Researchers: Obesity can amplify bone and muscle loss
2014-04-16
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. – Florida State University researchers have identified a new syndrome called "osteosarcopenic obesity" that links the deterioration of bone density and muscle mass with obesity.
"It used to be the thinking that the heavier you were the better your bones would be because the bones were supporting more weight," said Jasminka Ilich-Ernst, the Hazel Stiebeling Professor of Nutrition at Florida State. "But, that's only true to a certain extent."
The syndrome, outlined in the May issue of Ageing Research Reviews, explains how many obese individuals experience ...
Researchers develop a new drug to combat the measles
2014-04-16
A novel antiviral drug may protect people infected with the measles from getting sick and prevent them from spreading the virus to others, an international team of researchers says.
Scientists from the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University, the Emory Institute for Drug Development and the Paul-Ehrlich Institute in Germany developed the drug and tested it in animals infected with a virus closely related to one that causes the measles. As reported in the current issue of the journal Science Translational Medicine, virus levels were significantly ...
Celldex's Phase 1 study of CDX-1401 published in Science Translational Medicine
2014-04-16
HAMPTON, NJ (April 16, 2014): Celldex Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ: CLDX) announced today that final data from its Phase 1 study of CDX-1401 in solid tumors, including long-term patient follow-up, have been published in Science Translational Medicine (Vol 6 Issue 232). The data demonstrate robust antibody and T cell responses and evidence of clinical benefit in patients with very advanced cancers and suggest that CDX-1401 may predispose patients to better outcomes on subsequent therapy with checkpoint inhibitors. CDX-1401 is an off-the-shelf vaccine consisting of a fully ...
Meteorites yield clues to red planet's early atmosphere
2014-04-16
Geologists who analyzed 40 meteorites that fell to Earth from Mars unlocked secrets of the Martian atmosphere hidden in the chemical signatures of these ancient rocks. Their study, published April 17 in the journal Nature, shows that the atmospheres of Mars and Earth diverged in important ways very early in the 4.6 billion year evolution of our solar system.
The results will help guide researchers' next steps in understanding whether life exists, or has ever existed, on Mars and how water—now absent from the Martian surface—flowed there in the past.
Heather Franz, ...
Mutant protein in muscle linked to neuromuscular disorder
2014-04-16
Sometimes known as Kennedy's disease, spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA) is a rare inherited neuromuscular disorder characterized by slowly progressive muscle weakness and atrophy. Researchers have long considered it to be essentially an affliction of primary motor neurons – the cells in the spinal cord and brainstem that control muscle movement.
But in a new study published in the April 16, 2014 online issue of Neuron, a team of scientists at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine say novel mouse studies indicate that mutant protein levels ...
Study provides crucial new information about how the ice ages came about
2014-04-16
An international team of scientists has discovered new relationships between deep-sea temperature and ice-volume changes to provide crucial new information about how the ice ages came about.
Researchers from the University of Southampton, the National Oceanography Centre and the Australian National University developed a new method for determining sea-level and deep-sea temperature variability over the past 5.3 million years. It provides new insight into the climatic relationships that caused the development of major ice-age cycles during the past two million years.
The ...
Searching for dark energy with neutrons
2014-04-16
All the particles we know to exist make up only about five per cent of the mass and energy of the universe. The rest – "Dark Matter" and "Dark Energy" – remains mysterious. A European collaboration lled by researchers from the Vienna University of Technology has now carried out extremely sensitive measurements of gravitational effects at very small distances at the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL) in Grenoble. These experiments provide limits for possible new particles or fundamental forces, which are a hundred thousand times more restrictive than previous estimations.
Undiscovered ...
Ancient shark fossil reveals new insights into jaw evolution
2014-04-16
The skull of a newly discovered 325-million-year-old shark-like species suggests that early cartilaginous and bony fishes have more to tell us about the early evolution of jawed vertebrates—including humans—than do modern sharks, as was previously thought. The new study, led by scientists at the American Museum of Natural History, shows that living sharks are actually quite advanced in evolutionary terms, despite having retained their basic "sharkiness" over millions of years. The research is published today in the journal Nature.
"Sharks are traditionally thought to ...
Scientists re-define what's healthy in newest analysis for Human Microbiome Project
2014-04-16
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – As scientists catalog the trillions of bacteria found in every nook and cranny of the human body, a new look by the University of Michigan shows wide variation in the types of bacteria found in healthy people.
Based on their findings in today's
Nature, there is no single healthy microbiome. Rather each person harbors a unique and varied collection of bacteria that's the result of life history as well their interactions with the environment, diet and medication use.
"Understanding the diversity of community types and the mechanisms that result ...
Sperm meets egg: Protein essential for fertilization discovered
2014-04-16
Researchers at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute have discovered interacting proteins on the surface of the sperm and the egg essential to begin mammalian life. These proteins, which allow the sperm and egg to recognize one another, offer new paths towards improved fertility treatments and the development of new contraceptives.
Fertilisation occurs when an egg and a sperm recognise each other and fuse together to form an embryo. The Izumo protein displayed on the sperm that recognises the egg was identified in 2005 by Japanese researchers who named it Izumo, after a ...
Hide and seek: Revealing camouflaged bacteria
2014-04-16
A research team at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel has discovered an protein family that plays a central role in the fight against the bacterial pathogen Salmonella within the cells. The so called interferon-induced GTPases reveal and eliminate the bacterium's camouflage in the cell, enabling the cell to recognize the pathogen and to render it innocuous. The findings are published in the current issue of the science magazine Nature.
Bacteria have developed countless strategies to hide themselves in order to evade attack by the immune system. In the body, Salmonella ...
Why your nose can be a pathfinder
2014-04-16
Waves in your brain make smells stick to your memories and inner maps.
When I was a child I used to sit in my grandfather's workshop, playing with wood shavings. Freshly shaven wood has a distinct smell of childhood happiness, and whenever I get a whiff of that scent my brain immediately conjures up images of my grandfather at his working bench, the heat from the fireplace and the dog next to it.
Researchers at the Kavli Institute for Systems Neuroscience have recently discovered the process behind this phenomenon. The brain, it turns out, connects smells to memories ...
Rice U. study: Performance measures for CEOs vary greatly
2014-04-16
HOUSTON – (April 16, 2014) – As companies file their annual proxy statements with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) this spring, a new study by Rice University and Cornell University shows just how S&P 500 companies have tied CEO compensation to performance. The study found large variations in the choice of performance measures, and the researchers said that companies tend to choose measures that are informative of CEO actions.
"On average, firms rely mostly on accounting-based performance measures, among which they put heavier weights on income measures, ...
Progress in the fight against quantum dissipation
2014-04-16
Scientists at Yale have confirmed a 50-year-old, previously untested theoretical prediction in physics and improved the energy storage time of a quantum switch by several orders of magnitude. They report their results in the April 17 issue of the journal Nature.
High-quality quantum switches are essential for the development of quantum computers and the quantum internet — innovations that would offer vastly greater information processing power and speed than classical (digital) computers, as well as more secure information transmission.
"Fighting dissipation is one ...
Why interest is crucial to your success
2014-04-16
DURHAM, N.C. -- Maintaining an interest in the goals you pursue can improve your work and reduce burnout, according to research from Duke University.
"Our research shows that interest is important in the process of pursuing goals. It allows us to perform at high levels without wearing out," said Paul O'Keefe, who conducted the studies as a doctoral student in Duke University's Department of Psychology & Neuroscience, along with associate professor Lisa Linnenbrink-Garcia. "This suggests that interest matters more than we suspected."
The studies, which appear online ...
Dartmouth-led study shows air temperature influenced African glacial movements
2014-04-16
Changes in air temperature, not precipitation, drove the expansion and contraction of glaciers in Africa's Rwenzori Mountains at the height of the last ice age, according to a Dartmouth-led study funded by the National Geographic Society and the National Science Foundation.
The results – along with a recent Dartmouth-led study that found air temperature also likely influenced the fluctuating size of South America's Quelccaya Ice Cap over the past millennium -- support many scientists' suspicions that today's tropical glaciers are rapidly shrinking primarily because of ...
Scientists unlock secrets of protein produced by disease-causing fungus
2014-04-16
SAN ANTONIO, Texas (April 16, 2014) — A team that includes scientists from the School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, Johns Hopkins University and St. Mary's University reported the structure of a protein that helps a common fungus to infect the body.
The fungal pathogen Candida albicans causes yeast infections, diaper rashes and oral thrush, and is the most common fungal pathogen to infect humans. It can also cause a life-threatening infection of the blood called disseminated candidiasis.
"In this study, we determined the ...
Vanderbilt researchers discover how intestinal cells build nutrient-absorbing surface
2014-04-16
The "brush border" – a densely packed array of finger-like projections called microvilli – covers the surfaces of the cells that line our intestines.
Vanderbilt University researchers have now discovered how intestinal cells build this specialized structure, which is critical for absorbing nutrients and defending against pathogens. The findings, published April 10 in the journal Cell, reveal a role for adhesion molecules in brush border assembly and increase our understanding of intestinal pathologies associated with inherited and infectious diseases.
Pathogens that destroy ...
Surveillance colonoscopy recommendations for average-risk patients with 1 to 2 small polyps consistent with guidelines
2014-04-16
DOWNERS GROVE, Ill. – April 16, 2014 – According to a new study, endoscopists' recommendations for timing of surveillance colonoscopy in average-risk patients with one to two small polyps are consistent with guideline recommendations in about 90 percent of cases. This may be an appropriate target for quality indicators. This is the first multicenter endoscopic database study to quantify adherence to guidelines for timing of repeat colonoscopy after one to two small polyps are found during screening colonoscopy in average-risk patients. The study appears in the April issue ...
Scientists capture ultrafast snapshots of light-driven superconductivity
2014-04-16
A new study pins down a major factor behind the appearance of superconductivity—the ability to conduct electricity with 100 percent efficiency—in a promising copper-oxide material.
Scientists used carefully timed pairs of laser pulses at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory's Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) to trigger superconductivity in the material and immediately take x-ray snapshots of its atomic and electronic structure as superconductivity emerged.
They discovered that so-called "charge stripes" of increased electrical charge melted away as superconductivity ...
Eavesdropping on brain cell chatter
2014-04-16
Everything we do — all of our movements, thoughts and feelings – are the result of neurons talking with one another, and recent studies have suggested that some of the conversations might not be all that private. Brain cells known as astrocytes may be listening in on, or even participating in, some of those discussions. But a new mouse study suggests that astrocytes might only be tuning in part of the time — specifically, when the neurons get really excited about something. This research, published in Neuron, was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders ...
How kids' brain structures grow as memory develops
2014-04-16
Our ability to store memories improves during childhood, associated with structural changes in the hippocampus and its connections with prefrontal and parietal cortices. New research from UC Davis is exploring how these brain regions develop at this crucial time. Eventually, that could give insights into disorders that typically emerge in the transition into and during adolescence and affect memory, such as schizophrenia and depression.
Located deep in the middle of the brain, the hippocampus plays a key role in forming memories. It looks something like two curving fingers ...
Theoretical biophysics: Adventurous bacteria
2014-04-16
To reproduce or to conquer the world? Surprisingly, bacteria also face this problem. Theoretical biophysicists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have now shown how these organisms should decide how best to preserve their species.
The bacterium Bacillus subtilis is quite adaptable. It moves about in liquids and on agar surfaces by means of flagella. Alternatively, it can stick to an underlying substrate. Actually, the bacteria proliferate most effectively in this stationary state, while motile bacteria reproduce at a notably lower rate.
In order to sustain ...
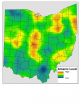
Significant baseline levels of arsenic found in Ohio soils are due to natural processes
2014-04-16
RICHLAND, Wash. – Geologic and soil processes are to blame for significant baseline levels of arsenic in soil throughout Ohio, according to a study published recently in the Journal of Environmental Quality.
The analysis of 842 soil samples from all corners of Ohio showed that every single sample had concentrations higher than the screening level of concern recommended by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The findings should not alarm the public, say the authors, who note that regulatory levels typically are set far below those thought to be harmful. Rather, the ...
Preterm births, multiples, and fertility treatment
2014-04-16
While it is well known that fertility treatments are the leading cause of increases in multiple gestations and that multiples are at elevated risk of premature birth, these results are not inevitable, concludes an article in Fertility and Sterility. The article identifies six changes in policy and practice that can reduce the odds of multiple births and prematurity, including expanding insurance coverage for in vitro fertilization (IVF) and improving doctor-patient communications about the risks associated with twins.
Financial pressures provide a powerful incentive for ...
[1] ... [3706]
[3707]
[3708]
[3709]
[3710]
[3711]
[3712]
[3713]
3714
[3715]
[3716]
[3717]
[3718]
[3719]
[3720]
[3721]
[3722]
... [8831]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.