[3131]
[3132]
[3133]
[3134]
[3135]
[3136]
[3137]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.