Age and diabetes duration linked to risk of death and macrovascular complications
2014-09-12
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) shows that age (or age at diagnosis) and duration of diabetes disease are linked to the risk of death and marcovascular complications (those in larger blood vessels), whereas only diabetes duration is linked to the risk of microvascular complications (in smaller blood vessels such as those in the eyes). This means younger people with diabetes are more at risk of microvascular complications since they are more likely to have diabetes for longer over their lifetimes ...
The Lancet: Combining gut hormone with insulin proves more effective at controlling type 2 diabetes than other common treatments
2014-09-12
Combined treatment with a drug that mimics the action of a gut hormone and basal insulin [1] is more effective at improving blood sugar control than other anti-diabetic treatments, with similar rates of hypoglycaemia (dangerously low blood sugar levels) and greater weight loss, a systematic review and meta-analysis published in The Lancet shows.
"Achieving normal blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes is compromised by the adverse side effects plaguing currently available treatments. Some anti-diabetic treatments increase risk of hypoglycaemia and weight gain ...
Many kidney failure patients have concerns about pursuing kidney transplantation
2014-09-12
Washington, DC (September 11, 2014) — Concerns about pursuing kidney transplantation are highly prevalent among kidney failure patients, particularly older adults and women, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (CJASN). Reducing these concerns may help decrease disparities in access to transplantation.
There are thousands of patients with kidney failure who lack access to kidney transplantation, and disparities persist in terms of race, age, sex, and other patient characteristics. To improve ...
Microbes evolve faster than ocean can disperse them
2014-09-12
Two Northeastern University researchers and their international colleagues have created an advanced model aimed at exploring the role of neutral evolution in the biogeographic distribution of ocean microbes.
Their findings were published Thursday in the journal Science. The paper—titled "Biogeographic patterns in ocean microbes emerge in a neutral agent-based model"—was co-authored by Ferdi Hellweger, a microbial ecology expert and an associate professor of civil and environmental engineering; his doctoral student Neil Fredrick, PhD'15; and oceanographer Erik van Sebille ...
Inflammation may be key to diabetes/heart disease link
2014-09-11
Inflammation may be the reason high blood sugar levels damage blood vessels, raising the possibility that anti-inflammatory medications might someday be used to lower the risk of blood vessel disease in people with diabetes, according to a study presented at the American Heart Association's High Blood Pressure Research Scientific Sessions 2014.
"These findings may explain why good blood sugar control is not sufficient to avoid the development of diabetes-induced cardiovascular diseases," said Carlos F. Sánchez-Ferrer, M.D., Ph.D., study author and professor of pharmacology ...
Cutting the cord on soft robots
2014-09-11
When it comes to the development of soft robots, researchers have finally managed to cut the cord.
Engineers at Harvard's School for Engineering and Applied Sciences and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering have developed the world's first untethered soft robot – a quadruped which can literally stand up and walk away from its designers.
Working in the lab of Charles River Professor of Engineering and Applied Sciences Robert Wood, a team of researchers that included Michael Tolley, Robert Shepherd, Bobak Mosadegh, Kevin Galloway, Michael Wehner ...
NASA research helps unravel mysteries of the Venusian atmosphere
2014-09-11
VIDEO:
New research shows giant holes in Venus' atmosphere -- which serve as extra clues for understanding this planet so different from our own.
Click here for more information.
Underscoring the vast differences between Earth and its neighbor Venus, new research shows a glimpse of giant holes in the electrically charged layer of the Venusian atmosphere, called the ionosphere. The observations point to a more complicated magnetic environment than previously thought – which ...
Tipping the balance of behavior
2014-09-11
Humans with autism often show a reduced frequency of social interactions and an increased tendency to engage in repetitive solitary behaviors. Autism has also been linked to dysfunction of the amygdala, a brain structure involved in processing emotions. Now Caltech researchers have discovered antagonistic neuron populations in the mouse amygdala that control whether the animal engages in social behaviors or asocial repetitive self-grooming. This discovery may have implications for understanding neural circuit dysfunctions that underlie autism in humans.
This discovery, ...
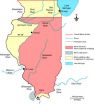
Original northern border of Illinois was south of Chicago and Lake Michigan
2014-09-11
URBANA, Ill. – Chicago residents today might have had a Wisconsin zip code if the originally proposed northern boundary of Illinois had been approved. It was a straight line from the southernmost tip of Lake Michigan to just south of the Rock and Mississippi River confluence. University of Illinois soil scientist Ken Olson said that had the proposed northern border not been changed, the state of Illinois would have a much smaller population and footprint with the northern 51 miles of the Illinois Territory ceded to Wisconsin when it became a state in 1848.
Olson says ...
Diabetes researchers find faster way to create insulin-producing cells
2014-09-11
University of British Columbia, in collaboration with BetaLogics Venture, a division of Janssen Research & Development, LLC, has published a study highlighting a protocol to convert stem cells into insulin-producing cells. The new procedure could be an important step in the fight against Type 1 diabetes.
The protocol can turn stem cells into reliable, insulin-producing cells in about six weeks, far quicker than the four months it took using previous methods.
"We are a step closer to having an unlimited supply of insulin-producing cells to treat patents with Type ...
One-minute point-of-care anemia test shows promise in new study
2014-09-11
A simple point-of-care testing device for anemia could provide more rapid diagnosis of the common blood disorder and allow inexpensive at-home self-monitoring of persons with chronic forms of the disease.
The disposable self-testing device analyzes a single droplet of blood using a chemical reagent that produces visible color changes corresponding to different levels of anemia. The basic test produces results in about 60 seconds and requires no electrical power. A companion smartphone application can automatically correlate the visual results to specific blood hemoglobin ...
Meditation may mitigate migraine misery
2014-09-11
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Sept. 11, 2014 – Meditation might be a path to migraine relief, according to a new study by researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center.
"Stress is a well-known trigger for headaches and research supports the general benefits of mind/body interventions for migraines, but there hasn't been much research to evaluate specific standardized meditation interventions," said Rebecca Erwin Wells, M.D., assistant professor of neurology at Wake Forest Baptist and lead author of the study published in the online edition of the journal Headache.
The study ...
Yogic breathing shows promise in reducing symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder
2014-09-11
MADISON, Wis. — One of the greatest casualties of war is its lasting effect on the minds of soldiers. This presents a daunting public health problem: More than 20 percent of veterans returning from the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan have post-traumatic stress disorder, according to a 2012 report by RAND Corp.
A new study from the Center for Investigating Healthy Minds at the Waisman Center of the University of Wisconsin-Madison offers hope for those suffering from the disorder. Researchers there have shown that a breathing-based meditation practice called Sudarshan Kriya ...
Volunteer 'eyes on the skies' track peregrine falcon recovery in California
2014-09-11
In recovery from the deadly legacy of DDT, American peregrine falcons (Falco peregrines anatum) faced new uncertainty in 1992, when biologists proposed to stop rearing young birds in captivity and placing them in wild nests. Tim Wootton and Doug Bell published models that year in ESA's journal Ecological Applications, projecting population trends for the falcon in California, with and without direct human intervention in the falcons' reproductive lives. They concluded that the birds would continue to recover without captive rearing, though the population growth rate might ...
NASA research gives guideline for future alien life search
2014-09-11
Astronomers searching the atmospheres of alien worlds for gases that might be produced by life can't rely on the detection of just one type, such as oxygen, ozone, or methane, because in some cases these gases can be produced non-biologically, according to extensive simulations by researchers in the NASA Astrobiology Institute's Virtual Planetary Laboratory.
The researchers carefully simulated the atmospheric chemistry of alien worlds devoid of life thousands of times over a period of more than four years, varying the atmospheric compositions and star types. "When we ...
Few mild-to-moderate Parkinson's disease patients suffer from malnutrition, yet almost one-third are at risk
2014-09-11
Amsterdam, NL, 11 September 2014 – Patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) can experience difficulties with food preparation and ingestion, which could contribute to poor nutrition and place them at risk for malnourishment. Published studies have also suggested that PD is associated with low weight, however, few studies included control groups. A report published in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease counters this conclusion in patients with mild-to-moderate PD, finding that the incidence or risk of malnutrition is no different for patients with mild-to-moderate PD compared ...
African American women receive less breast reconstruction after mastectomy
2014-09-11
Dartmouth researchers have found that African American women are 55 percent less likely to receive breast reconstruction after mastectomy regardless of where they received their care. They report on their findings in "The influence of race/ethnicity and place of service on breast reconstruction for Medicare beneficiaries with mastectomy," recently published in SpringerPlus.
"We wanted to understand whether the racial disparity observed in breast reconstruction among women with breast cancer was related to where women received care, independent of race," said Tracy Onega, ...
Commensal bacteria help orchestrate immune response in lung
2014-09-11
Studies in mice demonstrate that signals from the bacteria that harmlessly—and often beneficially—inhabit the human gastrointestinal tract boost the immune system's ability to kill a major respiratory pathogen, Klebsiella pneumoniae, according to a paper published online ahead of print in the journal Infection and Immunity.
The research is yet another example of how important these "commensal" bacteria are to human health and physiology, says Thomas B. Clarke, of Imperial College London, UK, the lone author of this paper.
"Numerous studies have shown that changes ...
Researchers make scientific history with new cellular connection
2014-09-11
Researchers led by Dr. Helen McNeill at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute have revealed an exciting and unusual biochemical connection. Their discovery has implications for diseases linked to mitochondria, which are the primary sources of energy production within our cells.
Dr. McNeill's team has an international reputation for their work in understanding how cells become organized into tissues and how growth is regulated during development. The group focuses on mutations in the fat (ft) gene. The protein product of this gene, called 'Fat', acts at the cell membrane ...
Primary care doctors reluctant to provide genetics assessment in routine care
2014-09-11
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Primary care providers report many challenges to integrating genetics services into routine primary care, according to research published today in Genetics in Medicine.
Medical genetics medicine has traditionally been used to identify and diagnose rare diseases, but in the last decade it has been increasingly helpful in determining patients at risk for genetically-based conditions who can benefit from preventive health care, says the study's senior author, Beth Tarini, M.D., M.S., F.A.A.P., assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Michigan ...
Penn medicine study reveals profile of patients most likely to delay hospice enrollment
2014-09-11
One in six cancer patients enroll in hospice only during their last three days of life, according to a new study from a team from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Their findings, published online last month in the Journal of Clinical Oncology (JCO) also reveal a profile of patients who may be most at risk of these late admissions.
"Waiting until the final days of life to begin hospice can shortchange patients and their families – skipping over many benefits of hospice care and limiting the opportunity to improve patients' quality of ...
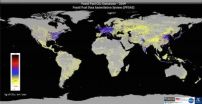
Study maps 15 years of carbon dioxide emissions on Earth
2014-09-11
TEMPE, Ariz. – World leaders face multiple barriers in their efforts to reach agreement on greenhouse gas emission policies. And, according to Arizona State University researchers, without globally consistent, independent emissions assessments, climate agreements will remain burdened by errors, self-reporting, and the inability to verify emissions progress.
Now, an international research team led by ASU scientists has developed a new approach to estimate CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuels — one that provides crucial information to policymakers. Called the "Fossil ...
Dartmouth research links genetic mutation and melanoma progression
2014-09-11
Dartmouth researchers have found that the genetic mutation BRAFV600E, frequently found in metastatic melanoma, not only secretes a protein that promotes the growth of melanoma tumor cells, but can also modify the network of normal cells around the tumor to support the disease's progression. Targeting this mutation with Vemurafenib reduces this interaction, and suggests possible new treatment options for melanoma therapy. They report on their findings in "BRAFV600E melanoma cells secrete factors that activate stromal fibroblasts and enhance tumourigenicity," which was recently ...
Ceramics don't have to be brittle
2014-09-11
Imagine a balloon that could float without using any lighter-than-air gas. Instead, it could simply have all of its air sucked out while maintaining its filled shape. Such a vacuum balloon, which could help ease the world's current shortage of helium, can only be made if a new material existed that was strong enough to sustain the pressure generated by forcing out all that air while still being lightweight and flexible.
Caltech materials scientist Julia Greer and her colleagues are on the path to developing such a material and many others that possess unheard-of combinations ...
Scientists report first semiaquatic dinosaur, Spinosaurus
2014-09-11
WASHINGTON (Sept. 11, 2014)—Scientists today unveiled what appears to be the first truly semiaquatic dinosaur, Spinosaurus aegyptiacus. New fossils of the massive Cretaceous-era predator reveal it adapted to life in the water some 95 million years ago, providing the most compelling evidence to date of a dinosaur able to live and hunt in an aquatic environment. The fossils also indicate that Spinosaurus was the largest known predatory dinosaur to roam the Earth, measuring more than 9 feet longer than the world's largest Tyrannosaurus rex specimen. These findings, published ...
[1] ... [3347]
[3348]
[3349]
[3350]
[3351]
[3352]
[3353]
[3354]
3355
[3356]
[3357]
[3358]
[3359]
[3360]
[3361]
[3362]
[3363]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.