'Tailored' water -- the latest in lawn care
2014-07-11
In Santa Fe, Albuquerque, and other major cities in New Mexico, nearly every public golf course is now watered with treated municipal wastewater rather than precious potable water supplies. Across the U.S. Southwest as a whole, more than 40% of all golf courses receive treated effluent. Reusing the effluent increases the sustainability of golf courses.
Additionally, golf courses and homeowners alike fertilize their lawns during the growing season. The major nutrient in fertilizer is nitrate. A New Mexico State University turfgrass expert has a new vision for even more ...
Non-invasive test could be used to predict premature birth and delivery of small babies
2014-07-11
Testing for the presence of specific molecules present in the urine of pregnant women can give an indication in early pregnancy of whether a baby will be born premature or the fetus will suffer poor growth, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Medicine. Identifying these conditions early in pregnancy could potentially help reduce complications and manage any difficulties, although more work is needed before the findings can be translated to clinical settings.
Researchers from Imperial College London and the University of Crete analyzed the metabolites ...
Women under-represented in academic medicine
2014-07-11
Women are under-represented in academic medicine resulting in a waste of public investment due to loss of research talent. Writing in the July issue of the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, authors of an essay on women and academic medicine say that as a consequence of female under-representation, some areas of medicine are under-researched at a cost to patients and society. Discriminatory practices and unconscious bias, they say, continue to occur in academic medicine, despite a substantial fall in traditional discrepancies between men and women in medicine in ...
Heart health benefits of light drinking brought into question
2014-07-11
A reduction in alcohol consumption, even for light-to-moderate drinkers, could be linked to improved cardiovascular health, including a reduced risk of coronary heart disease, lower body mass index and blood pressure, according to new research published in The BMJ.
These latest findings challenge the results of previous observational studies which found that the consumption of light-to-moderate amounts of alcohol (12-25 units per week) may have a protective effect on cardiovascular health.
The research, led by the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine with University ...
Injected vaccine could help eradicate polio
2014-07-11
Re-introducing a type of polio vaccine that fell out of favour in the 1960s could hasten eradication of the disease, according to new research.
The study, by Imperial College London and the Christian Medical College in Vellore, India, suggests that the injected polio vaccine (IPV), which is rarely used today in countries affected by polio, could provide better and longer lasting protection against infection if used in combination with the more commonly used live oral polio vaccine (OPV).
The findings are published today in The Lancet.
Vaccination protects an individual ...
The Lancet: World's most advanced dengue vaccine candidate shows promise in phase 3 trial
2014-07-11
The first dengue vaccine candidate (CYD-TDV) to reach phase 3 clinical testing has shown moderate protection (56%) against the disease in Asian children, according to new research published in The Lancet.
Dengue is a mosquito-borne disease that infects around 390 million people each year, of whom about 96 million suffer from symptomatic infection. WHO estimates that the global burden of dengue has risen 30-fold over the past 50 years, with over half of the world's population at risk of the disease.
There is no licensed vaccine available to treat or prevent dengue ...
The Lancet: Extra dose of inactivated polio vaccine boosts immunity in children and could speed up global eradication efforts
2014-07-11
Giving children under 5 years old an extra dose of inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) helps to boost their immunity to the poliovirus and should be added to vaccination programmes in polio-endemic countries and those facing a high risk of imported cases, suggests new research published in The Lancet.
Lead author Dr Jacob John from Christian Medical College, India explains, "Adding a supplementary IPV dose to children already vaccinated with oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) may hasten polio eradication by boosting herd immunity in endemic regions, act as a booster to prevent ...
The Lancet: Novel treatment for drug-resistant tuberculosis shows promise, but concerns for patient safety remain
2014-07-11
In a viewpoint published this week in The Lancet, the Community Research Advisors Group (CRAG) argue that research into bedaquiline – a new drug, fast tracked for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) – should proceed cautiously in people with drug-sensitive tuberculosis. CRAG, an international, community-based advisory board for the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Tuberculosis Trials Consortium, writing in The Lancet independently, urge researchers to balance the goal of shortening treatment for drug-sensitive TB with patient safety.
Bedaquiline ...
Cost of expensive medication in dialysis catheters may be offset by reduced complications
2014-07-11
Washington, DC (July 10, 2014) — Using an expensive agent to prevent blood clots in kidney failure patients' dialysis catheters may turn out to be less costly overall due to its ability to reduce medical complications, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN).
Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) is a medication used to break up blood clots that occur in the vessels of patients having a heart attack. A recent clinical trial revealed that using rt-PA once per week plus the anticlotting agent ...
High stress, hostility, depression linked with increased stroke risk
2014-07-10
Higher levels of stress, hostility and depressive symptoms are associated with significantly increased risk of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) in middle-age and older adults, according to new research in the American Heart Association journal Stroke.
A TIA is a stroke caused by a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain.
Researchers investigated how psychological factors might influence risk for chronic disease, using data from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), an ongoing study on cardiovascular disease risk factors in participants living ...
After a concussion, which teens will have emotional symptoms?
2014-07-10
CHICAGO – After a concussion, teens who are sensitive to light or noise may be more likely to also have emotional symptoms such as anxiety, according to a study released today that will be presented at The Sports Concussion Conference in Chicago, July 11 to 13, 2014, hosted by the American Academy of Neurology, the world's leading authority on diagnosing and managing sports concussion. The conference will feature the latest scientific advances in diagnosing and treating sports concussion from leading experts in the field.
The symptoms after a concussion can vary widely ...
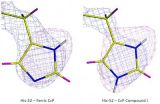
Neutron crystallography solves long-standing biological mystery
2014-07-10
The controversy centres around a family of enzymes known as heme enzymes, due to the presence of a heme group in their active site. At the centre of the heme cofactor is an iron (Fe) atom, which becomes oxidised (ferryl) when a reacting heme is in an intermediate state called Compound I. The question that has remained unanswered for decades is whether this oxidation involves just an oxygen atom (O), or a hydroxyl group (OH). Resolving this fundamental question has implications for understanding oxidative processes within living cells, which is critically important for drug ...
Astronomers find 7 dwarf galaxies with new telescope
2014-07-10
Meet the seven new dwarf galaxies.
Yale University astronomers, using a new type of telescope made by stitching together telephoto lenses, recently discovered seven celestial surprises while probing a nearby spiral galaxy. The previously unseen galaxies may yield important insights into dark matter and galaxy evolution, while possibly signaling the discovery of a new class of objects in space.
For now, scientists know they have found a septuplet of new galaxies that were previously overlooked because of their diffuse nature: The ghostly galaxies emerged from the night ...
Study provides new approach to forecast hurricane intensity
2014-07-10
VIDEO:
This is the one-of-a-kind, Alfred C. Glassell, Jr., SUSTAIN research facility at the UM Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, where Haus and colleagues will conduct further studies on...
Click here for more information.
MIAMI – New research from University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science suggests that physical conditions at the air-sea interface, where the ocean and atmosphere meet, is a key component to improve forecast ...
Extinct sea scorpion gets a Yale eye exam, with surprising results
2014-07-10
Poor peepers are a problem, even if you are a big, bad sea scorpion.
One minute, you're an imperious predator, scouring the shallow waters for any prey in sight. The next, thanks to a post-extinction eye exam by Yale University scientists, you're reduced to trolling for weaker, soft-bodied animals you stumble upon at night.
Such is the lot of the giant pterygotid eurypterid, the largest arthropod that ever lived. A new paper by Yale paleontologists, published in the journal Biology Letters, dramatically re-interprets the creature's habits, capabilities, and ecological ...
Despite setback, 'Mississippi Baby' represents significant breakthrough in effort to end AIDS
2014-07-10
Washington, D.C.—July 10, 2014—In response to today's announcement that the "Mississippi Baby," believed to have been functionally cured of HIV, has now been found to have detectable levels of the virus, the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation (EGPAF) expresses disappointment in this setback but remains hopeful that the scientific breakthrough that allowed the child's HIV levels to remain undetectable for more than two years will continue to help researchers understand how to control HIV and ultimately develop a cure.
"Although we had high hopes that the child ...
Hubble spots spiral bridge of young stars linking two ancient galaxies
2014-07-10
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has photographed an unusual structure 100,000 light years long, which resembles a corkscrew-shaped string of pearls and winds around the cores of two colliding galaxies.
The unique structure of the star spiral may yield new insights into the formation of stellar superclusters that result from merging galaxies and gas dynamics in this rarely seen process.
"We were surprised to find this stunning morphology. We've long known that the 'beads on a string' phenomenon is seen in the arms of spiral galaxies and in tidal bridges between interacting ...
Active shooter training increases comfort level of emergency responders
2014-07-10
(Boston) – Emergency Medical Service (EMS) responders felt better prepared to respond to an active shooter incident after receiving focused tactical training according to a new study in the journal Prehospital and Disaster Medicine. This is the first study to specifically examine the EMS provider comfort level with respect to entering a scene where a shooter has not yet been neutralized or working with law enforcement personnel during that response.
Incidents such as the Columbine High School shooting, the Virginia Tech campus shooting, the 2009 Fort Hood shooting, the ...
Scorpions are master architects, according to new research from Ben-Gurion University
2014-07-10
BEER-SHEVA, Israel – Ben-Gurion University of the Negev scientists have discovered that scorpions create a platform in their burrows where they warm up before the evening hunt.
As ectothermic animals, scorpions rely on energy from the environment to regulate
their internal temperature. The researchers believe that this platform provides a safe, warm spot for the scorpions to increase their body temperature before they leave their hiding places to forage at night.
After trapping the wild large-clawed scorpions (Scorpio maurus palmatus) in Israel's Negev desert the ...
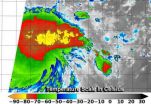
NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite sees power within newborn Tropical Depression 09W
2014-07-10
As the Northwestern Pacific is bidding goodbye to Tropical Cyclone Neoguri, another tropical depression has formed. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Depression 09W (TD09W) and captured infrared data on the storm indicating some powerful thunderstorms within.
Because TD09W is close to land areas, watches are already in effect. On July 10, a tropical storm watch is in force for Guam, Rota, Tinian and Saipan.
Tropical depression 09W was formerly known as low pressure System 92W. VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite taken July 10 at ...
Scripps Florida scientists shed new light on nerve cell growth
2014-07-10
JUPITER, FL, July 10, 2014 – Amidst the astounding complexity of the billions of nerve cells and trillions of synaptic connections in the brain, how do nerve cells decide how far to grow or how many connections to build? How do they coordinate these events within the developing brain?
In a new study, scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have shed new light on these complex processes, showing that a particular protein plays a far more sophisticated role in neuron development than previously thought.
The study, published in the journal ...
On the link between periodontitis and atherosclerosis
2014-07-10
Chronic oral infection with the periodontal disease pathogen, Porphyromonas gingivalis, not only causes local inflammation of the gums leading to tooth loss but also is associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis. A study published on July 10th in PLOS Pathogens now reveals how the pathogen evades the immune system to induce inflammation beyond the oral cavity.
Like other gram-negative bacteria, P. gingivalis has an outer layer that consists of sugars and lipids. The mammalian immune system has evolved to recognize parts of this bacterial coating, which then ...
New research finds ocean's most abundant organisms have clear daily cycles
2014-07-10
Imagine the open ocean as a microbial megacity, teeming with life too small to be seen. In every drop of water, hundreds of types of bacteria can be found. Now scientists have discovered that communities of these ocean microbes have their own daily cycles—not unlike the residents of a bustling city who tend to wake up, commute, work, and eat at the same times.
What's more, it's not all about the sun. Light-loving photoautotrophs—bacteria that need solar energy to help them photosynthesize food from inorganic substances—have been known to sun themselves on a regular schedule. ...
Window of opportunity against HIV comes from 'fitness bottleneck'
2014-07-10
New research on HIV transmission shows that viral fitness is an important basis of a "genetic bottleneck" imposed every time a new person is infected. The findings define a window of opportunity for drugs or vaccines to prevent or limit infection.
HIV represents evolution on overdrive. Every infected individual contains a swarm of viruses that exhibit variability in their RNA sequence, and new mutations are constantly appearing. Yet nearly every time someone new is infected, this diverse population of viruses gets squeezed down to just one individual.
The genetic bottleneck ...
Study points to potential new target for antibiotics against E. coli, other bugs
2014-07-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have identified a protein that is essential to the survival of E. coli bacteria, and consider the protein a potential new target for antibiotics.
In the study, the researchers confirmed that this protein, called MurJ, flips a fatty molecule from one side of a bacterial cell membrane to the other. If that molecule isn't flipped, the cell cannot construct a critical layer that keeps pressurized contents of the cell contained. If those contents aren't contained, the cell bursts.
E. coli is part of the gram-negative family of bacteria, characterized ...
[1] ... [3494]
[3495]
[3496]
[3497]
[3498]
[3499]
[3500]
[3501]
3502
[3503]
[3504]
[3505]
[3506]
[3507]
[3508]
[3509]
[3510]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.