Teal Montgomery & Henderson has a Doctor in the House
2014-03-22
Teal Montgomery & Henderson announces that one of its attorneys is also a licensed physician. This distinction makes the law firm unique in the legal industry and allows it to have a deeper insight and understanding of medical evidence in litigation.
Thomas Q. Winter spent 25 years in the medical field before deciding to expand into law. He graduated in 1967 from Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine with his Doctor of Medicine. After medical school, Mr. Winter went through surgical training for four years and was certified by The American Board of ...
Healy Scanlon Law Firm files lawsuit in fatal I-94 trucking accident
2014-03-22
On February 25, 2014, attorneys at Healy Scanlon Law Firm (formerly The Healy Law Firm) in Chicago filed a lawsuit on behalf of the family for a husband and father who was killed as a result of the chain reaction collision that temporarily shut down Interstate 94 near Michigan City, Indiana on Thursday January 23, 2014. The accident involved at least 45 vehicles, including approximately 19 semi tractor- trailers, and resulted in injuries to at least 20 people. The decedent is survived by his wife and four adult children and was one of the three people who lost their lives ...
Kristie Koepplin Serves as President of AORN of Orange County
2014-03-22
Capistrano Surgicenter Perioperative Nurse Kristie Koepplin has been recognized for showing dedication, leadership and excellence in operating room nursing.
Recognized for many years of invaluable contributions in her field, Ms. Koepplin has found professional success with Capistrano Surgicenter, a dermatology office. For more than a decade and a half, in her role as a perioperative nurse, she has supervised the autoclave department, ordered supplies for the operating room and worked with the inventor of the tumescent liposuction technique.
A brilliant example of ...
Waiving liability: Is it ironclad?
2014-03-22
It was a most amazing story in the news recently: as reported by kbtx.com, a young girl was taken skydiving by her father for her sixteenth birthday, something she had always wanted to do. She was taking a static-line jump, where the parachute is supposed to open when the jumper exists the plane. Jumping out of the plane at 3,000 feet, the girl's parachute failed to open properly and she spiraled to the earth. Amazingly, she not only survived, but was expected to leave the intensive care after only a few days and still faced a long recovery for her serious injuries. Although ...
Warrantless search of mailed package was not justified
2014-03-22
Under the Fourth Amendment of the United States Constitution, a warrantless search is considered unreasonable unless the situation is covered by one of a number of exceptions to the law. One of those exceptions is related to "exigent circumstances"--a situation which, by its nature, requires immediate action.
In the case of Robey v. Superior Court, the California Supreme Court discussed an incident in which the police claimed they had exigent circumstances to search a package containing marijuana . . . but the court disagreed.
A shipping package . . . and ...
Downtown motorcycle accident results in the death of a Charleston man
2014-03-22
A local Charleston man recently lost his life in a tragic motorcycle accident in the downtown area. The 29-year-old victim grew up in Mount Pleasant.
The incident occurred on the Huger Street off ramp to the Arthur Ravenel Jr. Bridge. After the accident, the motorcycle was mangled, and a broken light pole rested in a field close by.
The victim was discovered by a pedestrian, who was walking his dog. The witness noticed the broken light pole and ultimately uncovered the crashed motorcycle and victim's body, which was found just a few feet away. According to the witness, ...
Pradaxa poses serious health risk to several users
2014-03-22
When patients consume medicine, the intention is to relieve medical issues or symptoms --not create them. However, some drugs are found to be defective, causing further issues for those who consume the product.
For example, Pradaxa is a commonly used blood thinner; however, it is one of the most complained about medications in the country, according to ABC News. In fact, several complaints were filed with the Food and Drug Administration regarding the drug in the past few years.
Since the medication was approved in 2010, Pradaxa has been linked to approximately 1,158 ...
Thousands injured from transvaginal mesh device, litigation continues
2014-03-22
Surgical mesh was first approved by the FDA in the 1950s to repair hernias. In the 1990s, the product was expanded to treat pelvic organ prolapsed and stress urinary incontinence conditions, particularly for women post childbirth. However, thousands of women have suffered injuries from transvaginal mesh. Many had to undergo additional surgical procedures, such as blood transfusions and draining, to correct the problems from the defective medical device.
As of today, roughly 40,000 lawsuits have been filed against various manufacturers of the defective transvaginal mesh ...
"Bike cams" capturing danger posed to bicyclists in Chicago
2014-03-22
After an unusually cold winter in Chicago, spring is just around the corner. With the rise in temperature and the melting snow in sight, cyclists are itching to get back out on the road (at least those who did not brave the cold and snow and bike anyway). Bicyclists have reason to be excited. Last summer Chicago increased its number of bike lanes and added the bike sharing program "Divvy" to its city streets, which now has 400 bike stations across the city. Chicago is part of a growing movement that encourages bicycling even in urban environments for health and ...
Infant blindness case could proceed based on medical expert's report
2014-03-22
To prove medical malpractice, a patient often will need the opinions and reports of medical experts. These experts generally will provide a report which discusses the applicable standards of care in an area and how the health-care providers failed to meet those standards.
In addition, the report must establish "causation"--that is, the relationship between the health-care provider's failure and the injury to the patient. Enough key facts, including information related to causation, must be included in the report for it to be valid, or else the health-care provider ...
Even theoretical physics has trouble determining a child custody schedule
2014-03-22
It comes as little surprise to most people that establishing a workable child custody schedule is difficult. The relationship between the parents, the age of the child, work schedules, and a host of other issues can influence a parent's desires and compromises when establishing a child custody plan that works in the best interests of the child.
You wouldn't necessarily think it would take a theoretical physicist to figure it out, though.
Yet that is exactly what one scientist did when figuring out a schedule to see all his children at the same time. The physicist, ...
Circumstantial evidence offered did not prove intent to sell marijuana
2014-03-22
The possession of marijuana with intent to sell is a more serious offense than simple possession and such intent may be shown by direct or circumstantial evidence. In determining if there was intent to sell, factors which may be considered include the packaging of the controlled substance, the quantity found, the presence of cash or drug paraphernalia, and the suspect's activities.
If the circumstantial evidence of the intent to sell is not adequate, the charge may not withstand scrutiny, as seen in the North Carolina Court of Appeals case of In re N.J.
Possession ...
Study suggests new treatment guidelines to reduce TBI fatalities
2014-03-22
Anyone in Orleans County, Louisiana, who has experienced a brain injury or been close to someone affected by one knows how devastating these injuries are. A traumatic brain injury can be fatal or cause cognitive effects that last for life, which is why TBIs and means of treatment are the subject of many widespread research efforts. A recent study offers hope for future TBI victims by suggesting ways to improve the treatment of TBI patients, lowering the risk of fatalities and other complications.
Monitoring guidelines reduce deaths
The study spanned 8 years and used ...
Police checkpoint stop of defendant's vehicle was invalid
2014-03-22
In State v. White, the Court of Appeals of North Carolina upheld the trial court's decision to suppress all evidence obtained as a result of the stop of the defendant's vehicle at a police checkpoint conducted in violation of a state statute.
Background
In September 2009, the defendant was arrested for driving while impaired and driving while his license was revoked. The defendant filed a motion to suppress evidence obtained in the checkpoint stop of his vehicle, asserting that the stop violated federal and state constitutional provisions and a North Carolina statute ...
Milanoo Shows Summer & Spring Custom-Made Series Wedding Dresses in A Video
2014-03-22
Spring has come and summer is just around the corner. There is no doubt that this is a perfect time for a wedding ceremony. Nice weather and beautiful scenery, good for honey moon and taking great photos. In this season, Milanoo launches a great summer & spring custom-made series wedding dresses. And in this video, Milanoo shows one dress of the summer & spring custom-made series.
from this video,we can learn about the design inspiration of this pure white trumpet dress and some ideas on how to make up to match this wedding dress. We can see the qualified lace ...
Ralph Scozzafava Celebrates 30 Years of Being an Executive
2014-03-22
In many ways, Ralph Scozzafava is a classic American success story. For thirty years he has been associated with some of the top global organizations in the business world, and he has guided them to profitability, often under very trying circumstances.
Today, Ralph Scozzafava lives in St. Louis, Missouri, the home of Furniture Brands International. Ralph Scozzafava served as Furniture Brands' Chief Executive Officer and the Chairman of the Board, where he was accountable for all facets of $1.1 Billion, publicly traded company. Ralph Scozzafava developed Furniture Brands' ...
Melvin McDonald of French Valley Offers Valuable Basketball Advice
2014-03-22
Basketball is a complicated game, and requires a large commitment of time to study and practice. Melvin McDonald of French Valley, a basketball coach of many years, seeks to inform and educate people on how to develop a better approach and attitude about the game of basketball.
Melvin McDonald of French Valley relishes any opportunity to speak on or to teach the game of basketball. Players and fellow coaches alike look to Melvin for insights into the game. They rely on his basketball expertise and experience as a guide for a better, more disciplined approach to a game ...
Yardley, PA Dentist Wants Patients To Be Wide Awake and Aware of Sleep Apnea
2014-03-22
March 2-9th was National Sleep Awareness Week. In recognition of that week, Dr. Smolen wants patients to be aware of sleep apnea and its negative impact on their overall health.
"Most patients don't know they are dealing with sleep apnea. . One's bedtime partner may make you aware of irregular sleeping patterns. The symptoms may include snoring, stopped breathing during sleep and daytime tiredness. If a patient is newly diagnosed with sleep apnea, it's time to be aware of treatment options," explains Dr. Smolen.
With a lack of sleep, patients may notice ...
Ongoing Extreme Winter Season Causes Skin Care Disaster
2014-03-22
Extreme weather conditions have made this winter colder than usual. Those people suffering from eczema or psoriasis, looking for the best dry skin moisturizer, personally experience the dry skin nightmare during these winter months. Cold winds, low humidity and the use of heaters can worsen just about anyone's skin but are especially hard on those with eczema and psoriasis. Finding the right dry skin moisturizer could make a big difference in how many outbreaks you face this winter.
According to the US National Library of Medicine, dry itchy skin occurs more often in ...
Permafrost thaw: No upside
2014-03-21
The climate is warming in the arctic at twice the rate of the rest of the globe creating a longer growing season and increased plant growth, which captures atmospheric carbon, and thawing permafrost, which releases carbon into the atmosphere. Woods Hole Research Center (WHRC) Assistant Scientist Sue Natali and colleagues engineered first-of-a-kind warming experiments in the field to determine net gains or losses in carbon emissions. The study entitled "Permafrost degradation stimulates carbon loss from experimentally warmed tundra," published in the journal Ecology found ...
Stem cell findings may offer answers for some bladder defects and disease
2014-03-21
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — For the first time, scientists have succeeded in coaxing laboratory cultures of human stem cells to develop into the specialized, unique cells needed to repair a patient's defective or diseased bladder.
The breakthrough, developed at the UC Davis Institute for Regenerative Cures and published today in the scientific journal Stem Cells Translational Medicine, is significant because it provides a pathway to regenerate replacement bladder tissue for patients whose bladders are too small or do not function properly, such as children with spina bifida ...
Keck Medicine of USC research may point to better predictor of prostate cancer survival
2014-03-21
New research by USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center scientists demonstrates that measuring circulating tumor cells (CTCs) – the cells that spread cancer through the body – may be a better predictor of patient survival than the prostate specific antigen (PSA).
The research was published March 10, 2014 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology by a team led by Amir Goldkorn, M.D., assistant professor of medicine at USC Norris, part of Keck Medicine of USC. Goldkorn's team discovered that elevated CTC counts after chemotherapy indicated as much as a five-fold higher risk of ...
Cold snare polypectomy effective for removal of small colorectal polyps in patients on anticoagulants
2014-03-21
DOWNERS GROVE, Ill. – March 21, 2014 – In recognition of National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month, GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy has published a special issue for March on colorectal cancer. The issue includes a new study that compares cold snare polypectomy with conventional polypectomy for the removal of small colorectal polyps in anticoagulated patients. The study showed that delayed bleeding requiring hemostasis (stoppage of bleeding) occurred significantly less often after cold snare polypectomy than during conventional polypectomy despite continuation of anticoagulants. ...
Genetic signature reveals new way to classify gum disease
2014-03-21
NEW YORK, NY (March 21, 2014) — Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) have devised a new system for classifying periodontal disease based on the genetic signature of affected tissue, rather than on clinical signs and symptoms. The new classification system, the first of its kind, may allow for earlier detection and more individualized treatment of severe periodontitis, before loss of teeth and supportive bone occurs. The findings were published recently in the online edition of the Journal of Dental Research.
Currently, periodontal disease is classified ...
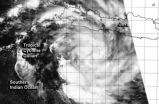
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Gillian reborn near Java
2014-03-21
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the reborn tropical cyclone known as Gillian on March 21 and captured a visible image of the storm, located just south of the island of Java.
Java is highly populated island of Indonesia that includes the capital city of Jakarta. Java is divided into four provinces, East, West and Central Java and Banten. There are also two special regions of Java called Jakarta and Yogyakarta.
The MODIS instrument that flies aboard Aqua captured a visible image of Gillian on March 21 at 06:55 UTC/2:55 a.m. EDT. The image showed bands of thunderstorms ...
[1] ... [3839]
[3840]
[3841]
[3842]
[3843]
[3844]
[3845]
[3846]
3847
[3848]
[3849]
[3850]
[3851]
[3852]
[3853]
[3854]
[3855]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.