Aquagenx Innovative Water Quality Test Named Exemplary U.S. Water Technology by U.S. Water Partnership
2014-03-28
Aquagenx, LLC, a provider of innovative microbial water quality testing products that detect potential health risks, was named an Exemplary U.S. Water Technology by the U.S. Water Partnership, a public-private partnership within the U.S. Department of State. The Compartment Bag Test (CBT) was recognized as a groundbreaking water quality test that overcomes the lack of simple, accessible, self-contained, cost-effective solutions to detect and quantify fecal bacteria in water, which causes millions of deaths annually around the globe.
The U.S. Department of State highlighted ...
Chiropractor in Burke, VA - Dr. Todd P. Sullivan Achieves Certification in Functional Movement Screen (FMS) and Selective Functional Movement Assessment (SFMA)
2014-03-28
Dr. Todd P. Sullivan of NOVA Chiropractic & Wellness Center, is now certified in Functional Movement Screen (FMS) and trained in Selective Functional Movement Assessment (SFMA).
The Functional Movement Screen (FMS) is a screening tool that captures human and movement patterns and are critical to normal function, and documents if there are any imbalances, dysfunctions, and restrictions. The screen will determine the greatest areas of movement deficiency as well as demonstrate limitations or asymmetries. These imbalances and deficiencies that are discovered through ...
Outlandish New Book Being Released April 1st Promises Humorous Path to World Peace
2014-03-28
Saving the world is usually no laughing matter. But the members of My Hyena Comedy believe the opposite is true.
For over ten years, My Hyena Comedy has been on a mission to make the world a better place by sharing their quirky, and often juvenile, sense of humor with others through their infamous podcast and website (MyHyena.com). This April Fool's Day they're promoting the healing power of humor through the release of their new paperback book "unHOLY SKITS! Politicians, Prostitutes, and Kinky Koalas" ($14.95).
"Is it silly for us to think that that we can save ...
Bravo Reality Celeb's Shocking Brutally Honest Support of "Biggest Loser" Rachel Frederickson!
2014-03-28
Shonda Lewis, founder of Arnold Sports Festival's Rock Star Bikini (RSB) (http://www.rockstarbikini.com), who appeared on Bravo's Millionaire Matchmaker, is telling the world lay off "Biggest Loser," Rachel Frederickson.
Lewis, who also appeared on Tyra and Essence, echoed The Huffington Post U.K., which said we should applaud Frederickson's effort to lose weight.
"What she is putting herself through is hard. I know what it feels like," Lewis said. "It makes me sad to see people tearing her down."
"Lewis knows what she's talking about in the fitness world, and ...
Esophageal function implicated in life-threatening experiences in infants, study suggests
2014-03-28
About 1 percent of all emergency room visits are prompted by near-death experiences in infants, such as extended periods without breathing or sudden changes in skin pallor or muscle tone. What causes these frightening experiences is often unknown, but the result can be long hospital stays and neurological impairment.
Now, a study of these apparent life-threatening events — called ALTEs for short — suggests that infants who experience them have abnormal regulation of esophageal and airway function compared to healthy babies. The findings, published online March 28 in ...
QUB discovery signals new treatment for those at high risk of breast and ovarian cancer
2014-03-28
Cancer researchers at Queen's University Belfast have made a breakthrough which could signal new treatments for women at high risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
Currently around one in 1,000 women in the UK carry what is known as a BRCA1 mutation - the same condition that prompted well-known actress Angelina Jolie to undergo a double mastectomy. They have up to an 85 per cent risk of developing breast cancer, and up to 40 per cent risk of developing ovarian cancer, in their lifetimes.
Until now, preventive surgery - mastectomy (breasts) and oophorectomy (ovaries) - ...
Stool samples provide marker for bowel disease
2014-03-28
A novel method for distinguishing different types of bowel disease using the stool samples of patients has been created by a group of researchers in the UK.
It works by analysing the chemical compounds emitted from the samples and could provide cheaper, quicker and more accurate diagnoses, at the point of care, for a group of diseases that have, up until now, been very hard to distinguish.
The preliminary results of the test, which have been published today, 28 March, in IOP Publishing's Journal of Breath Research, show that patients with either inflammatory bowel disease ...
New Parkinson's disease chemical messenger discovered
2014-03-28
A new chemical messenger that is critical in protecting the brain against Parkinson's disease has been identified by scientists at the Medical Research Council (MRC) Protein Phosphorylation and Ubiquitylation Unit at the University of Dundee.
The research team led by Dr Miratul Muqit had previously discovered that mutations in two genes – called PINK1 and Parkin – lead to Parkinson's.
Now they have made a completely unexpected discovery about the way the two genes interact, which they say could open up exciting new avenues for research around Parkinson's and offer new ...
Smoking bans cut premature births and childhood asthma attacks
2014-03-28
Banning smoking in public places has helped to cut premature births by 10 per cent, new research shows.
The study of data from parts of North America and Europe where smoking bans have been introduced also showed a 10 per cent fall in hospital attendance for childhood asthma attacks.
The findings reveal that the impact of anti-smoking laws varies between countries but overall the effect on child health around the world is very positive.
Laws that prohibit smoking in public places, such as bars, restaurants and work places, are already proven to protect adults from ...
What psychosocial factors can help IVF patients?
2014-03-28
The whole 'infertility journey' is an emotional rollercoaster and whilst IVF treatment might be successful for some, not knowing if you will be in the 25 per cent who become pregnant demands some serious coping skills. After reviewing research that explored which psychosocial factors are associated with the emotional adjustment of IVF patients, researchers have highlighted which key psychosocial factors could help identify patients at high risk of stress.
The aim of the study, led by PhD student, Helen Rockliff, from the University of Bristol's School of Clinical Sciences, ...
Public smoking bans associated with reduction in premature births and childhood asthma
2014-03-28
Boston, MA – In the first comprehensive study to look at how anti-smoking laws are affecting the health of children, researchers from University of Edinburgh collaborated with researchers from Maastricht University, Hasselt University, Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women's Hospital, to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis examining the effect of smoke-free legislation on child health. They found that the introduction of new laws that ban smoking in public places in North America and Europe has been followed by a decrease in rates of premature births and ...
Using tobacco to thwart infectious disease?
2014-03-27
An international research group led by Arizona State University professor Qiang "Shawn" Chen has developed a new generation of potentially safer and more cost-effective therapeutics against West Nile virus, and other pathogens.
The therapeutics, known as monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) and their derivatives, were shown to neutralize and protect mice against a lethal dose challenge of West Nile virus---even as late as 4 days after the initial infection.
"The overarching goal of our research is to create an innovative, yet sustainable and accessible, low cost solution to ...
How rotavirus infection accelerates autoimmune diabetes in a mouse model
2014-03-27
A combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors is believed to cause autoimmune (type 1) diabetes. A study published on March 27th in PLOS Pathogens gets at the mechanisms by which rotavirus infection contributes to autoimmune diabetes in a mouse model of the disease.
NOD (for non-obese diabetic) mice are prone to develop diabetes, and infection with rotavirus accelerates onset of the disease. Barbara Coulson and colleagues, from The University of Melbourne, Australia, tested the hypothesis that the virus does this by inducing "bystander activation". ...
Genetic variation linked to heart disease risk through RNA machinery
2014-03-27
Researchers have pinpointed a new mechanism of how natural variation in our DNA alters an individual's risk for developing heart disease by interfering with the ability of a developmental gene to interact with a specialized type of RNA. This work expands on previous work identifying the "hidden" causes of complex disease risk, with the goal of unlocking new pathways and potential drug targets for cardiovascular disease.
This latest study led by Thomas Quertermous, MD at Stanford University and Georg Sczakiel, PhD at the University of Lübeck (Germany) was a joint effort ...
Ancient African cattle first domesticated in Middle East
2014-03-27
Geneticists and anthropologists previously suspected that ancient Africans domesticated cattle native to the African continent nearly 10,000 years ago. Now, a team of University of Missouri researchers has completed the genetic history of 134 cattle breeds from around the world. In the process of completing this history, they found that ancient domesticated African cattle originated in the "Fertile Crescent," a region that covered modern day Iraq, Jordan, Syria and Israel.
In their study published in PLOS Genetics, Prof. Decker (University of Missouri) and a team of international ...
Autoimmune drug may help prevent kidney disease caused by diabetes
2014-03-27
Washington, DC (March 27, 2014) — A drug currently used to treat autoimmune disease may also help prevent the kidney-damaging effects of diabetes, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN). The findings suggest that clinical trials should be designed to test the drug in diabetic patients.
Kidney disease is one of the most serious complications of diabetes. Diabetics who develop kidney disease, or diabetic nephropathy, due to high blood glucose levels may eventually require dialysis or a kidney transplant. ...
Major depression linked with nearly twice the risk of kidney failure in diabetics
2014-03-27
Washington, DC (March 27, 2014) — Major depression may increase diabetes patients' risk of developing kidney failure, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (CJASN). Additional studies are needed to determine whether treatment for depression can improve kidney health in patients with diabetes.
Individuals with diabetes have a high prevalence of depressive symptoms, which has previously been linked with negative health outcomes such as cardiovascular disease and premature death. Little is known ...
Gulf War illness not in veterans' heads, but in their mitochondria
2014-03-27
Researchers at the UC San Diego School of Medicine have demonstrated for the first time that veterans of the 1990-91 Persian Gulf War who suffer from "Gulf War illness" have impaired function of mitochondria – the energy powerhouses of cells.
The findings, published in the March 27, 2014 issue of PLOS ONE, could help lead to new treatments benefitting affected individuals – and to new ways of protecting servicepersons (and civilians) from similar problems in the future, said principal investigator Beatrice A. Golomb MD, PhD, professor of medicine.
Golomb, with associate ...
Stroke patients should receive customized palliative care
2014-03-27
People recovering from a stroke should have a well-coordinated medical team to personalize care, optimize quality of life and minimize suffering, according to a scientific statement published in the American Heart Association journal Stroke.
The statement is the first in the United States to outline fundamental palliative care for stroke survivors. Palliative care is patient- and family-centered care that improves life by anticipating, preventing and treating suffering.
"The majority of stroke patients need access to some form of palliative medicine," said Robert Holloway, ...
Consistent blood pressure control may cut rate of second stroke in half
2014-03-27
Stroke survivors who consistently control their blood pressure may reduce the likelihood of a second stroke by more than half, according to new research in the American Heart Association journal Stroke.
For the study, researchers analyzed the results from the Vitamin Intervention for Stroke Prevention (VISP) trial, which enrolled 3,680 ischemic stroke patients ages 35 and older in 1996-2003. Ischemic strokes are caused by a clot or other blockage in a blood vessel supplying the brain. Participants had been tested for several risk factors, including blood pressure levels ...
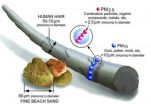
US clean-air efforts stay on target
2014-03-27
HOUSTON – (March 27, 2014) – National efforts in the last decade to clear the air of dangerous particulate matter have been so successful that most urban areas have already attained the next benchmark, according to new research by Rice University.
Atmospheric researchers at Rice studied the state implementation plans (SIPs) from 23 regions mandated by the Environmental Protection Agency to reduce particulate matter (PM) smaller than 2.5 microns (PM 2.5) to less than 15 micrograms per cubic meter by 2009.
The Rice analysis appears this week in the Journal of the Air ...
Mechanical forces driving breast cancer lead to key molecular discovery
2014-03-27
The stiffening of breast tissue in breast-cancer development points to a new way to distinguish a type of breast cancer with a poor prognosis from a related, but often less deadly type, UC San Francisco researchers have found in a new study.
The findings, published online March 16, 2014 in Nature Medicine, may lead eventually to new treatment focused not only on molecular targets within cancerous cells, but also on mechanical properties of surrounding tissue, the researchers said.
In a mouse model of breast cancer, scientists led by Valerie Weaver, PhD, professor of ...
Notre Dame scientists develop largest developmental proteomic data set for any animal
2014-03-27
Now that the human genome is sequenced, University of Notre Dame researchers are focusing on the study of the proteome, which is the protein content of an organism, tissue or cell. Bioanalytical chemist Norman Dovichi and molecular biologist Paul Huber have successfully tracked the changing patterns of protein expression during early development of Xenopus laevis, or African clawed frog, embryos. They have developed the largest data set on developmental proteomics for any organism, and have included the single-cell zygote.
Their research has uncovered an unexpected amount ...
The circadian clock is like an orchestra with many conductors
2014-03-27
ANN ARBOR—You've switched to the night shift and your weight skyrockets, or you wake at 7 a.m. on weekdays but sleep until noon on weekends—a social jet lag that can fog your Saturday and Sunday.
Life runs on rhythms driven by circadian clocks, and disruption of these cycles is associated with serious physical and emotional problems, says Orie Shafer, a University of Michigan assistant professor of molecular, cellular and developmental biology.
Now, new findings from Shafer and U-M doctoral student Zepeng Yao challenge the prevailing wisdom about how our body clocks ...
Scientists synthesize first functional 'designer' chromosome in yeast
2014-03-27
An international team of scientists led by Jef Boeke, PhD, director of NYU Langone Medical Center's Institute for Systems Genetics, has synthesized the first functional chromosome in yeast, an important step in the emerging field of synthetic biology, designing microorganisms to produce novel medicines, raw materials for food, and biofuels.
Over the last five years, scientists have built bacterial chromosomes and viral DNA, but this is the first report of an entire eukaryotic chromosome, the threadlike structure that carries genes in the nucleus of all plant and animal ...
[1] ... [3761]
[3762]
[3763]
[3764]
[3765]
[3766]
[3767]
[3768]
3769
[3770]
[3771]
[3772]
[3773]
[3774]
[3775]
[3776]
[3777]
... [8789]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.