Analysis finds mixed results for use of thrombolytic therapy for blood clot in lungs
2014-06-17
In an analysis that included data from 16 trials performed over the last 45 years, among patients with pulmonary embolism, receipt of therapy to dissolve the blood clot (thrombolysis) was associated with lower rates of death, but increased risks of major bleeding and intracranial hemorrhage, according to a study in the June 18 issue of JAMA. The authors note that these findings may not apply to patients with low-risk pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary embolism (PE; a blockage of the main artery of the lung or one of its branches) is an important cause of illness and death, ...
Survey suggests that self-reported health of young adults has improved
2014-06-17
Findings of a large survey indicate that since 2010, when young adults could be covered under their parents' health insurance plans until age 26, self-reported health among this group has improved, along with a decrease in out-of-pocket health care expenditures, according to a study in the June 18 issue of JAMA.
Beginning September 23, 2010, the Affordable Care Act allowed young adults to be covered under their parents' plans until 26 years of age. This dependent coverage provision increased insurance coverage and access among young adults. However, little is known about ...
TNF inhibitors for treatment of bowel disease not linked with increased risk of cancer
2014-06-17
In a study that included more than 56,000 patients with inflammatory bowel disease, use of a popular class of medications known as tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists was not associated with an increased risk of cancer over a median follow-up of 3.7 years, although an increased risk of malignancy in the long term, or with increasing number of doses, cannot be excluded, according to a study in the June 18 issue of JAMA.
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) antagonists are drugs that have been shown to be beneficial in reducing the inflammation in inflammatory ...
Study compares survival for treatments of uncommon eye cancer
2014-06-17
In patients with advanced uveal melanoma, treatment with the agent selumetinib, compared with chemotherapy, resulted in an improved cancer progression-free survival time and tumor response rate, but no improvement in overall survival, according to a study in the June 18 issue of JAMA. The modest improvement in clinical outcomes was accompanied by a high rate of adverse events.
Uveal melanoma arises from melanocytes within the choroid layer of the eye. There are about 1,500 new cases of uveal melanoma per year in the U.S., which is biologically distinct from skin related ...
'Trophy wife' stereotype is largely a myth, new study shows
2014-06-17
Don't be so quick to judge.
Most people are familiar with the "trophy wife" stereotype that attractive women marry
rich men, placing little importance on their other traits, including physical appearance,
and that men look for pretty wives but don't care about their education or earnings.
New research, however, by University of Notre Dame Sociologist Elizabeth McClintock,
shows the trophy wife stereotype is largely a myth fueled by selective observation that
reinforces sexist stereotypes and trivializes women's careers.
In "Beauty and Status: The Illusion ...
Move over, silicon, there's a new circuit in town
2014-06-17
When it comes to electronics, silicon will now have to share the spotlight. In a paper recently published in Nature Communications, researchers from the USC Viterbi School of Engineering describe how they have overcome a major issue in carbon nanotube technology by developing a flexible, energy-efficient hybrid circuit combining carbon nanotube thin film transistors with other thin film transistors. This hybrid could take the place of silicon as the traditional transistor material used in electronic chips, since carbon nanotubes are more transparent, flexible, and can be ...
Anonymous peer feedback through social networking helped residents improve their skills
2014-06-17
Surgical residents who received anonymous feedback from their peers through a social networking site on their robotic surgery skills improved more than those who did not receive any peer feedback on their procedures, UCLA researchers found.
The study is the first to examine the use of social networking to facilitate peer review of surgical procedure videos, said senior author Dr. Jim Hu, UCLA's Henry E. Singleton Professor of Urology and director of robotic and minimally invasive surgery in the urology department at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
The study ...
Death by prescription painkiller
2014-06-17
The number of deaths involving commonly prescribed painkillers is higher than the number of deaths by overdose from heroin and cocaine combined, according to researchers at McGill University. In a first-of-its-kind review of existing research, the McGill team has put the spotlight on a major public health problem: the dramatic increase in deaths due to prescribed painkillers, which were involved in more than 16,000 deaths in 2010 in the U.S. alone. Currently, the US and Canada rank #1 and #2 in per capita opioid consumption.
"Prescription painkiller overdoses have received ...
Former athletes finish first in race for top jobs
2014-06-17
ITHACA, N.Y. – Whether you were a quarterback or point guard, past participation in competitive team sports marks you as a winner in the competition for better jobs, according to a new Cornell University study.
"Participation in competitive youth sports 'spills over' to occupationally advantageous traits that persist across a person's life," says Kevin M. Kniffin, postdoctoral research associate at Cornell's Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management and lead researcher.
Research by Kniffen and his co-authors, published online this week in the Journal of Leadership ...
3-D breast imaging could revolutionize cancer screening
2014-06-17
Leesburg, VA, June 17, 2014—In community-based radiology practice, mammography screening with 3D digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) yielded lower recall rates, an increased overall cancer detection rate, and an increased detection rate for invasive cancer compared with 2D digital mammography (DM).
In the largest report to date, researchers at Washington Radiology Associates, PC, with offices in Washington, DC; Virginia; and Maryland, conducted a study of more than 59,000 patients. The results were striking: an increase in the detection rate for cancer overall of 28.6% ...
Hyperthyroidism patients more likely to take extended sick leave than healthy peers
2014-06-17
Washington, DC—People who have hyperthyroidism are more likely to take sick leave for extended periods than their healthy colleagues, particularly in the first year after diagnosis, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is overactive. The thyroid, which is located in the front of the neck, secretes hormones that regulate how the body uses energy, consumes oxygen and produces heat.
The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease, ...
Pitt psychology researchers explore how engineers create
2014-06-17
PITTSBURGH—Simply put, engineers make things. But is finding that "new" invention a massive mental leap from point A to point B, or are there scores of unnoticed intermediate steps in between?
The University of Pittsburgh's Joel Chan and Christian Schunn say that not enough has been done to understand how engineers create. Understanding the process, they say, may provide a road map for speeding up innovation.
Chan, a graduate student in psychology in Pitt's Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences, and his mentor Schunn, a professor of psychology as well as a ...
Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived value
2014-06-17
Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived value among patients, new study says
TORONTO, June 17, 2014—Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling tests heightened their perceived importance among patients with early breast cancer who were deciding whether to have chemotherapy, a new study says.
Gene expression profiling tests, such as Oncotype Dx, analyze the patterns of 21 different genes within cancer cells to help predict how likely it is that a women's cancer will recur within 10 years after initial treatment and how beneficial ...
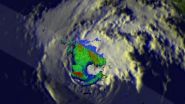
TRMM eyes rainfall in dissipating former Hurricane Cristina
2014-06-17
VIDEO:
On June 14, NASA's TRMM satellite found rain falling at a rate of almost 97 mm (about 3.8 inches) per hour in the northwestern side of Cristina's eye wall where...
Click here for more information.
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over a dissipating former Hurricane Cristina and found it still contained heavy rain as it rapidly weakened.
Hurricane Cristina had sustained winds of over 130 ...
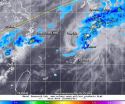
Tropical depression Hagibis gets a second chance
2014-06-17
Tropical Depression Hagibis appeared out for the count when it made landfall along southeastern China on June 16, but moved back into the South China Sea where it regenerated and sped northeast through the East China Sea. The next day, the TRMM satellite noticed power had come back to Hagibis in the form of some moderate rainfall in the depression's northeastern quadrant.
On June 17 at 10:30 UTC (6:30 a.m. EDT) the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over the regenerated Hagibis and the Precipitation Radar instrument gathered data on the storm's ...
Sleep education program spurs preschoolers to snooze 30 minutes longer at night
2014-06-17
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Taking part in an educational sleep program resulted in a 30-minute average increase in sleep duration at a one-month follow-up for preschoolers, according to a new study from the University of Michigan.
In the study, published in the journal SLEEP, families in two Head Start programs participated in the Sweet Dreamzzz Early Childhood Sleep Education Program™. The Detroit-area nonprofit organization, Sweet Dreamzzz, Inc. developed the program and offers it for free when funding allows. Head Start programs aim to give preschool opportunities to low-income ...
Dynamic spectroscopy duo
2014-06-17
From allowing our eyes to see, to enabling green plants to harvest energy from the sun, photochemical reactions – reactions triggered by light – are both ubiquitous and critical to nature. Photochemical reactions also play essential roles in high technology, from the creation of new nanomaterials to the development of more efficient solar energy systems. Using photochemical reactions to our best advantage requires a deep understanding of the interplay between the electrons and atomic nuclei within a molecular system after that system has been excited by light.
A major ...
Why species matter
2014-06-17
UC Santa Barbara doctoral candidate Caitlin Fong travels to French Polynesia often but not for vacation. She goes there to study a coral reef ecosystem influenced by human impacts such as overfishing and nutrient pollution.
Her work focuses not only on biological changes but also methods scientists use to determine within-group group responses to ecological processes. The findings are published in ESA Ecology, a journal of the Ecological Society of America.
Fong and Peggy Fong, a professor in UCLA's Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, conducted a study assessing ...
Not so fast -- our fishy friends can also feel pain
2014-06-17
Do you still believe that fish are dumb and cannot feel pain? That we do not have to worry much about how they are cared for or caught? Think again, says Culum Brown of Macquarie University in Australia, in a review article in Springer's journal Animal Cognition. The research notes that fish cognition and their sensory perception are generally on par with that of other animals. Brown therefore argues that more consideration should be given to fish welfare and anti-cruelty issues.
The Australian researcher says that most people rarely think about fish other than as food, ...
$2.4 million NIH center grant to develop a cleaner, healthier environment in Detroit
2014-06-17
DETROIT — With over $2.4 million in new federal funding, Wayne State University researchers, regional collaborators at Henry Ford Health System, the University of Michigan and Michigan State University, and community partners will study how exposures to stressors that are prevalent in the urban industrialized environment — both chemical and non-chemical — impact human health in Detroit and beyond.
The grant, Center for Urban Responses to Environmental Stressors (CURES), is one of approximately 20 select P30 Core Centers funded by the National Institute of Environmental ...
Do 'walkable' neighborhoods reduce obesity, diabetes?
2014-06-17
June 17, 2014 (San Francisco) – People who live in neighborhoods that are conducive to walking experienced a substantially lower rate of obesity, overweight and diabetes than those who lived in more auto-dependent neighborhoods, according to a pair of studies presented at the American Diabetes Association's 74th Scientific Sessions®.
Researchers in Canada compared adults living in the most and least "walkable" metropolitan areas in southern Ontario and found a lower risk of developing diabetes over a 10-year period for those who lived in neighborhoods with less sprawl, ...
Heparin derivative suppresses neuroblastoma tumor growth
2014-06-17
DURHAM, N.C. -- Researchers at Duke Medicine have identified a new strategy for treating neuroblastoma using a modified version of heparin, a century-old injectable drug that thins the blood to prevent clots from forming.
The study, conducted in mice and published June 17, 2014, in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, found that when heparin is altered to remove its blood-thinning properties, it can suppress and shrink neuroblastoma tumors without causing severe bleeding.
"Our research translates mechanistic insights about heparin into a potential new therapy for ...
Urban Water Management Workshop stresses more collaboration and innovation
2014-06-17
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Where sustainability of water management is concerned, we must pay more attention to long-term solutions. Efficient water management and policy ought to be promoted at the local level. And a "portfolio approach" to water management is encouraged, one that includes information campaigns, different types of pricing, supply and reuse options, and technology-based rebate programs.
These are some of the key messages that emerged from the first Urban Water Management Workshop that took place earlier this month at the University of California, Riverside.
Sponsored ...
Swell new sensors
2014-06-17
WASHINGTON D.C., June 17, 2014 – Using microscopic polymer light resonators that expand in the presence of specific gases, researchers at MIT's Quantum Photonics Laboratory have developed new optical sensors with predicted detection levels in the parts-per-billion range. Optical sensors are ideal for detecting trace gas concentrations due to their high signal-to-noise ratio, compact, lightweight nature, and immunity to electromagnetic interference.
Although other optical gas sensors had been developed before, the MIT team conceived an extremely sensitive, compact way ...
Ultra-thin wires for quantum computing
2014-06-17
WASHINGTON D.C., June 17, 2014 - Take a fine strand of silica fiber, attach it at each end to a slow-turning motor, gently torture it over an unflickering flame until it just about reaches its melting point and then pull it apart. The middle will thin out like a piece of taffy until it is less than half a micron across -- about 200 times thinner than a human hair.
That, according to researchers at the Joint Quantum Institute at the University of Maryland, is how you fabricate ultrahigh transmission optical nanofibers, a potential component for future quantum information ...
[1] ... [3544]
[3545]
[3546]
[3547]
[3548]
[3549]
[3550]
[3551]
3552
[3553]
[3554]
[3555]
[3556]
[3557]
[3558]
[3559]
[3560]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.