Cocaine, amphetamine users more likely to take their own lives
2014-12-16
Stimulants use such as cocaine and amphetamine is associated with a nearly two-fold greater likelihood of suicidal behaviour amongst people who inject drugs, say researchers at the University of Montreal and the CHUM Research Centre. Drug addiction had already been identified as a major risk factor for suicide, and it is in fact the cause of ten percent of deaths among drug users. The data from this groundbreaking study could help develop and evaluate more appropriate suicide prevention efforts in this highly vulnerable population.
The researchers were able to explore ...
Study recommends GPs should be more open when referring patients for cancer investigations
2014-12-16
GPs should consider a more overt discussion with patients when referring them for further investigation of symptoms which may indicate cancer, according to a paper published in the British Journal of General Practice.
In an NIHR-funded study, researchers from the Universities of Bristol, Cambridge, Durham and Exeter conducted interviews with patients being referred for possible lung and colorectal cancer.
They found that patients were rarely involved in the decision to be referred for investigation and that reasons for referral tended to be couched in non-specific ...
The surprising history of tinsel
2014-12-16
WASHINGTON, Dec. 16, 2014 -- It's been a holiday decoration staple for decades, and it turns out that silver stuff hanging from your tree has quite a storied past. Tinsel has been made out of everything from real silver, to lead to other dangerously flammable materials. This week's Speaking of Chemistry decks your halls with the history of tinsel. Check it out at http://youtu.be/fql3aCuu1l0.
INFORMATION:
Speaking of Chemistry is a production of Chemical & Engineering News, a weekly magazine of the American Chemical Society. The program features fascinating, weird and ...
Discovery aims to fight destructive bee disease
2014-12-16
University of Guelph researchers hope their new discovery will help combat a disease killing honeybee populations around the world.
The researchers have found a toxin released by the pathogen that causes American foulbrood disease -- Paenibacillus larvae (P. larvae) -- and developed a lead-based inhibitor against it.
The study was published in the December issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
The finding provides much-needed insight into how the infection occurs, said Rod Merrill, a professor in Guelph's Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology and a ...
New research unlocks a mystery of albinism
2014-12-16
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Newly published research provides the first demonstration of how a genetic mutation associated with a common form of albinism leads to the lack of melanin pigments that characterizes the condition.
About 1 in 40,000 people worldwide have type 2 oculocutaneous albinism, which has symptoms of unsually light hair and skin coloration, vision problems, and reduced protection from sunlight-related skin or eye cancers. Scientists have known for about 20 years that the condition is linked to mutations in the gene that produces the OCA2 protein, ...
Mayo Clinic physicians say high-definition scopes accurately assess polyps
2014-12-16
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. -- It may not be necessary for experienced gastroenterologists to send polyps they remove from a patient's colon to a pathologist for examination, according to a large study conducted by physician researchers at the Jacksonville campus of Mayo Clinic.
Their 522-patient study, published in the December issue of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, found that physicians correctly evaluated whether a polyp was precancerous or benign using high-definition optical lenses during a colonoscopy. Their assessment was 96 or 97 percent accurate -- depending on which of ...
Damming beavers are slowly changing the world
2014-12-16
There are consequences of the successful efforts worldwide to save beavers from extinction. Along with the strong increase in their population over the past 100 years, these furry aquatic rodents have built many more ponds, establishing vital aquatic habitat. In doing so, however, they have created conditions for climate changing methane gas to be generated in this shallow standing water, and the gas is subsequently released into the atmosphere. In fact, 200 times more of this greenhouse gas is released from beaver ponds today than was the case around the year 1900, estimates ...
Teen prescription opioid abuse, cigarette, and alcohol use trends down
2014-12-16
Use of cigarettes, alcohol, and abuse of prescription pain relievers among teens has declined since 2013 while marijuana use rates were stable, according to the 2014 Monitoring the Future (MTF) survey, released today by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). However, use of e-cigarettes, measured in the report for the first time, is high.
These 2014 results are part of an overall two-decade trend among the nation's youth. The MTF survey measures drug use and attitudes among eighth, 10th, and 12th graders, is funded by NIDA, and is conducted by researchers at the ...
Domestic abuse may affect children in womb
2014-12-16
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Domestic violence can affect children even before they're born, indicates new research by Michigan State University scientists.
The study is the first to link abuse of pregnant women with emotional and behavioral trauma symptoms in their children within the first year of life. Symptoms include nightmares, startling easily, being bothered by loud noises and bright lights, avoiding physical contact and having trouble experiencing enjoyment.
"For clinicians and mothers, knowing that the prenatal experience of their domestic violence can directly ...
Are transgender veterans at greater risk of suicide?
2014-12-16
New Rochelle, NY, December 16, 2014--Veterans of the U.S. armed forces who have received a diagnosis consistent with transgender status are more likely to have serious suicidal thoughts and plans and to attempt suicide. A new study shows that this group has a higher risk of suicide death than the general population of veterans, as described in an article in LGBT Health, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the LGBT Health website until January 16, 2015.
Based on data gathered from the VA National Patient Care ...
Antibiotic resistance is a gut reaction
2014-12-16
Scientists from the Institute of Food Research and the University of East Anglia have discovered how certain gut bacteria can protect themselves and others in the gut from antibiotics.
The bacteria produce compounds, called cephalosporinases, which inactivate and destroy certain antibiotics such as penicillin derivatives and cephalosporins, protecting themselves and other beneficial bacteria that live in close proximity. However, they may also give protection from these antibiotics to harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella.
The gut is home to hundreds of trillions of bacteria, ...
Back to future with Roman architectural concrete
2014-12-16
No visit to Rome is complete without a visit to the Pantheon, Trajan's Markets, the Colosseum, or the other spectacular examples of ancient Roman concrete monuments that have stood the test of time and the elements for nearly two thousand years. A key discovery to understanding the longevity and endurance of Roman architectural concrete has been made by an international and interdisciplinary collaboration of researchers using beams of X-rays at the Advanced Light Source (ALS) of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab).
Working ...
E-cigarettes may recruit lower risk teens to nicotine use
2014-12-16
Researchers at the Norris Cotton Cancer Center and University of Hawaii Cancer Center find that one-third of Hawaiian adolescents have tried e-cigarettes, half of whom have never used another tobacco product.
"This is a markedly different pattern of use compared to their peers in the continental U.S., where teen e-cigarette use is less than half that rate and e-cigarette users are mainly also cigarette smokers (dual-users)," reported James D. Sargent, MD, a pediatrician at Dartmouth Hitchcock's Norris Cotton Cancer Center in a paper published December 15, 2014 in the ...
Urban stream contamination increasing rapidly due to road salt
2014-12-16
Average chloride concentrations often exceed toxic levels in many northern United States streams due to the use of salt to deice winter pavement, and the frequency of these occurrences nearly doubled in two decades.
Chloride levels increased substantially in 84 percent of urban streams analyzed, according to a U.S. Geological Survey study that began as early as 1960 at some sites and ended as late as 2011. Levels were highest during the winter, but increased during all seasons over time at the northern sites, including near Milwaukee, Wisconsin; Chicago, Illinois; Denver, ...
What was the 'Paleo diet'? There was far more than one, study suggests
2014-12-16
ATLANTA--The Paleolithic diet, or caveman diet, a weight-loss craze in which people emulate the diet of plants and animals eaten by early humans during the Stone Age, gives modern calorie-counters great freedom because those ancestral diets likely differed substantially over time and space, according to researchers at Georgia State University and Kent State University.
Their findings are published in The Quarterly Review of Biology.
"Based on evidence that's been gathered over many decades, there's very little evidence that any early hominids had very specialized diets ...
Men in recovery from Ebola should wear condoms for at least 3 months
2014-12-16
Los Angeles, CA (November 16, 2014) A new article reports that despite a clear lack of research on male survivors of Ebola, the current recommended practice of waiting at least three months after recovery to have unprotected sex should be upheld. This study was published today in Reproductive Sciences, a SAGE journal.
"Our exercise demonstrated that the current recommendations to prevent the sexual spread of Ebola are based on one mere observation," the researchers wrote. "Despite the evident need to conduct more research, for now, health care professionals should strongly ...
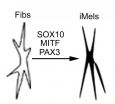
New technology directly reprograms skin fibroblasts for a new role
2014-12-16
PHILADELPHIA - As the main component of connective tissue in the body, fibroblasts are the most common type of cell. Taking advantage of that ready availability, scientists from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, the Wistar Institute, Boston University School of Medicine, and New Jersey Institute of Technology have discovered a way to repurpose fibroblasts into functional melanocytes, the body's pigment-producing cells. The technique has immediate and important implications for developing new cell-based treatments for skin diseases such as ...
Top blood transfusion-related complication more common than previously reported
2014-12-16
Two studies published in the January issue of Anesthesiology, the official medical journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists® (ASA®), shed new light on the prevalence of transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) and transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), the number one and two leading causes of blood transfusion-related deaths in the United States. According to researchers, postoperative TRALI is significantly underreported and more common than previously thought, with an overall rate of 1.4 percent. While the rate of TACO was found ...
Targeting inflammatory pathway reduces Alzheimer's disease in mice
2014-12-16
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia and is characterized by the formation of β-amyloid plaques throughout the brain. Proteins known as chemokines regulate inflammation and the immune response. In both patients with AD and mouse AD models, the chemokine CXCL10 is found in high concentrations in the brain and may contribute to AD. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation indicates that activation of the CXCL10 receptor, CXCR3, contributes to AD pathology. Using a murine model of AD, Michael Heneka and colleagues at the University ...
Microbial-induced pathway promotes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
2014-12-16
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disorder and affects approximately 1 billion people worldwide. It is not clear how this disease develops, but recent studies suggest that the bacterial population in the gut influences NAFLD. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation provides a link between molecular signaling pathways in the gut, the intestinal microbiome, and development of NAFLD. Frank Gonzalez and colleagues at the National Cancer Institute found that disruption of the gut microflora prevented development of NAFLD in mice fed ...
How to treat Ebola during pregnancy
2014-12-15
A pregnant woman in Africa who has contracted Ebola is likely to suffer with a spontaneous abortion, pregnancy-related hemorrhage, or the death of her newborn. Although the risk of caring for a pregnant woman with Ebola in the United States may be rare, the Association of Women's Health, Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses (AWHONN) has published a practice brief in its Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing to guide nursing care for pregnant women and newborns.
"Nurses play a vital role in caring for patients with Ebola," said Dr. Debra Bingham, who is Vice President ...
Shame on us
2014-12-15
Emotions are complicated and never more so than in the realm of the scientific, where commonly accepted definitions are lacking.
In a paper published in the journal Qualitative Inquiry, UC Santa Barbara's Thomas Scheff examines the basic emotions of grief, fear/anxiety, anger, shame and pride as they appear in scientific literature in an attempt to take a first step in defining them. "Emotion terms, especially in English, are wildly ambiguous," Scheff writes in the paper's introduction.
An emeritus professor of sociology at UCSB, Scheff set out to explore why the language ...
Herceptin found to improve long-term survival of HER2-positive breast cancer patients
2014-12-15
VCU Massey Cancer Center physician-researcher Charles E. Geyer, Jr., M.D., was the National Protocol Officer for one component of a large national study involving two National Cancer Institute (NCI)-supported clinical trials that demonstrated that trastuzumab significantly improves the long-term survival of HER-2 positive breast cancer patients. The combined study was designed to determine the long-term safety and efficacy of the drug trastuzumab, which is commonly known as Herceptin and is primarily used alongside chemotherapy to treat HER2-positive breast cancer. The ...
Switching to vehicles powered by electricity from renewables could save lives
2014-12-15
Driving vehicles that use electricity from renewable energy instead of gasoline could reduce the resulting deaths due to air pollution by 70 percent. This finding comes from a new life cycle analysis of conventional and alternative vehicles and their air pollution-related public health impacts, published Monday, Dec. 15, 2014, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study also shows that switching to vehicles powered by electricity made using natural gas yields large health benefits. Conversely, vehicles running on corn ethanol or vehicles powered ...
Non-Gluten proteins identified as targets of immune response to wheat in celiac disease
2014-12-15
NEW YORK, NY (December 15, 2014)--Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center have found that, in addition to gluten, the immune systems of patients with celiac disease react to specific types of non-gluten protein in wheat. The results were reported online in the Journal of Proteome Research.
Celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder that affects about 1 percent of the U.S. population, is triggered by the ingestion of wheat and related cereals in genetically susceptible individuals. The immune response results in inflammation and tissue damage in the small intestine, ...
[1] ... [3119]
[3120]
[3121]
[3122]
[3123]
[3124]
[3125]
[3126]
3127
[3128]
[3129]
[3130]
[3131]
[3132]
[3133]
[3134]
[3135]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.