Animalistic descriptions of violent crimes increase punishment of perpetrators
2014-08-04
Describing criminals and criminal activities with animal metaphors leads to more retaliation against perpetrators by inducing the perception that they're likely to continue engaging in violence, a new Aggressive Behavior study suggests.
When surveying jury?eligible adults, investigators varied animalistic descriptions of a violent crime and examined its effect on the severity of the punishment for the act. Compared with non?animalistic descriptions, animalistic descriptions resulted in significantly harsher punishment for the perpetrator due to an increase in perceived ...
Evolutionary explanation for why some lessons more easily learned than others
2014-08-04
It's easy to guess why it doesn't take long to learn to avoid certain behaviors and embrace others. But how do we know what drives these predilections? A study led by Aimee Dunlap at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, and co-authored by University of Minnesota researcher David Stephens, offers insight into the evolutionary underpinning of animals' innate ability to quickly absorb critical life lessons.
Animals are flooded with stimuli, but survival often depends on their ability to form specific associations that enhance fitness while ignoring others entirely. Psychologists ...
Enhancing biofuel yields from biomass with novel new method
2014-08-04
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — A team of researchers, led by Professor Charles E. Wyman, at the University of California, Riverside's Bourns College of Engineering have developed a versatile, relatively non-toxic, and efficient way to convert raw agricultural and forestry residues and other plant matter, known as lignocellulosic biomass, into biofuels and chemicals.
The patent-pending method, called Co-solvent Enhanced Lignocellulosic Fractionation (CELF), brings researchers closer to solving the long elusive goal of producing fuels and chemicals from biomass at high enough yields ...
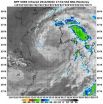
NASA catches the brief life of Tropical Storm Nakri
2014-08-04
The low pressure area known as System 96W struggled to organize for a week and finally became Tropical Storm Nakri on August 2 as the Suomi NPP satellite passed overhead. Nakri had a short life, however, as it dissipated the following day while approaching South Korea.
On Saturday, August 2, at 9 p.m. EDT, Nakri's maximum sustained winds were near 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph). At that time it was centered about 100 nautical miles southeast of Kunsan Air Base, near 35.0 north and 125.0 east. It was moving to the north at 14 knots (16.1 mph/21.9 kph).
When NASA-NOAA's Suomi ...
NASA sees Typhoon Halong's eye wink
2014-08-04
As Super Typhoon Halong tracks north through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean, NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites have seen the powerful storm appear to wink at space as it developed and "opened" an eye and then close its eye as clouds moved over it. That wink appears to be a sign of eyewall replacement in the powerful storm.
On August 2 at 01:45 UTC (August 1 at 9:45 p.m. EDT) NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of a wide-eyed Super Typhoon Halong moving through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. At the time of the image, Halong was a powerful Category 5 Super Typhoon ...
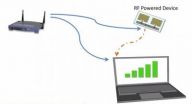
No-power Wi-Fi connectivity could fuel internet of things reality
2014-08-04
Imagine a world in which your wristwatch or other wearable device communicates directly with your online profiles, storing information about your daily activities where you can best access it – all without requiring batteries. Or, battery-free sensors embedded around your home could track minute-by-minute temperature changes and send that information to your thermostat to help conserve energy.
This not-so-distant "Internet of Things" reality would extend connectivity to perhaps billions of devices. Sensors could be embedded in everyday objects to help monitor and track ...
NASA's IBEX and Voyager spacecraft drive advances in outer heliosphere research
2014-08-04
San Antonio -- Aug. 4, 2014 -- Scientists yesterday highlighted an impressive list of achievements in researching the outer heliosphere at the 40th International Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) Scientific Assembly in Moscow.
"Between NASA's Voyager and IBEX missions, it's an incredible time for outer heliospheric science," says Dr. Dave McComas, IBEX principal investigator and assistant vice president of the Space Science and Engineering Division at Southwest Research Institute, who also will be recognized with a 2014 COSPAR Space Science Award at the assembly. "Ten ...
Children in immigrant families more likely to be sedentary
2014-08-04
Immigrant children from all racial and ethnic backgrounds are more likely to be sedentary than U.S.-born white children, according to a new study by sociologists at Rice University. The researchers said their findings should remind pediatricians and parents of children in immigrant families to encourage physical activity.
The research revealed that children of immigrants from all racial and ethnic backgrounds have lower levels of physical activity than U.S.-born white children, even when adjustments are made for socio-demographic and neighborhood characteristics. A low ...
New tools advance bio-logic
2014-08-04
Researchers at Rice University and the University of Kansas Medical Center are making genetic circuits that can perform more complex tasks by swapping protein building blocks.
The modular genetic circuits engineered from parts of otherwise unrelated bacterial genomes can be set up to handle multiple chemical inputs simultaneously with a minimum of interference from their neighbors.
The work reported in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Synthetic Biology gives scientists more options as they design synthetic cells for specific tasks, such as the production of ...
GW researcher reveals how amphibians crossed continents
2014-08-04
There are more than 7,000 known species of amphibians that can be found in nearly every type of ecosystem on six continents. But there have been few attempts to understand exactly when and how frogs, toads, salamanders and caecilians have moved across the planet throughout time.
Armed with DNA sequence data, Alex Pyron, an assistant professor of biology at the George Washington University, sought to accurately piece together the 300-million-year storyline of their journey.
Dr. Pyron has succeeded in constructing a first-of-its-kind comprehensive diagram of the geographic ...
How should flood risk assessments be done in a changing climate?
2014-08-04
Growing consensus on climate and land use change means that it is reasonable to assume, at the very least, that flood levels in a region may change. Then why, ask Rosner et al. in a new study, do the dominant risk assessment techniques used to decide whether to build new flood protection infrastructure nearly always start with an assumption of "no trend" in flood behavior?
In an argument grounded in an analysis of the inherent limitations of statistical analyses, the authors suggest that researchers' typical starting assumption that flood behavior is not changing—even ...
Insights on whale shark populations and evidence for their historic rise and recent decline
2014-08-04
In the largest study on the genetics of whale sharks conducted to date, researchers found that the world's biggest fish likely exist in 2 distinct populations with minimal connectivity between the Indo-Pacific and the Atlantic Ocean. The findings suggest that mixing of whale sharks between the Indian and Atlantic was and is rare.
The Molecular Ecology investigators also found a significant and likely recent population expansion, but a very recent bottleneck might have gone undetected as genetic diversity at Ningaloo Reef in Australia has declined during 5 consecutive ...
Study assesses shark attacks on Atlantic spotted dolphins near the Bahamas
2014-08-04
A Marine Mammal Science analysis on failed shark attacks on the approximately 120 Atlantic spotted dolphins that are residents of the waters near Bimini, The Bahamas, has found that a total of 14 dolphins (15% of 92 cataloged animals) showed some sign of shark attack, and a further 15 (16%) exhibited scars that could not conclusively be classified as shark induced or not.
Of 14 the shark attacks, there was no difference in scars or wounds between the sexes, and there was no significant difference between the location of bodily scars and wounds. No shark-related injuries ...
Humane strategy reduces shark attacks
2014-08-04
A simple and humane technique may be an effective strategy to reduce human encounters with sharks without harming populations of threatened shark species.
Instead of using advanced (and relatively untested) technology to attempt to repel sharks or nondiscriminatory nets that kill other threatened sea life as bycatch, researchers have simply caught sharks and moved them to where they would not pose a threat to swimmers. The Shark Monitoring Program of Recife, Brazil, reported approximately 100% survival of protected species and a 97% decrease in shark attacks when the ...
Researchers develop food safety social media guide
2014-08-04
To help protect public health, researchers from North Carolina State University have developed guidelines on how to use social media to communicate effectively about food safety.
"In a crisis context, the framework can be used by health officials, businesses or trade organizations affected by foodborne illness to help them reach key audiences with information that could be used to reduce the risk of foodborne illness," says Dr. Ben Chapman, an associate professor at NC State whose research focuses on food safety and lead author of the paper outlining the guidance. Key ...
CU Denver study shows excess parking at some Denver sports stadiums
2014-08-04
DENVER (Aug. 4, 2014) – Sports stadiums in Denver suffer from excess parking, creating unattractive concrete spaces, heat islands, and missed economic opportunities, according to a new study from the University of Colorado Denver.
"We tend to think the more parking, the better," said Wesley Marshall, PhD, PE, assistant professor of civil engineering at the CU Denver College of Engineering and Applied Science. "But too much parking can be as bad as too little."
The study began as a research project for CU Denver engineering student Alejandro Henao and was recently published ...
Weakness of leukaemic stem cells discovered
2014-08-04
FRANKFURT. Despite improved therapy, only one out of every two adult patients survive acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). The mean survival time for this disease, which predominantly occurs in the elderly, is less than a year for patients over 65 years. It is assumed that leukaemic stem cells, which cannot be completely eliminated during treatment, are the origin of relapse. However, as has been discovered by a team of Frankfurt-based researchers, these cells do have a weakness: In the current edition of the high impact journal "Cancer Research", they report that the enzyme ...
Very early treatment may be key to combatting inherited metabolic disorder
2014-08-04
A European Journal of Neuroscience study suggests that it is critical to treat lysosomal storage disorders early, before symptoms arise. These genetic disorders, which are caused by the malfunction of enzymes that normally degrade various substances within cells, lead to numerous ailments including neurological problems.
Although few therapeutic options are available, clinical trials of treatments including lysosomal enzyme replacement are underway. Researchers who used enzyme replacement to treat mice with early, mid- and later-stages of a lysosomal storage disease found ...
Maternal singing during skin-to-skin contact benefits both preterm infants and their mothers
2014-08-04
A mother who sings to her preterm infant while providing 'kangaroo care,' or holding with direct skin-to-skin contact, may see improvements in both her child's and her own health. The finding comes from an Acta Paediatrica study of 86 mother-infant pairs in a neonatal intensive care unit in Meir Hospital in Israel.
Compared with preterm infants whose mothers just held them with direct skin-to-skin contact but did not sing, infants whose mothers both held them and sang to them had improved heart rate variability patterns. This combined effect of holding and singing also ...
Inadequately managed allergies cause significant economic burden in Europe
2014-08-04
New research indicates that avoidable indirect costs per patient insufficiently treated for allergy equal 2,405.00 Euros per year due to absence from work and reduced working capacity. On the other hand, appropriate therapy is available at an average cost of 125 Euros per patient annually, which represents only 5% of the cost of untreated disease.
"Between 55 and 151 billion Euros EU wide could be saved every year by better management of allergies," said Dr. Torsten Zuberbier, lead author of the Allergy study.
INFORMATION: END ...
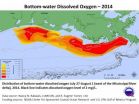
NOAA, EPA-supported scientists find average but large Gulf dead zone
2014-08-04
NOAA- and EPA-supported scientists have mapped the Gulf of Mexico dead zone, an area with low oxygen water, measuring 5,052 square miles this summer--approximately the size of the state of Connecticut. The measurements were taken during the 30th annual hypoxia survey cruise from July 27 to August 2.
This area falls within the predicted range of 4,633 to 5,708 square miles forecast by a suite of NOAA-sponsored models, and confirms the accuracy of the models and their utility for guiding management of nutrients in the Mississippi River watershed.
The size is smaller than ...
Eating baked or broiled fish weekly boosts brain health, Pitt study says
2014-08-04
PITTSBURGH, Aug. 4, 2014 – Eating baked or broiled fish once a week is good for the brain, regardless of how much omega-3 fatty acid it contains, according to researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. The findings, published online recently in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, add to growing evidence that lifestyle factors contribute to brain health later in life.
Scientists estimate that more than 80 million people will have dementia by 2040, which could become a substantial burden to families and drive up health care costs, noted senior ...
Media exposure and sympathetic nervous system reactivity predict PTSD symptoms in adolescents
2014-08-04
In a Depression and Anxiety study that surveyed youth following the terrorist attack at the 2013 Boston marathon, adolescents with lower levels of sympathetic reactivity (the flight or fight response) before the attack developed posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms only following high exposure to media coverage of the attack. Adolescents with high levels of sympathetic reactivity developed higher levels of PTSD symptoms regardless of how much media coverage they saw.
"This study tells us more about which children are most vulnerable to symptoms of PTSD and emphasizes ...
Most gay and bisexual men in the United States have used lubricants during sexual activity
2014-08-04
More than 90% of gay and bisexual men in the United States have used lubricants to enhance a wide range of sexual activities, including but not limited to anal intercourse, researchers report in a Journal of Sexual Medicine study.
By minimizing potential skin tears, lubricants may help reduce the likelihood of HIV transmission between partners.
Public health practitioners and clinicians may find the study's results useful in their efforts to incorporate lubricant use into sexual health promotion efforts. "These findings show the need for a new generation of sexual health ...
Survival increases with clinical team debriefing after in-hospital cardiac arrest
2014-08-04
A new study found that staff members who joined structured team debriefings after emergency care for children suffering in-hospital cardiac arrests improved their CPR performance and substantially increased the rates of patients surviving with favorable neurological outcomes.
The study team, at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP), said their research suggests that including all members of the intensive care unit (ICU) team, not just those immediately involved in the cardiac arrests, broadens learning and may improve compliance with standardized national guidelines ...
[1] ... [3397]
[3398]
[3399]
[3400]
[3401]
[3402]
[3403]
[3404]
3405
[3406]
[3407]
[3408]
[3409]
[3410]
[3411]
[3412]
[3413]
... [8788]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.