Lessons offered by emerging carbon trading markets
2014-03-21
DURHAM, N.C. -- Although markets for trading carbon emission credits to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have stalled in United States federal policy-making, carbon markets are emerging at the state level within the U.S. and around the world, teaching us more about what does and doesn't work.
In a Policy Forum article in the March 21 edition of Science magazine, Duke University's Richard Newell, William Pizer and Daniel Raimi discuss the key lessons from a decade of experience with carbon markets. They also discuss what it might take for these markets to develop and possibly ...
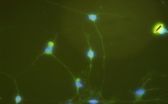
Who reprograms rat astrocytes into neurons?
2014-03-21
To date, it remains poorly understood whether astrocytes can be easily reprogrammed into neurons. Mash1 and Brn2 have been previously shown to cooperate to reprogram fibroblasts into neurons. Dr. Yongjun Wang and team from Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China found that and found that Brn2 was expressed in astrocytes from 2-month-old Sprague-Dawley rats, but Mash1 was not detectable. Thus, the researchers hypothesized that Mash1 alone could be used to reprogram astrocytes into neurons. Murine stem cell virus (MSCV)-Mash1 recombinant plasmid was constructed ...
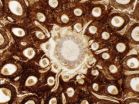
Unique chromosomes preserved in Swedish fossil
2014-03-21
Researchers from Lund University and the Swedish Museum of Natural History have made a unique discovery in a well-preserved fern that lived 180 million years ago. Both undestroyed cell nuclei and individual chromosomes have been found in the plant fossil, thanks to its sudden burial in a volcanic eruption.
The well-preserved fossil of a fern from the southern Swedish county of Skåne is now attracting attention in the research community. The plant lived around 180 million years ago, during the Jurassic period, when Skåne was a tropical region where the fauna was dominated ...
A study using Drosophila flies reveals new regulatory mechanisms of cell migration
2014-03-21
Cell migration is highly coordinated and occurs in processes such as embryonic development, wound healing, the formation of new blood vessels, and tumour cell invasion. For the successful control of cell movement, this process has to be determined and maintained with great precision. In this study, the scientists used tracheal cells of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster to unravel the signalling mechanism involved in the regulation of cell movements.
The research describes a new molecular component that controls the expression of a molecule named Fibroblast Growth ...
Switching an antibiotic on and off with light
2014-03-21
This news release is available in German. Scientists of the KIT and the University of Kiev have produced an antibiotic, whose biological activity can be controlled with light. Thanks to the robust diarylethene photoswitch, the antimicrobial effect of the peptide mimetic can be applied in a spatially and temporally specific manner. This might open up new options for the treatment of local infections, as side effects are reduced. The researchers present their photoactivable antibiotic with the new photomodule in a "Very Important Paper" of the journal "Angewandte Chemie". ...
cfaed presents the new microchip 'Tomahawk 2' at the DATE'14 in Dresden
2014-03-21
The Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden (cfaed) presents its new microchip 'Tomahawk 2' at the DATE'14 Conference in the International Congress Center Dresden from March 24 to 28, 2014. The new Tomahawk is extremely fast, energy-efficient and resilient. It is a heterogeneous multi-processor which can easily integrate very different kinds of devices. The researchers of the Cluster of Excellence for microelectronics of Technische Universität Dresden use the new prototype to prepare the so-called 'tactile internet'. With this, very big data volumes shall be transmitted ...
New study shows we work harder when we are happy
2014-03-21
Happiness makes people more productive at work, according to the latest research from the University of Warwick.
Economists carried out a number of experiments to test the idea that happy employees work harder. In the laboratory, they found happiness made people around 12% more productive.
Professor Andrew Oswald, Dr Eugenio Proto and Dr Daniel Sgroi from the Department of Economics at the University of Warwick led the research.
This is the first causal evidence using randomized trials and piece-rate working. The study, to be published in the Journal of Labor Economics, ...
Surprising new way to kill cancer cells
2014-03-21
Northwestern Medicine scientists have demonstrated that cancer cells – and not normal cells – can be killed by eliminating either the FAS receptor, also known as CD95, or its binding component, CD95 ligand.
"The discovery seems counterintuitive because CD95 has previously been defined as a tumor suppressor," said lead investigator Marcus Peter, professor in medicine-hematology/Oncology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. "But when we removed it from cancer cells, rather than proliferate, they died."
The findings were published March 20 in Cell Reports. ...
Stem cell study finds source of earliest blood cells during development
2014-03-21
Irvine, Calif., March 20, 2014 — Hematopoietic stem cells are now routinely used to treat patients with cancers and other disorders of the blood and immune systems, but researchers knew little about the progenitor cells that give rise to them during embryonic development.
In a study published April 8 in Stem Cell Reports, Matthew Inlay of the Sue & Bill Gross Stem Cell Research Center and Stanford University colleagues created novel cell assays that identified the earliest arising HSC precursors based on their ability to generate all major blood cell types (red blood ...
New infrared technique aims to remotely detect dangerous materials
2014-03-21
For most people, infrared technology calls to mind soldiers with night-vision goggles or energy audits that identify where heat escapes from homes during the winter season.
But for two Brigham Young University professors, infrared holds the potential to spot from afar whether a site is being used to make nuclear weapons.
Statistics professor Candace Berrett developed a model that precisely characterizes the material in each pixel of an image taken from a long-wave infrared camera. The U.S. National Nuclear Security Administration funded the project through a grant ...
The gene family linked to brain evolution is implicated in severity of autism symptoms
2014-03-21
The same gene family that may have helped the human brain become larger and more complex than in any other animal also is linked to the severity of autism, according to new research from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
The gene family is made up of over 270 copies of a segment of DNA called DUF1220. DUF1220 codes for a protein domain – a specific functionally important segment within a protein. The more copies of a specific DUF1220 subtype a person with autism has, the more severe the symptoms, according to a paper published in the PLoS Genetics. ...
Stanford professor maps by-catch as unintended consequence of global fisheries
2014-03-21
Seabirds, sea turtles and marine mammals such as dolphins may not appear to have much in common, other than an affinity for open water. The sad truth is that they are all unintended victims – by-catch – of intensive global fishing. In fact, accidental entanglement in fishing gear is the single biggest threat to some species in these groups.
A new analysis co-authored by Stanford biology Professor Larry Crowder provides an unprecedented global map of this by-catch, starkly illustrating the scope of the problem and the need to expand existing conservation efforts in certain ...
Homeless with TBI more likely to visit ER
2014-03-21
TORONTO, March 21, 2014—Homeless and vulnerably housed people who have suffered a traumatic brain injury at some point in their life are more likely to visit an Emergency Department, be arrested or incarcerated, or be victims of physical assault, new research has found.
"Given the high costs of Emergency Department visits and the burden of crime on society, these findings have important public health and criminal justice implications," the researchers from St. Michael's Hospital wrote today in the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation.
Traumatic brain injuries, such as ...
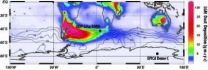
Dust in the wind drove iron fertilization during ice age
2014-03-21
Researchers from Princeton University and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich have confirmed that during the last ice age iron fertilization caused plankton to thrive in a region of the Southern Ocean.
The study published in Science confirms a longstanding hypothesis that wind-borne dust carried iron to the region of the globe north of Antarctica, driving plankton growth and eventually leading to the removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Plankton remove the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere during growth and transfer it ...
Obesity and depression linked in teen girls says new Rutgers-Camden study
2014-03-21
Depression and obesity have long been associated, but how they relate over time is less clear. New research from a Rutgers University–Camden professor shows that adolescent females who experience one of the disorders are at a greater risk for the other as they get older.
"Adolescence is a key developmental period for both obesity and depression, so we thought it significant to look at the onset of these disorders at an early age," says Naomi Marmorstein, an associate professor of psychology at Rutgers–Camden.
By assessing a statewide sample of more than 1,500 males ...
UV exposure found to lower folate levels in young women
2014-03-21
Women who are pregnant or trying to fall pregnant and taking a folic acid supplement may be at risk of reducing their folate benefit through sun exposure, a new QUT study has warned.
In a paper titled Exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation is associated with decreased folate status in women of childbearing age, published in the Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B:Biology, QUT researchers found UV exposure significantly depleted folate levels.
Professor Michael Kimlin and Dr David Borradale, from QUT's AusSun Research Lab, said the study of 45 young healthy ...
The MIS 3 glacial advances in the Nyainqentanglha and possible linkage to the North Atlantic cooling
2014-03-21
Chronologies of glacial advances during the last glacial period are not contemporaneous throughout the Tibetan Plateau. Professor YI Chaolu and his research group from the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, dated glacial boulders on moraines from the last glacial period in the Nyainqentanglha Mountains, Tibet. They suggested that glacial advances that occurred during a relatively warm period (MIS 3) between two cold stages of the last glacial episode in the Nyainqentanglha may correlate with millennial-scale climate change (Heinrich) events. ...
Now even more likely that there are particles smaller than Higgs out there
2014-03-21
Nobody has seen them yet; particles that are smaller than the Higgs particle. However theories predict their existence, and now the most important of these theories have been critically tested. The result: The existence of the yet unseen particles is now more likely than ever.
"I gave them a very critical review", says Thomas Ryttov, particle physicist and associate professor at the Center for Cosmology and Particle Physics Phenomenology (CP ³ - Origins), University of Southern Denmark.
He refers to the theories, that over the last app. five years have been put forward ...
Cholesterol transporter structure decoded
2014-03-21
This news release is available in German. The word "cholesterol" is directly linked in most people's minds with high-fat foods, worrying blood test results, and cardiovascular diseases. However, despite its bad reputation, cholesterol is essential to our wellbeing: It stabilizes cell membranes and is a raw material for the production of different hormones in the cell's power plants – the mitochondria. Now, for the first time, scientists in Göttingen have solved the high-resolution structure of the molecular transporter TSPO, which introduces cholesterol into mitochondria. ...
Significant variations between NHS hospitals in adverse outcomes for treatment of DCIS
2014-03-21
Glasgow, UK: Analysis of data from the UK NHS Breast Screening Programme has shown significant variations in the outcomes of treatment for women with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) between UK hospitals.
Dr Jeremy Thomas, a consultant pathologist at the Western General Hospital, Edinburgh, UK, told the European Breast Cancer Conference today (Friday) that although the majority of women with DCIS received the correct surgery for their disease, large numbers of women were undergoing mastectomy for DCIS either as a result of failed breast conservation surgery or for tumours ...
A third of women might benefit from more frequent mammograms
2014-03-21
Glasgow, UK: A study of over 50,000 women participating in the UK NHS Breast Screening Programme has found that, while three-yearly screening intervals are appropriate for the majority of women, approximately one third of women are at higher risk of developing cancer and might benefit from more frequent mammograms.
Professor Gareth Evans, from the University of Manchester (UK), told the 9th European Breast Cancer Conference (EBCC-9) today (Friday) that identifying the degree of risk of developing breast cancer in individual women would enable healthcare professionals ...
Harms outweigh benefits for women aged 70 and over in national breast cancer screening programs
2014-03-21
Extending national breast cancer screening programmes to women over the age of 70 does not result in a decrease in the numbers of cancers detected at advanced stages, according to new research from The Netherlands.
Instead, researchers told the European Breast Cancer Conference that their findings suggest that extending screening programmes to older women results in a large proportion of women being over-treated, and at risk from the harmful effects of such treatment, because these women were more likely to die from other causes than from any tumours detected in the ...
What role will social media and online evidence play in your divorce?
2014-03-21
What role will social media and online evidence play in your divorce?
Article provided by Stolar & Pollins, PLLC
Visit us at http://www.stolarpollinslaw.com
If you are like most Americans, you are a member of at least one social media or networking site. Whether it be a site based around making professional or career-oriented connections (like LinkedIn, for example) or one that fosters more casual relationships (like Facebook, Twitter or Google+), most of us log on to social media at least a few times a week. The relationships and connections we foster there ...
FMCSA aggressively targeting fatigued truckers
2014-03-21
FMCSA aggressively targeting fatigued truckers
Article provided by Davis Law Group, P.A.
Visit us at http://www.davislawgroupnc.com
In 2013, new rules were announced by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) concerning the amount of time that truck drivers would be allowed to drive each week. These rules limited drivers to 70-hour work weeks, which drivers could restart only after a 34-hour rest period. This must include two nights where drivers were sleeping from 1 A.M. to 5 A.M.
The agency made these changes to help address the issue of truck ...
New Mexico court rules that prescription error lawsuit filed too late
2014-03-21
New Mexico court rules that prescription error lawsuit filed too late
Article provided by The Law Offices of Salazar, Sullivan & Jasionowski
Visit us at http://www.salazarandsullivan.com/Practice-Areas/
The New Mexico Court of Appeals recently ruled that a medical malpractice and wrongful death lawsuit based on an alleged prescription error had been filed too late. The deceased individual was prescribed a medication that allegedly interacted dangerously with another medication that he was taking. He died over a year later, and his family filed the lawsuit more ...
[1] ... [3841]
[3842]
[3843]
[3844]
[3845]
[3846]
[3847]
[3848]
3849
[3850]
[3851]
[3852]
[3853]
[3854]
[3855]
[3856]
[3857]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.