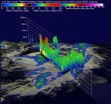
Tropical Storm Odile taken on by 2 NASA satellites
2014-09-12
As Tropical Storm Odile continues to affect Mexico's west coast and stir up dangerous surf, NASA's TRMM and Aqua satellites provided forecasters information on clouds and rainfall in the coast-hugging storm. On September 12, A Tropical Storm Watch remained in effect from Manzanillo to Cabo Corrientes, Mexico.
Tropical Storm Odile formed on September 10, 2014 in the same area where Norbert formed.
Gathering Rainfall and Thunderstorm Height Information
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew over tropical storm Odile on September 11, 2014 at ...
CCNY analysis explains rich bird biodiversity in Neotropics
2014-09-12
Applying analyses designed by City College of New York biologist Mike Hickerson, a team of international researchers is challenging a commonly held view that explains how so many species of birds ended up in the Neotropics, an area rich in rain forest extending from Mexico to the southernmost tip of South America. It is home to the most bird species on Earth.
"The unanswered question has been—how did this extraordinary bird diversity originate?" said Dr. Brian Smith, lead author of a paper on the subject published in the journal Nature this week and an assistant curator ...
Fluid mechanics suggests alternative to quantum orthodoxy
2014-09-12
The central mystery of quantum mechanics is that small chunks of matter sometimes seem to behave like particles, sometimes like waves. For most of the past century, the prevailing explanation of this conundrum has been what's called the "Copenhagen interpretation" — which holds that, in some sense, a single particle really is a wave, smeared out across the universe, that collapses into a determinate location only when observed.
But some founders of quantum physics — notably Louis de Broglie — championed an alternative interpretation, known as "pilot-wave theory," which ...
Corn spots: Study finds important genes in defense response
2014-09-12
When corn plants come under attack from a pathogen, they sometimes respond by killing their own cells near the site of the attack, committing "cell suicide" to thwart further damage from the attacker. This cell sacrifice can cause very small, often microscopic, spots or lesions on the plant.
But up until now it's been difficult to understand how the plant regulates this "spotty" defense mechanism because the response is so quick and localized.
Researchers at North Carolina State University have identified a number of candidate genes and cellular processes that appear ...
Experts call for massive global response to tackle Ebola
2014-09-12
AUDIO:
Professor Peter Piot, Director of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, explains how he co-discovered the Ebola virus in 1976, and gives his views on the current Ebola...
Click here for more information.
The current Ebola outbreak now requires a "rapid response at a massive global scale", according to experts at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine.
Writing an editorial in Science, Professor Peter Piot, co-discoverer of the virus, says that the ...
Stanford-led study assesses the environmental costs and benefits of fracking
2014-09-12
A strange thing happened on the way to dealing with climate change: Advances in hydraulic fracturing put trillions of dollars' worth of previously unreachable oil and natural gas within humanity's grasp.
The environmental costs – and benefits – from "fracking," which requires blasting huge amounts of water, sand and chemicals deep into underground rock formations, are the subject of new research that synthesizes 165 academic studies and government databases. The survey covers not only greenhouse gas impacts but also fracking's influence on local air pollution, earthquakes ...
Piglet health
2014-09-12
Porcine neonatal coccidiosis is a serious parasitic infection of young piglets that severely damages the intestinal mucosa, leading to diarrhoea and reduced nutritional intake. As the infection reduces animal growth, and because secondary infections can result in increased mortality, the disease is responsible for substantial economic losses at affected pig farms.
"The developing immune system of neonatal piglets is not yet mature enough to deal with the parasites. For this reason, an infection shortly after birth results in weakened intestinal tissue with appropriate ...
Moving silicon atoms in graphene with atomic precision
2014-09-12
Richard Feynman famously posed the question in 1959: is it possible to see and manipulate individual atoms in materials? For a time his vision seemed more science fiction than science, but starting with groundbreaking experiments in the late 1980s and more recent developments in electron microscopy instrumentation it has become scientific reality. However, damage caused by the electron beam is often an issue in such experiments.
The present study focused on single-layer graphene with silicon atoms embedded into the lattice, previously created and studied by the collaborators ...
Cutting the cloud computing carbon cost
2014-09-12
Cloud computing involves displacing data storage and processing from the user's computer on to remote servers. It can provide users with more storage space and computing power that they can then access from anywhere in the world rather than having to connect to a single desktop or other computer with its finite resources. However, some observers have raised concerns about the increased energy demands of sustaining distributed servers and having them up and running continuously, where an individual user's laptop might be shut down when it is not in use or the resources utilization ...
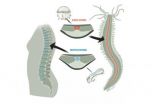
From worm muscle to spinal discs
2014-09-12
Thoughts of the family tree may not be uppermost in the mind of a person suffering from a slipped disc, but those spinal discs provide a window into our evolutionary past. They are remnants of the first vertebrate skeleton, whose origins now appear to be older than had been assumed. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have found that, unexpectedly, this skeleton most likely evolved from a muscle. The study, carried out in collaboration with researchers at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute in Janelia Farm, USA, is published ...
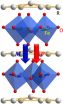
New family of materials for energy-efficient information storage and processing
2014-09-12
Switching the polarity of a magnet using an electric field (magnetoelectric memory [MEM] effect), can be a working principle of the next-generation technology for information processing and storage. Multiferroic materials are promising candidates for the MEM effect, due to the coexistence of electric and magnetic orders. On the other hand, the coexistence of spontaneous electric and magnetic polarizations is rare in known materials, which hinders the application potential of the MEM effect. This article briefly reviews a new family of multiferroic materials—hexagonal rare ...
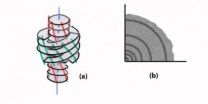
Conjecture on the lateral growth of Type I collagen fibrils
2014-09-12
Whatever the origin and condition of extraction of type I collagen fibrils, in vitro as well as in vivo, the radii of their circular circular cross sections stay distributed in a range going from 50 to 100 nm for the most part of them. Jean Charvolin and Jean-Francois Sadoc from the solid state physique laboratory at the Paris-Sud University propose therefore that, once the growth of the fibrils has been triggered by external biological factors, their lateral size be limited by internal physical stresses generated during the growth. Their conjecture is based ...
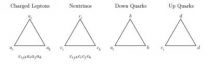
Extension of standard model by knot algebra
2014-09-12
This paper makes a connection between the quantum group SLq(2), which described knots, and the elementary particles of the standard model. The elements of the fundamental (j = 1/2) representation of SLq(2) are interpreted as creation operators for preons. The preons interact through a preonic vector field defined by elements of the adjoint (j = 1) representation. The leptons and quarks then appear (as required by the electroweak data) as elements of the j = 3/2 representation. Unexpectedly the electroweak quantum numbers of the so defined preons, leptons, and quarks agree ...
Scientists show that nicotine withdrawal reduces response to rewards across species
2014-09-12
Cigarette smoking is a leading cause of preventable death worldwide and is associated with approximately 440,000 deaths in the United States each year, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, but nearly 20 percent of the U.S. population continues to smoke cigarettes. While more than half of U.S. smokers try to quit every year, less than 10 percent are able to remain smoke-free, and relapse commonly occurs within 48 hours of smoking cessation. Learning about withdrawal and difficulty of quitting can lead to more effective treatments to help smokers ...
Favoritism linked to drug use in 'disengaged' families
2014-09-12
Before you revive the debate about which sibling in your family is the favorite, you'll want to know what the latest research shows.
Brigham Young University professor Alex Jensen analyzed 282 families with teenage siblings for a study that appears in the Journal of Family Psychology. Favoritism in parenting is a complex topic for sure, but here are some important take-aways.
Does it really matter?
Yes, at least for some families. Jensen looked at perceived preferential treatment in different types of family dynamics. For families that aren't very close to each other ...
Brain inflammation dramatically disrupts memory retrieval networks, UCI study finds
2014-09-12
Irvine, Calif., Sept. 10, 2014 — Brain inflammation can rapidly disrupt our ability to retrieve complex memories of similar but distinct experiences, according to UC Irvine neuroscientists Jennifer Czerniawski and John Guzowski.
Their study – which appears today in the Journal of Neuroscience – specifically identifies how immune system signaling molecules, called cytokines, impair communication among neurons in the hippocampus, an area of the brain critical for discrimination memory. The findings offer insight into why cognitive deficits occurs in people undergoing chemotherapy ...
No innocent bystander: Cartilage contributes to arthritis
2014-09-12
Melbourne researchers have discovered that cartilage plays an active role in the destruction and remodelling of joints seen in rheumatoid arthritis, rather than being an 'innocent bystander' as previously thought.
Dr Tommy Liu, Professor Ian Wicks, Dr Kate Lawler, Dr Ben Croker and colleagues from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute made the discovery while investigating the role of the protein SOCS3 in controlling inflammation during rheumatoid arthritis. The study was published in the journal Arthritis and Rheumatology.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects more than 400,000 ...
A meta-analysis of 3 types of peer norms and their relation with adolescent sexual behavior
2014-09-12
Researchers at Utrecht University and the New York State Psychiatric Institute collaborated on a meta-analysis of research on adolescent sexual behavior. The goal was to analyze how this behavior is related to adolescents' perceptions of three types of sexual peer norms, including how sexually active their peers are, how much their peers would approve of being sexually active, or how much they feel pressured by their peers to have sex. Awareness that these are different ways in which peers can affect adolescents' sexual behaviors is important for parents, teachers, and ...
Protein appears to protect against bone loss in arthritis
2014-09-12
AUGUSTA, Ga. – A small protein named GILZ appears to protect against the bone loss that often accompanies arthritis and its treatment, researchers report.
Arthritis as well as aging prompt the body to make more fat than bone, and the researchers have previously shown GILZ can restore a more youthful, healthy mix. It also tamps down inflammation, a major factor in arthritis.
Now they have early evidence that GILZ might one day be a better treatment option for arthritis patients than widely used synthetic glucocorticoids, which actually increase bone loss, said Dr. Xingming ...
Dendritic cells affect onset and progress of psoriasis
2014-09-12
Different types of dendritic cells in human skin have assorted functions in the early and more advanced stages of psoriasis report researchers in the journal EMBO Molecular Medicine. The scientists suggest that new strategies to regulate the composition of dendritic cells in psoriatic skin lesions might represent an approach for the future treatment of the disease.
"We urgently need new ways to treat psoriasis, treatments that will deliver improved benefits to patients and reduce the incidence of known side effects for existing drugs," says EMBO Member Maria Sibilia, ...
Gray matter matters when measuring our tolerance of risk
2014-09-12
There is a link between our brain structure and our tolerance of risk, new research suggests.
Dr Agnieszka Tymula, an economist at the University of Sydney, is one of the lead authors of a new study that identifies what might be considered the first stable 'biomarker' for financial risk-attitudes.
Using a whole-brain analysis, Dr Tymula and international collaborators found that the grey matter volume of a region in the right posterior parietal cortex was significantly predictive of individual risk attitudes. Men and women with higher grey matter volume in this region ...
Age and diabetes duration linked to risk of death and macrovascular complications
2014-09-12
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) shows that age (or age at diagnosis) and duration of diabetes disease are linked to the risk of death and marcovascular complications (those in larger blood vessels), whereas only diabetes duration is linked to the risk of microvascular complications (in smaller blood vessels such as those in the eyes). This means younger people with diabetes are more at risk of microvascular complications since they are more likely to have diabetes for longer over their lifetimes ...
The Lancet: Combining gut hormone with insulin proves more effective at controlling type 2 diabetes than other common treatments
2014-09-12
Combined treatment with a drug that mimics the action of a gut hormone and basal insulin [1] is more effective at improving blood sugar control than other anti-diabetic treatments, with similar rates of hypoglycaemia (dangerously low blood sugar levels) and greater weight loss, a systematic review and meta-analysis published in The Lancet shows.
"Achieving normal blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes is compromised by the adverse side effects plaguing currently available treatments. Some anti-diabetic treatments increase risk of hypoglycaemia and weight gain ...
Many kidney failure patients have concerns about pursuing kidney transplantation
2014-09-12
Washington, DC (September 11, 2014) — Concerns about pursuing kidney transplantation are highly prevalent among kidney failure patients, particularly older adults and women, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (CJASN). Reducing these concerns may help decrease disparities in access to transplantation.
There are thousands of patients with kidney failure who lack access to kidney transplantation, and disparities persist in terms of race, age, sex, and other patient characteristics. To improve ...
Microbes evolve faster than ocean can disperse them
2014-09-12
Two Northeastern University researchers and their international colleagues have created an advanced model aimed at exploring the role of neutral evolution in the biogeographic distribution of ocean microbes.
Their findings were published Thursday in the journal Science. The paper—titled "Biogeographic patterns in ocean microbes emerge in a neutral agent-based model"—was co-authored by Ferdi Hellweger, a microbial ecology expert and an associate professor of civil and environmental engineering; his doctoral student Neil Fredrick, PhD'15; and oceanographer Erik van Sebille ...
[1] ... [3346]
[3347]
[3348]
[3349]
[3350]
[3351]
[3352]
[3353]
3354
[3355]
[3356]
[3357]
[3358]
[3359]
[3360]
[3361]
[3362]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.