Architecture of signaling proteins enhances knowledge of key receptors
2014-06-22
DURHAM, N.C. -- A team of scientists from Duke Medicine, the University of Michigan and Stanford University has determined the underlying architecture of a cellular signaling complex involved in the body's response to stimuli such as light and pain.
This complex, consisting of a human cell surface receptor and its regulatory protein, reveals a two-step mechanism that has been hypothesized previously but not directly documented.
The findings, reported on June 22, 2014, in the journal Nature, provide structural images of a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) in action.
"It ...
Study shows greater potential for solar power
2014-06-22
Concentrating solar power (CSP) could supply a large fraction of the power supply in a decarbonized energy system, shows a new study of the technology and its potential practical application.
Concentrating solar power (CSP) could supply a substantial amount of current energy demand, according to the study published in the journal Nature Climate Change. In the Mediterranean region, for example, the study shows that a connected CSP system could provide 70-80% of current electricity demand, at no extra cost compared to gas-fired power plants. That percentage is similar to ...
Microenvironment of hematopoietic stem cells can be a target for myeloproliferative disorders
2014-06-22
The discovery of a new therapeutic target for certain kinds of myeloproliferative disease is, without doubt, good news. This is precisely the discovery made by the Stem Cell Physiopathology group at the CNIC (the Spanish National Cardiovascular Research Center), led by Dr. Simón Méndez–Ferrer. The team has shown that the microenvironment that controls hematopoietic stem cells can be targeted for the treatment of a set of disorders called myeloproliferative neoplasias, the most prominent of which are chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia ...
Family of proteins plays key role in cellular pump dynamics
2014-06-22
Case Western Reserve University scientists have discovered how a family of proteins — cation diffusion facilitators (CDFs) — regulates an important cellular cycle where a cell's energy generated is converted to necessary cellular functions. The finding has the potential to inform future research aimed at identifying ways to ensure the process works as designed and, if successful, could lead to significant breakthroughs in the treatment of Parkinson's, chronic liver disease and heart disease.
The results of this research were posted online June 22 by the journal Nature ...
Evidence found for the Higgs boson direct decay into fermions
2014-06-22
For the first time, scientists from the CMS experiment on the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN have succeeded in finding evidence for the direct decay of the Higgs boson into fermions. Previously, the Higgs particle could only be detected through its decay into bosons. "This is a major step forwards," explains Professor Vincenzo Chiochia from the University of Zurich's Physics Institute, whose group was involved in analyzing the data. "We now know that the Higgs particle can decay into both bosons and fermions, which means we can exclude certain theories predicting that ...
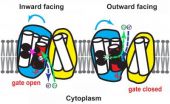
Protons power protein portal to push zinc out of cells
2014-06-22
Researchers at The Johns Hopkins University report they have deciphered the inner workings of a protein called YiiP that prevents the lethal buildup of zinc inside bacteria. They say understanding YiiP's movements will help in the design of drugs aimed at modifying the behavior of ZnT proteins, eight human proteins that are similar to YiiP, which play important roles in hormone secretion and in signaling between neurons.
Certain mutations in one of them, ZnT8, have been associated with an increased susceptibility to type 2 diabetes, but mutations that destroy its function ...
Molecular footballs could revolutionize your next World Cup experience!
2014-06-22
This work focuses on the interactions between molecules and in particular on "amphiphilic" molecules, which contain two distinct parts to them. Household detergent is a good example of a product that relies on interacting amphiphilic molecules. Detergent molecules comprise two distinct parts: one that prefers to form bonds with water (hydrophilic) and the other that likes oily substances (hydrophobic). Detergents are used for cleaning because when they are added to dirty water, they orient and assemble around oily dirt, forming small clusters that allow grease and dirt ...
Antidepressant use during pregnancy may lead to childhood obesity and diabetes
2014-06-21
Hamilton, ON (June 21, 2014) - Women who take antidepressants during pregnancy may be unknowingly predisposing their infants to type 2 diabetes and obesity later in life, according to new research from McMaster University.
The study finds a correlation between the use of the medication fluoxetine
during pregnancy and an increased risk of obesity and diabetes in children.
Currently, up to 20 per cent of woman in the United States and approximately seven per cent of Canadian women are prescribed an antidepressant during pregnancy.
"Obesity and Type 2 diabetes in ...
Church-going is not enough to affect job satisfaction and commitment, Baylor study finds
2014-06-20
A congregation's beliefs about work attitudes and practices affect a churchgoer on the job — but how much depends in part on how involved that person is in the congregation, according to a Baylor University study funded by the National Science Foundation.
"We already knew that about 60 percent of American adults are affiliated with congregations, but we wanted to delve into whether that carries over from weekend worship services to the work day," said Jerry Z. Park, Ph.D., associate professor of sociology in Baylor's College of Arts & Sciences. "It turns out it does make ...
Beaumont research finds advanced CT scanners reduce patient radiation exposure
2014-06-20
Computed tomography scans are an accepted standard of care for diagnosing heart and lung conditions. But clinicians worry that the growing use of CT scans could be placing patients at a higher lifetime risk of cancer from radiation exposure.
Beaumont Health System research, published in the June 20 online issue of the Journal of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, found that the use of advanced CT scanning equipment is helping to address this important concern.
The study, of 2,085 patients at nine centers in the U.S. and Middle East, found that using newer generation, ...
Inner ear stem cells hold promise for restoring hearing
2014-06-20
New Rochelle, NY, June 20, 2014—Spiral ganglion cells are essential for hearing and their irreversible degeneration in the inner ear is common in most types of hearing loss. Adult spiral ganglion cells are not able to regenerate. However, new evidence in a mouse model shows that spiral ganglion stem cells present in the inner ear are capable of self-renewal and can be grown and induced to differentiate into mature spiral ganglion cells as well as neurons and glial cells, as described in an article in BioResearch Open Access, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, ...
Miriam Hospital researchers analyze AUDs, sexual behavior among South African men
2014-06-20
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – In a study of South African men who drink alcohol in informal drinking environments or "shebeens," researchers from The Miriam Hospital have found a high prevalence of Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) that directly correlates to unprotected sex. Findings support the need for interventions targeting both alcohol and HIV-risk behaviors among South African men who drink alcohol in alcohol-serving venues. The study and its findings are published in the July issue of Drug and Alcohol Dependence.
Lori A. Scott-Sheldon, Ph.D., lead author and researcher at The ...
Researchers find gene critical for development of brain motor center
2014-06-20
Ottawa – June 20, 2014 – In a report published today in Nature Communications, an Ottawa-led team of researchers describe the role of a specific gene, called Snf2h, in the development of the cerebellum. Snf2h is required for the proper development of a healthy cerebellum, a master control centre in the brain for balance, fine motor control and complex physical movements.
Athletes and artists perform their extraordinary feats relying on the cerebellum. As well, the cerebellum is critical for the everyday tasks and activities that we perform, such as walking, eating and ...
New study explains how organs coordinate their development with the whole body
2014-06-20
This news release is available in Portuguese. This news release is available in Portuguese. A research group led by Christen Mirth at Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (Portugal) uncovered that the development of wings in fruit flies does not progress synchronously with the organism's development. Instead, it is coordinated with the whole body only at distinct 'milestones'. This study, published in the latest issue of the scientific journal PLOS Genetics*, helps explain how an organism facing environmental and physiological perturbations retains the ability to build ...
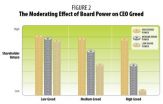
Greedy CEOs bad for business
2014-06-20
Yes, Virginia, there is greed. Greedy managers. Corporate greed. Greedy behavior. In fact, a web database search shows you can find such phrases in the business press over 18,000 times, confirming the subject's popularity in everyday media. But you need not fear greed, Virginia, because believe it or not, you can moderate it.
In a forthcoming article in the top-ranked Journal of Management, new research by University of Delaware assistant professor Katalin Takacs Haynes examines the effects of greed on shareholder wealth and looks at whether various contextual factors, ...
Children's Research Institute finds key to identifying, enriching mesenchymal stem cells
2014-06-20
DALLAS – June 20, 2014 – The Children's Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI) has identified a biomarker that enables researchers to accurately characterize the properties and function of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the body. MSCs are the focus of nearly 200 active clinical trials registered with the National Institutes of Health, targeting conditions such as bone fractures, cartilage injury, degenerative disc disease, and osteoarthritis.
The finding, published in the journal Cell Stem Cell on June 19, significantly advances the field of MSC ...
IOM: Effectiveness of PTSD treatments provided by DOD & VA unknown
2014-06-20
WASHINGTON -- The U.S. Department of Defense and U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs should track the outcomes of treatment for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) provided to service members and veterans and develop a coordinated and comprehensive strategy to do so, says a new congressionally mandated report from the Institute of Medicine. Without tracking outcomes, neither DOD nor VA knows whether it is providing effective or adequate PTSD care, for which they spent $294 million and more than $3 billion, respectively, in 2012. The report is the second of a two-phase ...
Researchers identify mitochondrial mutation linked to congenital myasthenic syndrome
2014-06-20
Amsterdam, NL, 20 June 2014 – Although significant progress has been made over the last 25 years to identify genetic abnormalities associated with congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS), many patients remain genetically undiagnosed. A report in the inaugural issue of the Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases identifies a gene defect in mitochondria, specifically the citrate carrier SLC25A1, that may underlie deficits in neuromuscular transmission seen in two siblings.
"While mitochondrial gene defects can cause a myriad of neurological disorders including myopathies and neuropathies, ...
Molecule regulates production of antibacterial agent used by immune cells
2014-06-20
Researchers have discovered how a protein molecule in immune cells promotes the production of nitric oxide, a potent weapon in the cells' arsenal to defend the body from bacterial attack. The protein may offer a target for reining in the inflammatory response, which must be able to fight infection without damaging tissue.
The study was published in the Journal of Innate Immunity.
NFATc3 is one of several related protein molecules known to play a role in regulating genes in the T and B cells of the immune system. Ravi Ranjan, research scientist at the University of Illinois ...
Benefits of PTSD treatment going unmeasured, says Institute of Medicine Report
2014-06-20
VIDEO:
IOM report out today demonstrates that the VA and US Department of Defense do not measure the effectiveness of treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder. Columbia University Mailman School of Public...
Click here for more information.
June 20, 2014 -- A report from the Institute of Medicine (IOM) finds that the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) and U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) do not measure the effectiveness of treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder ...
New research reveals that emperor penguins are more willing to relocate
2014-06-20
A new study led by the University of Minnesota offers new insights on the long-term future of emperor penguins by showing that the penguins may be behaving in ways that allow them to adapt to their changing environment better than we expected.
Researchers have long thought that emperor penguins were philopatric, which means they would return to the same location to nest each year. The new research study used satellite images to show that penguins may not be faithful to previous nesting locations.
Researchers involved in the new study found six instances in just three ...
No evidence of long-term PTSD risk in patients with awareness during surgery
2014-06-20
June 20, 2014 – Patients with confirmed episodes of awareness during anesthesia and surgery don't seem to be at increased risk of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or other problems with psychosocial well-being at long-term follow-up, reports a study in Anesthesia & Analgesia.
"We found no indication that intraoperative awareness with recall had any long-term effects on patients' psychosocial outcome," concludes the new research by Dr Tanja Laukkala of the Centre for Military Medicine in Helsinki, Finland. Anesthesiologists "should respond to the findings…with a ...
KIT researchers protect the princess from the pea
2014-06-20
This news release is available in German.
In the past years, invisibility cloaks were developed for various senses. Objects can be hidden from light, heat or sound. However, hiding of an object from being touched still remained to be accomplished. KIT scientists have now succeeded in creating a volume in which an object can be hidden from touching similar to a pea under the mattress of a princess. The results are now presented in the renowned Nature Communications journal.
Magicians and illusionists make things disappear by means of a skilled use of mental ...
Citing 'urgent, acute' mental health issues, especially in Africa, experts petition gov'ts to act
2014-06-20
Calling global mental health problems "acute and urgent," 37 leading medical authorities from 11 countries have published a joint declaration calling for basic mental health care in Africa.
The experts also call for global mental health objectives to be included among the United Nations' post-2015 Sustainable Development Goals, for a special UN General Assembly High Level Meeting on Mental Health by 2017, and for efforts to end the stigma and human rights violations inflicted on mental health patients.
Published in the journal Global Health Action, the declaration was ...
Menthol cigarettes linked to increased smoking among teens
2014-06-20
Teens who use menthol cigarettes smoke more cigarettes per day than their peers who smoke non-menthols, says a new study. The findings from the Propel Centre for Population Health Impact at the University of Waterloo mark the first time that menthol cigarettes have been directly linked to elevated nicotine addiction among youth in Canada.
"The appeal of menthol cigarettes among youth stems from the perception that they are less harmful than regular cigarettes. The minty taste helps mask the noxious properties, but the reality is that they are just as dangerous as any ...
[1] ... [3536]
[3537]
[3538]
[3539]
[3540]
[3541]
[3542]
[3543]
3544
[3545]
[3546]
[3547]
[3548]
[3549]
[3550]
[3551]
[3552]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.