Promising new method for rapidly screening cancer drugs
2014-12-15
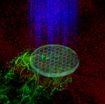
AMHERST, Mass. - Traditional genomic, proteomic and other screening methods currently used to characterize drug mechanisms are time-consuming and require special equipment, but now researchers led by chemist Vincent Rotello at the University of Massachusetts Amherst offer a multi-channel sensor method using gold nanoparticles that can accurately profile various anti-cancer drugs and their mechanisms in minutes.
As Rotello and his doctoral graduate student Le Ngoc, one of the lead authors, explain, to discover a new drug for any disease, researchers must screen billions ...
Climate policy pledges are an important step forward but fall short of 2°C
2014-12-15
Researchers have released one of the most comprehensive assessments of the timing and amount of greenhouse gas emissions that each of the world's major economies could produce under different scenarios, i.e. without new climate policies, for the currently discussed pledges, and under a scenario that limits future temperature rise to 2°C. "The pledges made so far lead to earlier emission peaking in many countries, with 1-1.5 °C less total warming than without these policies, but not sufficient to meet the 2oC target. Under the proposed commitments, cumulative CO2 ...
Ancient wisdom boosts sustainability of biotech cotton
2014-12-15
Advocates of biotech crops and those who favor traditional farming practices such as crop diversity often seem worlds apart, but a new study shows that these two approaches can be compatible. An international team led by Chinese scientists and Bruce Tabashnik at the University of Arizona's College of Agriculture and Life Sciences discovered that the diverse patchwork of crops in northern China slowed adaptation to genetically engineered cotton by a wide-ranging insect pest. The results are published in the advance online edition of Nature Biotechnology.
Genetically engineered ...
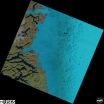
Migrating 'supraglacial' lakes could trigger future Greenland ice loss
2014-12-15
Predictions of Greenland ice loss and its impact on rising sea levels may have been greatly underestimated, according to scientists at the University of Leeds.
The finding follows a new study, which is published today in Nature Climate Change, in which the future distribution of lakes that form on the ice sheet surface from melted snow and ice - called supraglacial lakes - have been simulated for the first time.
Previously, the impact of supraglacial lakes on Greenland ice loss had been assumed to be small, but the new research has shown that they will migrate farther ...
Stunning zinc fireworks when egg meets sperm
2014-12-15
Sparks literally fly when a sperm and an egg hit it off. The fertilized mammalian egg releases from its surface billions of zinc atoms in "zinc sparks," one wave after another, a Northwestern University-led interdisciplinary research team has found.
Using cutting-edge technology they developed, the researchers are the first to capture images of these molecular fireworks and pinpoint the origin of the zinc sparks: tiny zinc-rich packages just below the egg's surface.
Zinc fluctuations play a central role in regulating the biochemical processes that ensure a healthy ...
Molecular 'hats' allow in vivo activation of disguised signaling peptides
2014-12-15
When someone you know is wearing an unfamiliar hat, you might not recognize them. Georgia Institute of Technology researchers are using just such a disguise to sneak biomaterials containing peptide signaling molecules into living animals.
When the disguised peptides are needed to launch biological processes, the researchers shine ultraviolet light onto the molecules through the skin, causing the "hat" structures to come off. That allows cells and other molecules to recognize and interact with the peptides on the surface of the material.
This light-activated triggering ...
Joslin discovery may hold clues to treatments that slow aging
2014-12-15
BOSTON - December 15, 2014 - In a study published today by Nature, researchers at Joslin Diabetes Center used a microscopic worm (C. elegans) to identify a new path that could lead to drugs to slow aging and the chronic diseases that often accompany it--and might even lead to better cosmetics.
The Joslin team looked at how treatments known to boost longevity in the one-millimeter long C. elegans (including calorie restriction and treatment with the drug rapamycin) affected the expression of genes that produce collagen and other proteins that make up the extra-cellular ...
Scientists observe the Earth grow a new layer under an Icelandic volcano
2014-12-15
New research into an Icelandic eruption has shed light on how the Earth's crust forms, according to a paper published today in Nature.
When the Bárðarbunga volcano, which is buried beneath Iceland's Vatnajökull ice cap, reawakened in August 2014, scientists had a rare opportunity to monitor how the magma flowed through cracks in the rock away from the volcano. The molten rock forms vertical sheet-like features known as dykes, which force the surrounding rock apart.
Study co-author Professor Andy Hooper from the Centre for Observation and Modelling ...
The Deep Carbon Observatory: Quantities, movements, forms & origins of Earth's carbon
2014-12-15
The carbon in the atmosphere, ocean, surface life, and other shallow, near surface reservoirs accounts for only about 10% of Earth's carbon. Where is the other 90%? What is it doing? Does it matter?
The Deep Carbon Observatory (DCO), an ambitious 10-year (2009-2019) program of exploration and experimentation, pursues the mysterious 90% while building a new scientific field with a network of scientists from more than 40 countries. Recent results from DCO researchers are filling in the global carbon puzzle with findings that extend our understanding of the origins and limits ...
Occasional heroin use may worsen HIV infection
2014-12-15
Researchers at Yale and Boston University and their Russian collaborators have found that occasional heroin use by HIV-positive patients may be particularly harmful to the immune system and worsens HIV disease, compared to persistent or no heroin use.
The findings are published in the journal AIDS and Behavior.
"We expected that HIV-positive patients who abused heroin on an ongoing basis would have the greatest decreases in their CD4 count, but this preliminary study showed that those who abused heroin intermittently had lower CD4 cell counts, indicating a weakened ...
Home umpires favor their own teams in test matches
2014-12-15
The introduction of neutral umpires in Test cricket led to a drop in the number of LBW decisions going in favour of home teams, a study has revealed.
The findings from research by economists, published by the Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, come amidst renewed debate on whether neutral umpiring is still required in Test matches following the introduction of the Decision Review System (DRS).
Economists Dr Abhinav Sacheti and Professor David Paton from Nottingham University Business School and Dr Ian Gregory-Smith from the University of Sheffield analysed Leg ...
To know the enemy
2014-12-15
This news release is available in Japanese. New research published in the journal genesis, by Kenneth Baughman, Dr. Eiichi Shoguchi, Professor Noriyuki Satoh of the Marine Genomics Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University, and collaborators from Australia, reports an intact Hox cluster in the Crown of Thorns starfish, Acanthaster planci. This surprising result contrasts with the relatively disorganized Hox cluster found in sea urchins, which are also echinoderms, classification of animals including starfish, sea lilies, and sea cucumbers. ...
'Darwinian' test uncovers an antidepressant's hidden toxicity
2014-12-15
SALT LAKE CITY, Dec. 15, 2014 -- Because of undetected toxicity problems, about a third of prescription drugs approved in the U.S. are withdrawn from the market or require added warning labels limiting their use. An exceptionally sensitive toxicity test invented at the University of Utah could make it possible to uncover more of these dangerous side effects early in pharmaceutical development so that fewer patients are given unsafe drugs.
To prove the point, the U researchers ran their test on Paxil, an antidepressant that thousands of pregnant women used in the years ...
Linguistic methods uncover sophisticated meanings, monkey dialects
2014-12-15
The same species of monkeys located in separate geographic regions use their alarm calls differently to warn of approaching predators, a linguistic analysis by a team of scientists reveals. The study, which appears in the journal Linguistics and Philosophy, reveals that monkey calls have a more sophisticated structure than was commonly thought.
"Our findings show that Campbell's monkeys have a distinction between roots and suffixes, and that their combination allows the monkeys to describe both the nature of a threat and its degree of danger," explains the study's lead ...
Proteins drive cancer cells to change states
2014-12-15
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- A new study from MIT implicates a family of RNA-binding proteins in the regulation of cancer, particularly in a subtype of breast cancer. These proteins, known as Musashi proteins, can force cells into a state associated with increased proliferation.
Biologists have previously found that this kind of transformation, which often occurs in cancer cells as well as during embryonic development, is controlled by transcription factors -- proteins that turn genes on and off. However, the new MIT research reveals that RNA-binding proteins also play an important ...
A taxonomic toolkit ends a century of neglect for a genus of parasitic wasps
2014-12-15
In 1912, three species in the parasitic wasp genus Ophion were described by two different entomologists, increasing the number of known species in North America to eleven. It has long been known that the actual diversity is much higher; however, it took 102 years for any additional species to be described.
"The main reason for this is that everyone has assumed that Ophion are just too difficult to tell apart. Museum collections are full of unidentified Ophion, but nobody has wanted to face the challenge of sorting them out" said Marla Schwarzfeld, an entomologist who ...
Scientists' unique system of oral vaccine delivery to address global health threats
2014-12-15
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., December 15 -- Scientists at The Forsyth Institute and Tufts University have succeeded in describing and validating a unique system of oral vaccine delivery using a common bacteria found in the mouth. Findings published today by Elsevier in Microbes and Infection identify Streptococcus mitis as a successful vector for oral mucosal immunization, and further research will determine its potential clinical use in tuberculosis vaccine development.
"Although injected vaccines are traditionally viewed as effective means of immunization to protect internal organs, ...
Faces that distract from actions
2014-12-15
The sudden appearance of a face within our visual field can affect the motor action accompanying a gesture even if the face is totally unrelated to what we are doing and even if we try to ignore it. At one condition, though: the face must display an emotionally significant expression. A study conducted by scientists of the International School for Advanced Studies in Trieste, and just published in Psychonomic Bullettin & Review, describes the phenomenon in detail.
Many are the things that can influence our actions at the motor level. Among them, a particularly effective ...
New colorectal cancer risk factor identified
2014-12-15
New Rochelle, NY, December 15, 2014-Adiponectin, a collagen-like protein secreted by fat cells, derives from the ADIPOQ gene. Variations in this gene may increase risk for type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and various cancers. A new study that links specific variations in the ADIPOQ gene to either higher or lower colorectal cancer risk is published in Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available on the Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers website until January 11, 2014.
Xin ...
Aflibercept in diabetic macular oedema: Added benefit not proven
2014-12-15
Since August 2014, aflibercept (trade name Eylea) has been available also for patients with visual impairment due to diabetic macular oedema (DMO). The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined in a dossier assessment whether this drug offers an added benefit over the appropriate comparator therapy.
According to the findings, an added benefit in this therapeutic indication is not proven: The data showed no relevant differences between the treatment groups for patients in whom the fovea centralis is also affected. The drug manufacturer ...
Squid supplies blueprint for printable thermoplastics
2014-12-15
Squid, what is it good for? You can eat it and you can make ink or dye from it, and now a Penn State team of researchers is using it to make a thermoplastic that can be used in 3-D printing.
"Most of the companies looking into this type of material have focused on synthetic plastics," said Melik C. Demirel, professor of engineering science and mechanics. "Synthetic plastics are not rapidly deployable for field applications, and more importantly, they are not eco-friendly."
Demirel and his team looked at the protein complex that exists in the squid ring teeth (SRT). ...
Do you speak cow? Researchers listen in on 'conversations' between cattle
2014-12-15
The team from The University of Nottingham and Queen Mary University of London, spent ten months studying to the ways cows communicate with their young, carefully examining acoustic indicators of identity and age.
They identified two distinct maternal 'calls'. When cows were close to their calves, they communicated with them using low frequency calls. When they were separated - out of visual contact - their calls were louder and at a much higher frequency.
Calves called out to their mothers when they wanted to start suckling. And all three types of calls were individualised ...
War metaphors for cancer hurt certain prevention behaviors
2014-12-15
ANN ARBOR--It's not unusual for people to use war metaphors such as "fight" and "battle" when trying to motivate patients with cancer.
But a new University of Michigan study indicates that using those words can have an unintended negative effect.
David Hauser, a U-M doctoral student in psychology, and colleague Norbert Schwarz of the University of Southern California, found in three studies that exposure to metaphoric language relating cancer to an enemy significantly lessens the extent to which people consider cancer-prevention behaviors.
"Hearing metaphoric utterances ...
Potential new tool for cervical cancer detection and diagnosis
2014-12-15
WASHINGTON D.C., Dec. 15, 2014--Cervical cancer is, in many ways, a shining example of how successful the war on cancer can be. Thanks largely to the advent of Pap smear screening, U.S. cervical cancer deaths decreased dramatically, by more than 60 percent, between 1955 and 1992. In the last two decades, better treatment outcomes and more powerful imaging techniques have steadily pushed 5-year survival rates ever higher. The latest weapons in modern medicine's arsenal are two new vaccines that were recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for preventing ...
Mobile radio passive radar makes harbors safer
2014-12-15
Airports are now subject to careful security surveillance, but many coastal towns and ports are not; they often lack radar installations to keep track of small boats, meaning terrorists could easily use speedboats to approach the coastline and bring explosives on land. Now, researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Communication, Information Processing and Ergonomics FKIE in Bonn developed a passive surveillance system for littoral regions based on mobile radio illumination called Passive Coherent Location (PCL). It passively employs the continuous radio signals emitted ...
[1] ... [3122]
[3123]
[3124]
[3125]
[3126]
[3127]
[3128]
[3129]
3130
[3131]
[3132]
[3133]
[3134]
[3135]
[3136]
[3137]
[3138]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.